| Citation: | Xiang SY, Shi YC, Zhang YH, Guo XX, Zheng L et al. Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network. Opto-Electron Adv 6, 230140 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 |
Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
-
Abstract
Neuromorphic photonic computing has emerged as a competitive computing paradigm to overcome the bottlenecks of the von-Neumann architecture. Linear weighting and nonlinear spike activation are two fundamental functions of a photonic spiking neural network (PSNN). However, they are separately implemented with different photonic materials and devices, hindering the large-scale integration of PSNN. Here, we propose, fabricate and experimentally demonstrate a photonic neuro-synaptic chip enabling the simultaneous implementation of linear weighting and nonlinear spike activation based on a distributed feedback (DFB) laser with a saturable absorber (DFB-SA). A prototypical system is experimentally constructed to demonstrate the parallel weighted function and nonlinear spike activation. Furthermore, a four-channel DFB-SA laser array is fabricated for realizing matrix convolution of a spiking convolutional neural network, achieving a recognition accuracy of 87% for the MNIST dataset. The fabricated neuro-synaptic chip offers a fundamental building block to construct the large-scale integrated PSNN chip. -

-
References
[1] Indiveri G, Liu SC. Memory and information processing in neuromorphic systems. Proc IEEE 103, 1379–1397 (2015). doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2444094 [2] Roy K, Jaiswal A, Panda P. Towards spike-based machine intelligence with neuromorphic computing. Nature 575, 607–617 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1677-2 [3] Marković D, Mizrahi A, Querlioz D, Grollier J. Physics for neuromorphic computing. Nat Rev Phys 2, 499–510 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s42254-020-0208-2 [4] Nawrocki RA, Voyles RM, Shaheen SE. A mini review of neuromorphic architectures and implementations. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 63, 3819–3829 (2016). doi: 10.1109/TED.2016.2598413 [5] Schuman CD, Potok TE, Patton RM, Birdwell JD, Dean ME et al. A survey of neuromorphic computing and neural networks in hardware. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1705.06963 (2017). [6] Painkras E, Plana LA, Garside J, Temple S, Galluppi F et al. SpiNNaker: a 1-W 18-core system-on-chip for massively-parallel neural network simulation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 48, 1943–1953 (2013). doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2259038 [7] Benjamin BV, Gao PR, McQuinn E, Choudhary S, Chandrasekaran AR et al. Neurogrid: a mixed-analog-digital multichip system for large-scale neural simulations. Proc IEEE 102, 699–716 (2014). doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2313565 [8] Merolla PA, Arthur JV, Alvarez-Icaza R, Cassidy AS, Sawada J et al. A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345, 668–673 (2014). doi: 10.1126/science.1254642 [9] Shen JC, Ma D, Gu ZH, Zhang M, Zhu XL et al. Darwin: a neuromorphic hardware co-processor based on spiking neural networks. Sci China Inform Sci 59, 1–5 (2016). [10] Davies M, Srinivasa N, Lin TH, Chinya G, Cao YQ et al. Loihi: a neuromorphic manycore processor with on-chip learning. IEEE Micro 38, 82–99 (2018). doi: 10.1109/MM.2018.112130359 [11] Pei J, Deng L, Song S, Zhao MG, Zhang YH et al. Towards artificial general intelligence with hybrid Tianjic chip architecture. Nature 572, 106–111 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1424-8 [12] Wetzstein G, Ozcan A, Gigan S, Fan SH, Englund D et al. Inference in artificial intelligence with deep optics and photonics. Nature 588, 39–47 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2973-6 [13] Shastri BJ, Tait AN, Ferreira de Lima T, Pernice WHP, Bhaskaran H et al. Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat Photonics 15, 102–114 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00754-y [14] Zhou HL, Dong JJ, Cheng JW, Dong WC, Huang CR et al. Photonic matrix multiplication lights up photonic accelerator and beyond. Light Sci Appl 11, 30 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00717-8 [15] Huang CR, Sorger VJ, Miscuglio M, Al-Qadasi M, Mukherjee A et al. Prospects and applications of photonic neural networks. Adv Phys X 7, 1981155 (2022). [16] Qi HX, Du ZC, Hu XY, Yang JY, Chu SS et al. High performance integrated photonic circuit based on inverse design method. Opto-Electron Adv 5, 210061 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.210061 [17] Li CH, Du W, Huang YX, Zou JH, Luo LZ et al. Photonic synapses with ultralow energy consumption for artificial visual perception and brain storage. Opto-Electron Adv 5, 210069 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.210069 [18] Jiao SM, Liu JW, Zhang LW, Yu FH, Zuo GM et al. All-optical logic gate computing for high-speed parallel information processing. Opto-Electron Sci 1, 220010 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oes.2022.220010 [19] Meng XY, Zhang GJ, Shi NN, Li GY, Azaña J et al. Compact optical convolution processing unit based on multimode interference. Nat Commun 14, 3000 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38786-x [20] Zhang F, Guo YH, Pu MB, Chen LW, Xu MF et al. Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption. Nat Commun 14, 1946 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37510-z [21] He C, Zhao D, Fan F, Zhou HQ, Li X et al. Pluggable multitask diffractive neural networks based on cascaded metasurfaces. Opto-Electron Adv 7, 230005 (2024). [22] Maass W. Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw 10, 1659–1671 (1997). doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(97)00011-7 [23] Gütig R, Sompolinsky H. The tempotron: a neuron that learns spike timing–based decisions. Nat Neurosci 9, 420–428 (2006). doi: 10.1038/nn1643 [24] Ponulak F, Kasiński A. Supervised learning in spiking neural networks with ReSuMe: sequence learning, classification, and spike shifting. Neural Comput 22, 467–510 (2010). doi: 10.1162/neco.2009.11-08-901 [25] Feldmann J, Youngblood N, Wright CD, Bhaskaran H, Pernice WHP. All-optical spiking neurosynaptic networks with self-learning capabilities. Nature 569, 208–214 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1157-8 [26] Xiang SY, Ren ZX, Song ZW, Zhang YH, Guo XX et al. Computing primitive of fully VCSEL-based all-optical spiking neural network for supervised learning and pattern classification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32, 2494–2505 (2021). doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3006263 [27] Jha A, Huang CR, Peng HT, Shastri B, Prucnal PR. Photonic spiking neural networks and graphene-on-silicon spiking neurons. J Lightwave Technol 40, 2901–2914 (2022). doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3146157 [28] Xiang SY, Shi YC, Guo XX, Zhang YH, Wang HJ et al. Hardware-algorithm collaborative computing with photonic spiking neuron chip based on an integrated Fabry–Perot laser with a saturable absorber. Optica 10, 162–171 (2023). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.468347 [29] Tait AN, Ferreira de Lima T, Zhou E, Wu AX, Nahmias MA et al. Neuromorphic photonic networks using silicon photonic weight banks. Sci Rep 7, 7430 (2017). doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07754-z [30] Shen YC, Harris NC, Skirlo S, Prabhu M, Baehr-Jones T et al. Deep learning with coherent nanophotonic circuits. Nat Photonics 11, 441–446 (2017). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2017.93 [31] Cheng ZG, Ríos C, Pernice WHP, Wright CD, Bhaskaran H. On-chip photonic synapse. Sci Adv 3, e1700160 (2017). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700160 [32] Zhou HL, Zhao YH, Wang X, Gao DS, Dong JJ et al. Self-configuring and reconfigurable silicon photonic signal processor. ACS Photonics 7, 792–799 (2020). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.9b01673 [33] Feldmann J, Youngblood N, Karpov M, Gehring H, Li X et al. Parallel convolutional processing using an integrated photonic tensor core. Nature 589, 52–58 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03070-1 [34] Xu XY, Tan MX, Corcoran B, Wu JY, Boes A et al. 11 TOPS photonic convolutional accelerator for optical neural networks. Nature 589, 44–51 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03063-0 [35] Xu SF, Wang J, Shu HW, Zhang ZK, Yi SC et al. Optical coherent dot-product chip for sophisticated deep learning regression. Light Sci Appl 10, 221 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00666-8 [36] Zhang H, Gu M, Jiang XD, Thompson J, Cai H et al. An optical neural chip for implementing complex-valued neural network. Nat Commun 12, 457 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20719-7 [37] Guo XH, Xiang JL, Zhang YJ, Su YK. Integrated neuromorphic photonics: synapses, neurons, and neural networks. Adv Photonics Res 2, 2000212 (2021). doi: 10.1002/adpr.202000212 [38] Cheng JW, Zhao YH, Zhang WK, Zhou HL, Huang DM et al. A small microring array that performs large complex-valued matrix-vector multiplication. Front Optoelectron 15, 15 (2022). doi: 10.1007/s12200-022-00009-4 [39] Prucnal PR, Shastri BJ, Ferreira de Lima T, Nahmias MA, Tait AN. Recent progress in semiconductor excitable lasers for photonic spike processing. Adv Opt Photonics 8, 228–299 (2016). doi: 10.1364/AOP.8.000228 [40] Robertson J, Wade E, Kopp Y, Bueno J, Hurtado A. Toward neuromorphic photonic networks of ultrafast spiking laser neurons. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 26, 7700715 (2020). [41] Zhang YH, Robertson J, Xiang SY, Hejda M, Bueno J et al. All-optical neuromorphic binary convolution with a spiking VCSEL neuron for image gradient magnitudes. Photonics Res 9, B201–B209 (2021). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.412141 [42] Nahmias MA, Shastri BJ, Tait AN, Prucnal PR. A leaky integrate-and-fire laser neuron for ultrafast cognitive computing. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 19, 1800212 (2013). [43] Shastri BJ, Nahmias MA, Tait AN, Rodriguez AW, Wu B et al. Spike processing with a graphene excitable laser. Sci Rep 6, 19126 (2016). doi: 10.1038/srep19126 [44] Chakraborty I, Saha G, Sengupta G, Roy K. Toward fast neural computing using all-photonic phase change spiking neurons. Sci Rep 8, 12980 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31365-x [45] Selmi F, Braive R, Beaudoin G, Sagnes I, Kuszelewicz R et al. Relative refractory period in an excitable semiconductor laser. Phys Rev Lett 112, 183902 (2014). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.183902 [46] Peng HT, Angelatos G, Ferreira de Lima T, Nahmias MA, Tait AN et al. Temporal information processing with an integrated laser neuron. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 26, 5100209 (2020). [47] Xiang JL, Zhang YJ, Zhao YT, Guo XH, Su YK. All-optical silicon microring spiking neuron. Photonics Res 10, 939–946 (2022). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.445954 [48] Zheng DZ, Xiang SY, Guo XX, Zhang YH, Gu BL et al. Experimental demonstration of coherent photonic neural computing based on a Fabry–Perot laser with a saturable absorber. Photonics Res 11, 65–71 (2023). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.471950 [49] Shi YC, Li SM, Chen XF, Li LY, Li JS et al. High channel count and high precision channel spacing multi-wavelength laser array for future PICs. Sci Rep 4, 7377 (2014). doi: 10.1038/srep07377 [50] Shi YC, Xiang SY, Guo XX, Zhang YH, Wang HJ et al. Photonic integrated spiking neuron chip based on a self-pulsating DFB laser with a saturable absorber. Photonics Res 11, 1382–1389 (2023). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.485941 [51] Beck H, Yaari Y. Plasticity of intrinsic neuronal properties in CNS disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 9, 357–369 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nrn2371 [52] The MNIST database of handwritten digits. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/. [53] Alanis JA, Robertson J, Hejda M, Hurtado A. Weight adjustable photonic synapse by nonlinear gain in a vertical cavity semiconductor optical amplifier. Appl Phys Lett 119, 201104 (2021). doi: 10.1063/5.0064374 [54] Robertson J, Alanis JA, Hejda M, Hurtado A. Photonic synaptic system for MAC operations by interconnected vertical cavity surface emitting lasers. Opt Mater. Express 12, 1417–1426 (2022). doi: 10.1364/OME.450923 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
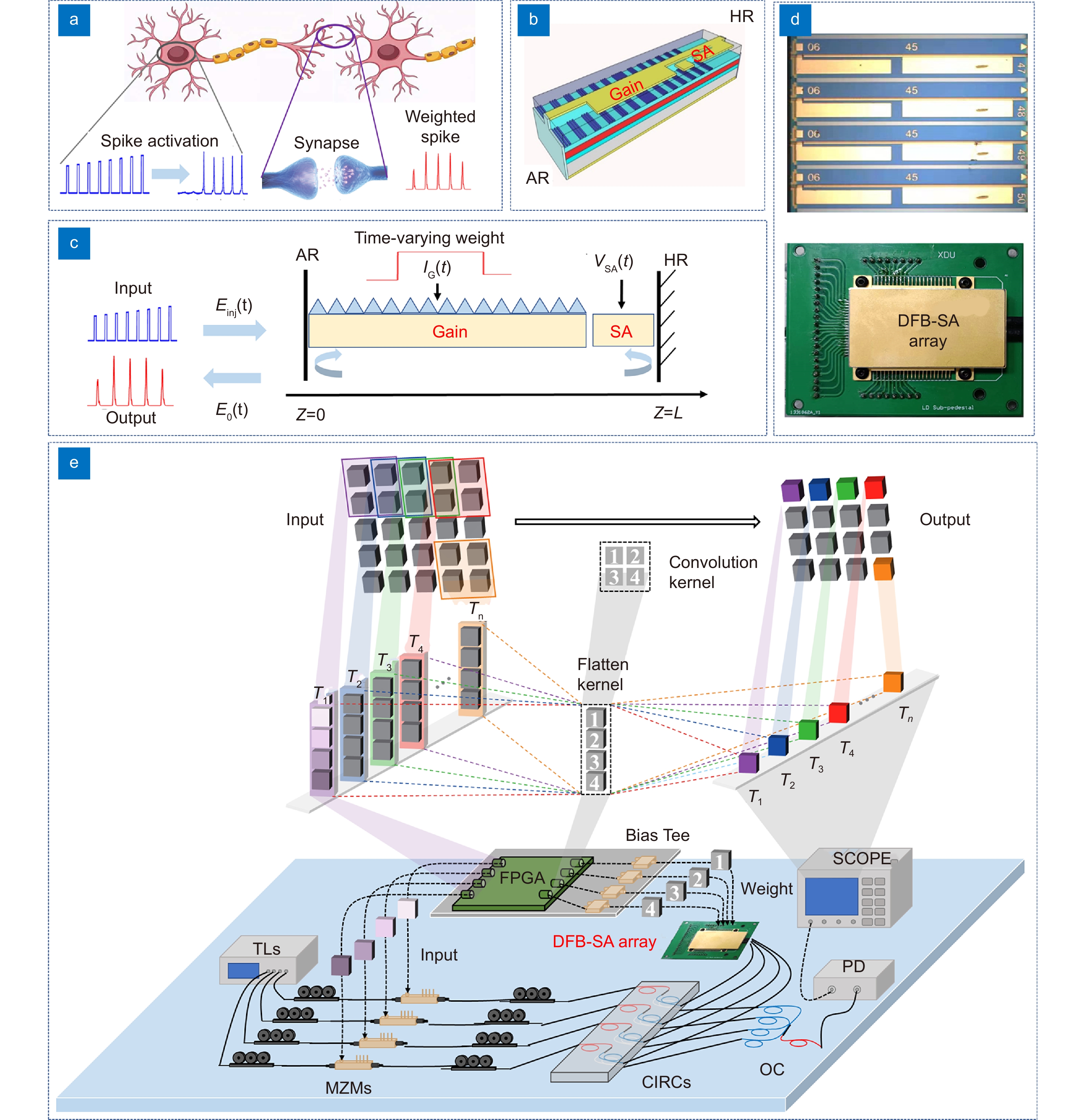
Figure 1.
The operation principle of photonic neuron-synaptic core. (a) The schematic diagram of biological neuron. (b) The structure and micrograph picture of the designed DFB-SA laser chip. (c) The spike processing in a DFB-SA laser. (d) The micrograph picture of the fabricated DFB-SA laser array chip and the compact packaged module. (e) Spike-based matrix convolution based on the four-channel DFB-SA laser array.
-
Figure 2.
Experimental demonstration of intrinsic excitability plasticity in a single fabricated DFB-SA laser chip. (a) Experimental setup of a DFB-SA laser for emulating the neuronal intrinsic plasticity and linear weighting. (b) Optical spectrum of the free-running DFB-SA laser. (c) Different excitability threshold, (d) different refractory period, and (e) different temporal integration behavior under different gain currents. VSA=−0.4V. The inset in (a) corresponds to the wire bonding of the fabricated DFB-SA laser chip.
-
Figure 3.
Continuously tunable weighted spike output for different static gain currents in a single fabricated DFB-SA laser chip. (a) The weighted output of a single spike for different gain currents. (b) The weighted spike trains for three representative gain current. (c) The spike peak amplitude as a function of gain current.
-
Figure 4.
Experimental demonstration of simultaneous implementation of neuron excitability threshold and synaptic linear weighting functions in a single DFB-SA laser. (a) Corresponds to static gain current at different level. (b) and (c) Correspond to step-wise and continuously-varying gain current, respectively. In (b) I G0=80 mA, I G = I M+ I G0.
-
Figure 5.
Spike-based neural computation in a photonic SNN consisting of two PRE DFB-SA lasers and one POST FP-SA laser. (a) Experimental setup of a full-functional prototypical photonic neuromorphic system. (b) Optical spectra of the DFB-SA lasers and FP-SA laser. (c) Spike-based AND. (d) Spike-based OR. With IG=100.1 mA and VSA=−0.1 V for the DFB-SA1 laser; IG=102.1 mA and VSA=−0.27 V for the DFB-SA2 laser; IG=56.9 mA and VSA=−0.25 V for the FP-SA laser.
-
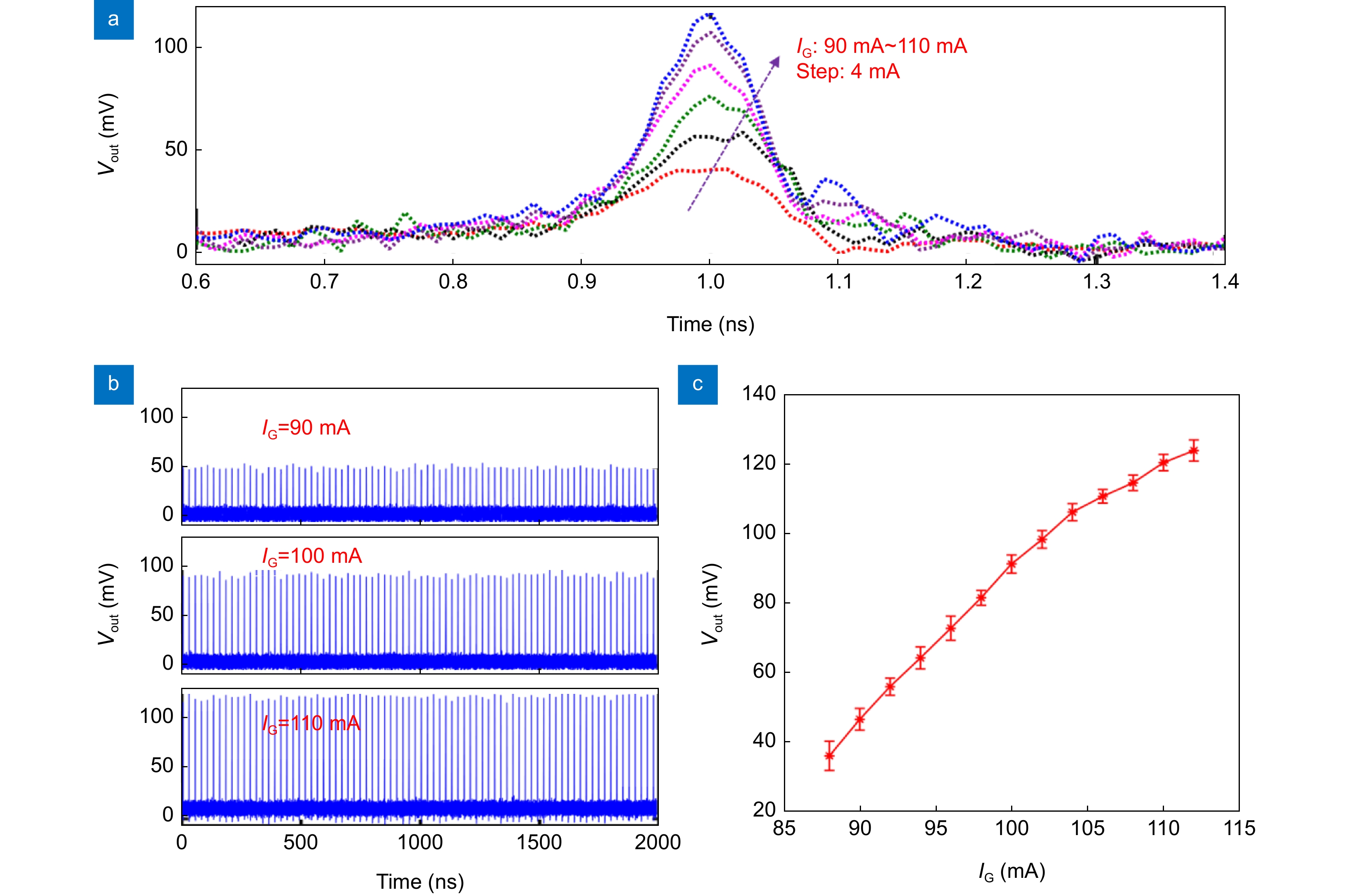
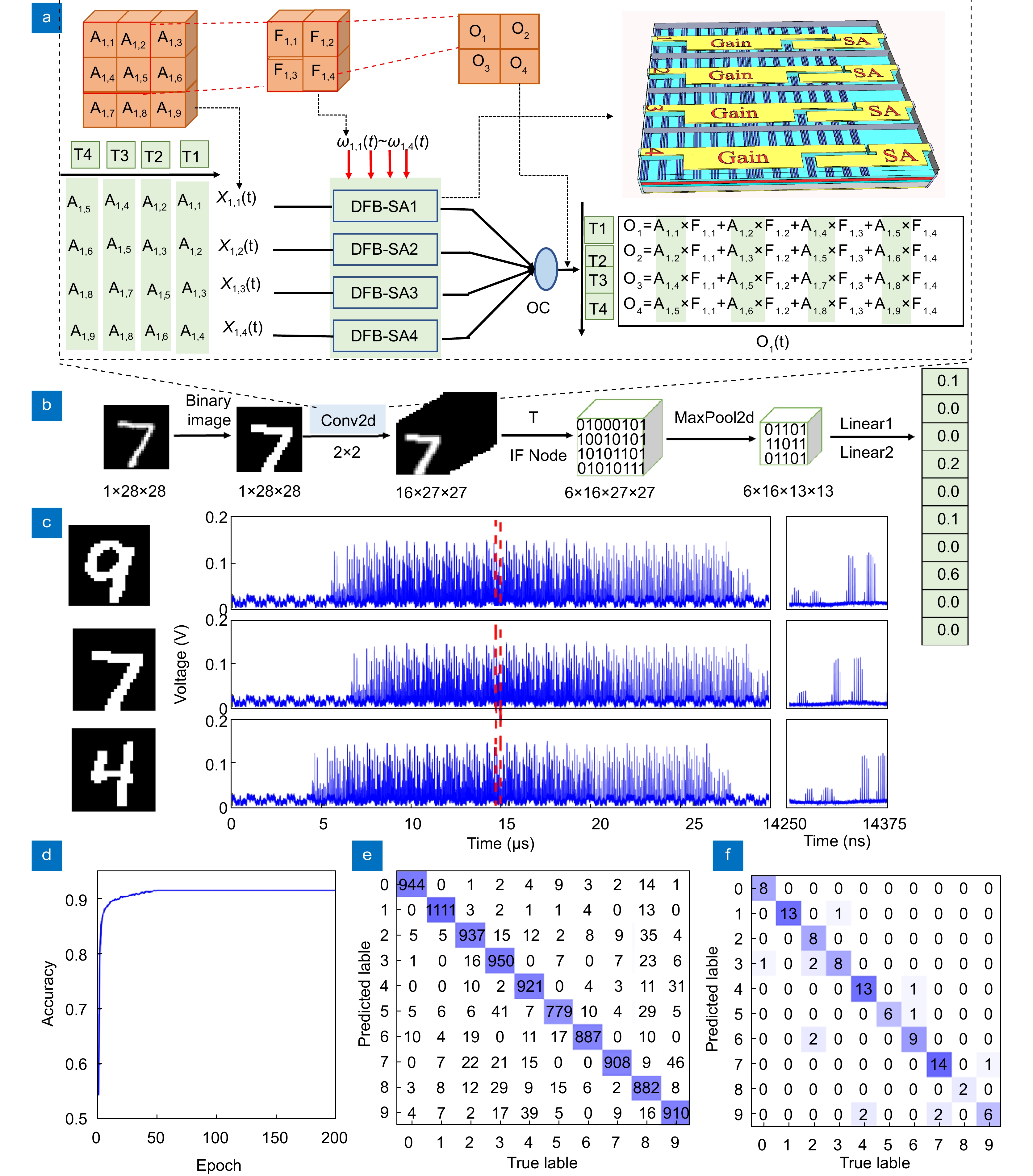
Figure 6.
Experimental results of matrix multiplication with a four-channel DFB-SA laser array. (a) Schematic diagram of the parallel linear weight with the DFB-SA laser array. (b) Network structure for spiking CNN. (c) The temporal output of the convolved results for 16 convolutional kernels for three input samples, the right column represents the enlargement of the region denoted by the dashed lines. (d–f) Represent the training accuracy, confusion matrix for software inference and hardware-software inference.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: