| Citation: | Han RZ, Zhang YC, Jiang QL et al. Ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced high spatial frequency periodic structures on silicon surfaces. Opto-Electron Sci 3, 230013 (2024). doi: 10.29026/oes.2024.230013 |
Ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced high spatial frequency periodic structures on silicon surfaces
-
Abstract
Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) have been extensively studied over the past few decades. In particular, the period and groove width of high-spatial-frequency LIPSS (HSFL) is much smaller than the diffraction limit, making it a useful method for efficient nanomanufacturing. However, compared with the low-spatial-frequency LIPSS (LSFL), the structure size of the HSFL is smaller, and it is more easily submerged. Therefore, the formation mechanism of HSFL is complex and has always been a research hotspot in this field. In this study, regular LSFL with a period of 760 nm was fabricated in advance on a silicon surface with two-beam interference using an 800 nm, 50 fs femtosecond laser. The ultrafast dynamics of HSFL formation on the silicon surface of prefabricated LSFL under single femtosecond laser pulse irradiation were observed and analyzed for the first time using collinear pump-probe imaging method. In general, the evolution of the surface structure undergoes five sequential stages: the LSFL begins to split, becomes uniform HSFL, degenerates into an irregular LSFL, undergoes secondary splitting into a weakly uniform HSFL, and evolves into an irregular LSFL or is submerged. The results indicate that the local enhancement of the submerged nanocavity, or the nanoplasma, in the prefabricated LSFL ridge led to the splitting of the LSFL, and the thermodynamic effect drove the homogenization of the splitting LSFL, which evolved into HSFL. -

-
References
[1] Chichkov BN, Momma C, Nolte S, Von Alvensleben F, Tünnermann A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl Phys A 63, 109–115 (1996). doi: 10.1007/BF01567637 [2] Sugioka K, Cheng Y. Ultrafast lasers—reliable tools for advanced materials processing. Light Sci Appl 3, e149 (2014). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.30 [3] Wang JC, Guo CL. Ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface pattern formation on metals. Appl Phys Lett 87, 251914 (2005). doi: 10.1063/1.2146067 [4] Zhang YC, Jiang QL, Cao KQ, Chen TQ, Cheng K et al. Extremely regular periodic surface structures in a large area efficiently induced on silicon by temporally shaped femtosecond laser. Photonics Res 9, 05000839 (2021). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.418937 [5] Jia TQ, Chen HX, Huang M, Zhao FL, Qiu JR et al. Formation of nanogratings on the surface of a ZnSe crystal irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. Phys Rev B 72, 125429 (2005). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.125429 [6] Liu YY, Wang YX, Yang M, Wu Q, Li ZX et al. Deep-subwavelength ripples on the ZnO surface obtained via metal-film-assisted femtosecond laser processing. Appl Surf Sci 573, 151576 (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151576 [7] Zhang DS, Liu RJ, Li ZG. Irregular LIPSS produced on metals by single linearly polarized femtosecond laser. Int J Extrem Manuf 4, 015102 (2022). doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ac376c [8] Li RH, Zhou YH, Liu ST, Huang M, Jiang SJ. Ink‐assisted laser‐induced heterogeneous permanent/erasable nanostructures on metals. Laser Photonics Rev 17, 2200769 (2023). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202200769 [9] Bricchi E, Klappauf BG, Kazansky PG. Form birefringence and negative index change created by femtosecond direct writing in transparent materials. Opt Lett 29, 119–121 (2004). doi: 10.1364/OL.29.000119 [10] Gu M, Li XP, Cao YY. Optical storage arrays: a perspective for future big data storage. Light Sci Appl 3, e177 (2014). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.58 [11] Wu C, Crouch CH, Zhao L, Carey JE, Younkin R et al. Near-unity below-band-gap absorption by microstructured silicon. Appl Phys Lett 78, 1850–1852 (2001). doi: 10.1063/1.1358846 [12] Lopez‐Santos C, Puerto D, Siegel J, Macias‐Montero M, Florian C et al. Anisotropic resistivity surfaces produced in ITO films by laser‐induced nanoscale self‐organization. Adv Opt Mater 9, 2001086 (2021). doi: 10.1002/adom.202001086 [13] Yong JL, Chen F, Yang Q, Jiang ZD, Hou X. A review of femtosecond-laser-induced underwater superoleophobic surfaces. Adv Mater Interfaces 5, 1701370 (2018). doi: 10.1002/admi.201701370 [14] Jiang QL, Chen L, Liu JK, Zhang YC, Zhang SA et al. Periodic transparent nanowires in ITO film fabricated via femtosecond laser direct writing. Opto-Electron Sci 2, 220002 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oes.2023.220002 [15] Chen L, Cao KQ, Li YL, Liu JK, Zhang SA et al. Large-area straight, regular periodic surface structures produced on fused silica by the interference of two femtosecond laser beams through cylindrical lens. Opto-Electron Adv 4, 200036 (2021). doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.200036 [16] Li YH, Zhang XY, Zou TT, Mu QQ, Yang JJ. Vivid structural color macropatterns created by flexible nanopainting of ultrafast lasers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14, 21758–21767 (2022). doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c04542 [17] Buividas R, Mikutis M, Juodkazis S. Surface and bulk structuring of materials by ripples with long and short laser pulses: Recent advances. Prog Quantum Electron 38, 119–156 (2014). doi: 10.1016/j.pquantelec.2014.03.002 [18] Bonse J, Hohm S, Kirner SV, Rosenfeld A, Kruger J. Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures-A Scientific Evergreen. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 23, 15 (2017). [19] Huang M, Zhao FL, Cheng Y, Xu NS, Xu ZZ. Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS Nano 3, 4062–4070 (2009). doi: 10.1021/nn900654v [20] Sipe JE, Young JF, Preston JS, van Driel HM. Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Phys Rev B 27, 1141–1154 (1983). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.27.1141 [21] Bonse J, Munz M, Sturm H. Structure formation on the surface of indium phosphide irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. J Appl Phys 97, 013538 (2005). doi: 10.1063/1.1827919 [22] Bonse J, Gräf S. Ten open questions about laser-induced periodic surface structures. Nanomaterials 11, 3326 (2021). doi: 10.3390/nano11123326 [23] Cheng K, Liu JK, Cao KQ, Chen L, Zhang YC et al. Ultrafast dynamics of single-pulse femtosecond laser-induced periodic ripples on the surface of a gold film. Phys Rev B 98, 184106 (2018). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.98.184106 [24] Okamuro K, Hashida M, Miyasaka Y, Ikuta Y, Tokita S et al. Laser fluence dependence of periodic grating Hashida structures formed on metal surfaces under femtosecond laser pulse irradiation. Phys Rev B 82, 165417 (2010). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.165417 [25] Miyaji G, Miyazaki K. Origin of periodicity in nanostructuring on thin film surfaces ablated with femtosecond laser pulses. Opt Express 16, 16265–16271 (2008). doi: 10.1364/OE.16.016265 [26] Wang L, Xu BB, Cao XW, Li QK, Tian WJ et al. Competition between subwavelength and deep-subwavelength structures ablated by ultrashort laser pulses. Optica 4, 637–642 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000637 [27] Xie HB, Zhao B, Cheng JL, Chamoli SK, Zou TT et al. Super-regular femtosecond laser nanolithography based on dual-interface plasmons coupling. Nanophotonics 10, 3831–3842 (2021). doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0329 [28] Derrien TJY, Koter R, Krüger J, Höhm S, Rosenfeld A et al. Plasmonic formation mechanism of periodic 100-nm-structures upon femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon in water. J Appl Phys 116, 074902 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4887808 [29] Reif J, Costache F, Henyk M, Pandelov SV. Ripples revisited: non-classical morphology at the bottom of femtosecond laser ablation craters in transparent dielectrics. Appl Surf Sci 197–198, 891–895 (2002). [30] Costache F, Henyk M, Reif J. Modification of dielectric surfaces with ultra-short laser pulses. Appl Surf Sci 186, 352–357 (2002). doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(01)00675-4 [31] Reif J, Varlamova O, Costache F. Femtosecond laser induced nanostructure formation: self-organization control parameters. Appl Phys A 92, 1019–1024 (2008). doi: 10.1007/s00339-008-4671-3 [32] Ionin AA, Kudryashov SI, Ligachev AE, Makarov SV, Seleznev LV et al. Nanoscale cavitation instability of the surface melt along the grooves of one-dimensional nanorelief gratings on an aluminum surface. JETP Lett 94, 266–269 (2011). doi: 10.1134/S0021364011160065 [33] Nathala CSR, Ajami A, Ionin AA, Kudryashov SI, Makarov SV et al. Experimental study of fs-laser induced sub-100-nm periodic surface structures on titanium. Opt Express 23, 5915–5929 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OE.23.005915 [34] Abere MJ, Torralva B, Yalisove SM. Periodic surface structure bifurcation induced by ultrafast laser generated point defect diffusion in GaAs. Appl Phys Lett 108, 153110 (2016). doi: 10.1063/1.4946861 [35] Bhardwaj VR, Simova E, Rajeev PP, Hnatovsky C, Taylor RS et al. Optically produced arrays of planar nanostructures inside fused silica. Phys Rev Lett 96, 057404 (2006). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.057404 [36] Pan AF, Wang WJ, Liu B, Mei XS, Yang HZ et al. Formation of high-spatial-frequency periodic surface structures on indium-tin-oxide films using picosecond laser pulses. Mater Des 121, 126–135 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.02.055 [37] Zhang H, Du K, Li XW. Enhancement and blueshift of high-frequency laser-induced periodic surface structures with preformed nanoscale surface roughness. Opt Express 27, 19973–19983 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.019973 [38] Li C, Cheng GH, Sedao X, Zhang W, Zhang H et al. Scattering effects and high-spatial-frequency nanostructures on ultrafast laser irradiated surfaces of zirconium metallic alloys with nano-scaled topographies. Opt Express 24, 1558–1568 (2016). doi: 10.1364/oe.24.011558 [39] Zhang H, Colombier JP, Li C, Faure N, Cheng GH et al. Coherence in ultrafast laser-induced periodic surface structures. Phys Rev B 92, 174109 (2015). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.92.174109 [40] Huang M, Cheng Y, Zhao FL, Xu ZZ. The significant role of plasmonic effects in femtosecond laser-induced grating fabrication on the nanoscale. Ann Phys-Berlin 525, 74–86 (2013). doi: 10.1002/andp.201200136 [41] Huang M, Xu ZZ. Spontaneous scaling down of femtosecond laser-induced apertures towards the 10-nanometer level: the excitation of quasistatic surface plasmons. Laser Photonics Rev 8, 633–652 (2014). doi: 10.1002/lpor.201300212 [42] Dufft D, Rosenfeld A, Das SK, Grunwald R, Bonse J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures revisited: a comparative study on ZnO. J Appl Phys 105, 034908 (2009). doi: 10.1063/1.3074106 [43] Rudenko A, Abou-Saleh A, Pigeon F, Mauclair C, Garrelie F et al. High-frequency periodic patterns driven by non-radiative fields coupled with Marangoni convection instabilities on laser-excited metal surfaces. Acta Mater 194, 93–105 (2020). doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.058 [44] Rudenko A, Mauclair C, Garrelie F, Stoian R, Colombier JP. Amplification and regulation of periodic nanostructures in multipulse ultrashort laser-induced surface evolution by electromagnetic-hydrodynamic simulations. Phys Rev B 99, 235412 (2019). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.235412 [45] Skolski JZP, Römer GRBE, Vincenc Obona J, Huis in 't Veld AJ. Modeling laser-induced periodic surface structures: finite-difference time-domain feedback simulations. J Appl Phys 115, 103102 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4867759 [46] Zhou K, Jia X, Jia TQ, Cheng K, Cao KQ et al. The influences of surface plasmons and thermal effects on femtosecond laser-induced subwavelength periodic ripples on Au film by pump-probe imaging. J Appl Phys 121, 104301 (2017). doi: 10.1063/1.4978375 [47] Xu J, Min CJ, Zhang YQ, Ni JL, Cao GW et al. Imaging ultrafast evolution of subwavelength-sized topography using single-probe structured light microscopy. Photonics Res 10, 1900–1908 (2022). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.458613 [48] Obara G, Shimizu H, Enami T, Mazur E, Terakawa M et al. Growth of high spatial frequency periodic ripple structures on SiC crystal surfaces irradiated with successive femtosecond laser pulses. Opt Express 21, 26323–26334 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OE.21.026323 [49] Cao KQ, Chen L, Wu HC, Liu JK, Cheng K et al. Large-area commercial-grating-quality subwavelength periodic ripples on silicon efficiently fabricated by gentle ablation with femtosecond laser interference via two cylindrical lenses. Opt Laser Technol 131, 106441 (2020). doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106441 [50] Jia X, Jia TQ, Peng NN, Feng DH, Zhang SA et al. Dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on silicon by high spatial and temporal resolution imaging. J Appl Phys 115, 143102 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4870445 [51] Liu JK, Jia X, Wu WS, Cheng K, Feng DH et al. Ultrafast imaging on the formation of periodic ripples on a Si surface with a prefabricated nanogroove induced by a single femtosecond laser pulse. Opt Express 26, 6302–6315 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OE.26.006302 [52] Hou SS, Huo YY, Xiong PX, Zhang Y, Zhang SA et al. Formation of long- and short-periodic nanoripples on stainless steel irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. J Phys D Appl Phys 44, 505401 (2011). doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/50/505401 [53] Zhang YH, Jiang QL, Long MQ, Han RZ, Cao KQ et al. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic structures: mechanisms, techniques, and applications. Opto-Electron Sci 1, 220005 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oes.2022.220005 [54] Yu XH, Qi DF, Wang HY, Zhang YW, Wang LT et al. In situ and ex-situ physical scenario of the femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. Opt Express 27, 10087–10097 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.010087 [55] Lin XM, Li XH, Zhang YB, Xie CX, Liu KJ et al. Periodic structures on germanium induced by high repetition rate femtosecond laser. Opt Laser Technol 101, 291–297 (2018). doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.11.028 [56] Li ZX, Wu Q, Jiang XD, Zhou X, Liu YY et al. Formation mechanism of high spatial frequency laser-induced periodic surface structures and experimental support. Appl Surf Sci 580, 152107 (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.152107 [57] Zhang N, Zhu XN, Yang JJ, Wang XL, Wang MW. Time-resolved shadowgraphs of material ejection in intense femtosecond laser ablation of aluminum. Phys Rev Lett 99, 167602 (2007). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.167602 [58] Nolte S, Momma C, Jacobs H, Tünnermann A, Chichkov BN et al. Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J Opt Soc Am B 14, 2716–2722 (1997). doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.14.002716 [59] Ionin AA, Kudryashov SI, Samokhin AA. Material surface ablation produced by ultrashort laser pulses. Phys Usp 60, 149–160 (2017). doi: 10.3367/UFNe.2016.09.037974 [60] Huang M, Zhao FL, Cheng Y, Xu NS, Xu ZZ. Mechanisms of ultrafast laser-induced deep-subwavelength gratings on graphite and diamond. Phys Rev B 79, 125436 (2009). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.79.125436 [61] Levy Y, Derrien TJY, Bulgakova NM, Gurevich EL, Mocek T. Relaxation dynamics of femtosecond-laser-induced temperature modulation on the surfaces of metals and semiconductors. Appl Surf Sci 374, 157–164 (2016). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.159 [62] Zhang TY, Guo BS, Jiang L, Chen ML, Zhan NW. Ultrafast observation of multiple shock waves evolution and interaction processes in femtosecond laser processing. Phys Fluids 35, 057114 (2023). doi: 10.1063/5.0146254 [63] Liu JK, Zhao H, Cheng K, Ju JQ, Feng DH et al. Ultrafast dynamics of the thin surface plasma layer and the periodic ripples formation on GaP crystal irradiated by a single femtosecond laser pulse. Opt Express 27, 37859–37876 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.037859 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced high spatial frequency periodic structures on silicon surfaces 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
(a) Confocal optical microscopy image of LSFL prefabricated on silicon surface, and (b) cross-sectional profile of LSFL.
-
Figure 2.
(a) Experiment setup of the collinear pump-probe imaging system; HWP is half wave plate, PBS is polarized beam splitter, and BS is beam splitter. (b) Spectra of the white-light pulse with (red solid curve) and without (black dotted curve) the short-wave-pass filter. (c) Laser spot area on the object plane with and without the concave lens. (d) The profile of the normalized intensity of blue light emission and laser field intensity along the arrow in (c).
-
Figure 3.
Optical images of surface microstructures before (a) and after (b–c) irradiation by a single laser pulse.
-
Figure 4.
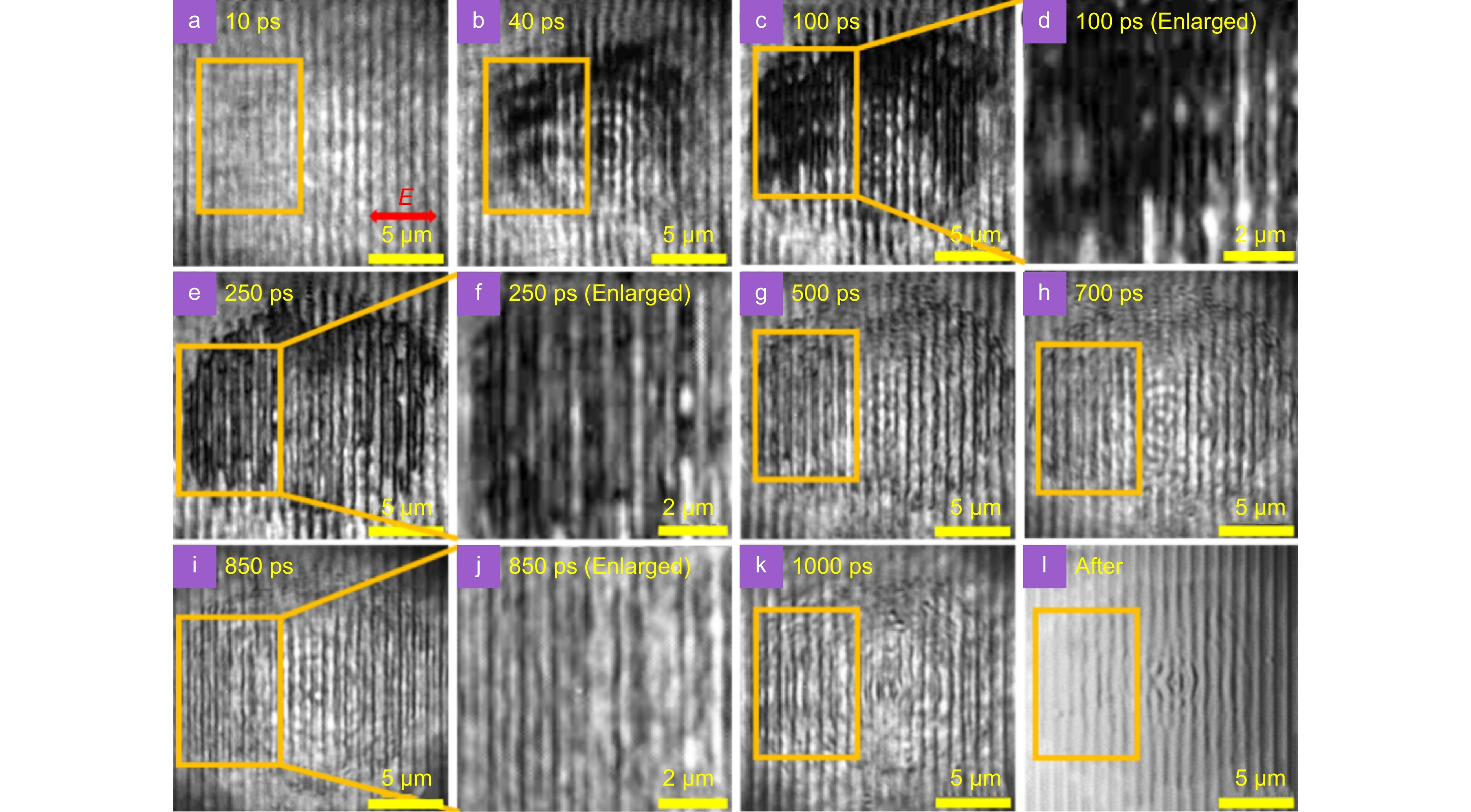
Optical micrographs of the silicon surface at different delay times after single-pulse laser irradiation. The horizontal double arrow shows the laser polarization direction.
-
Figure 5.
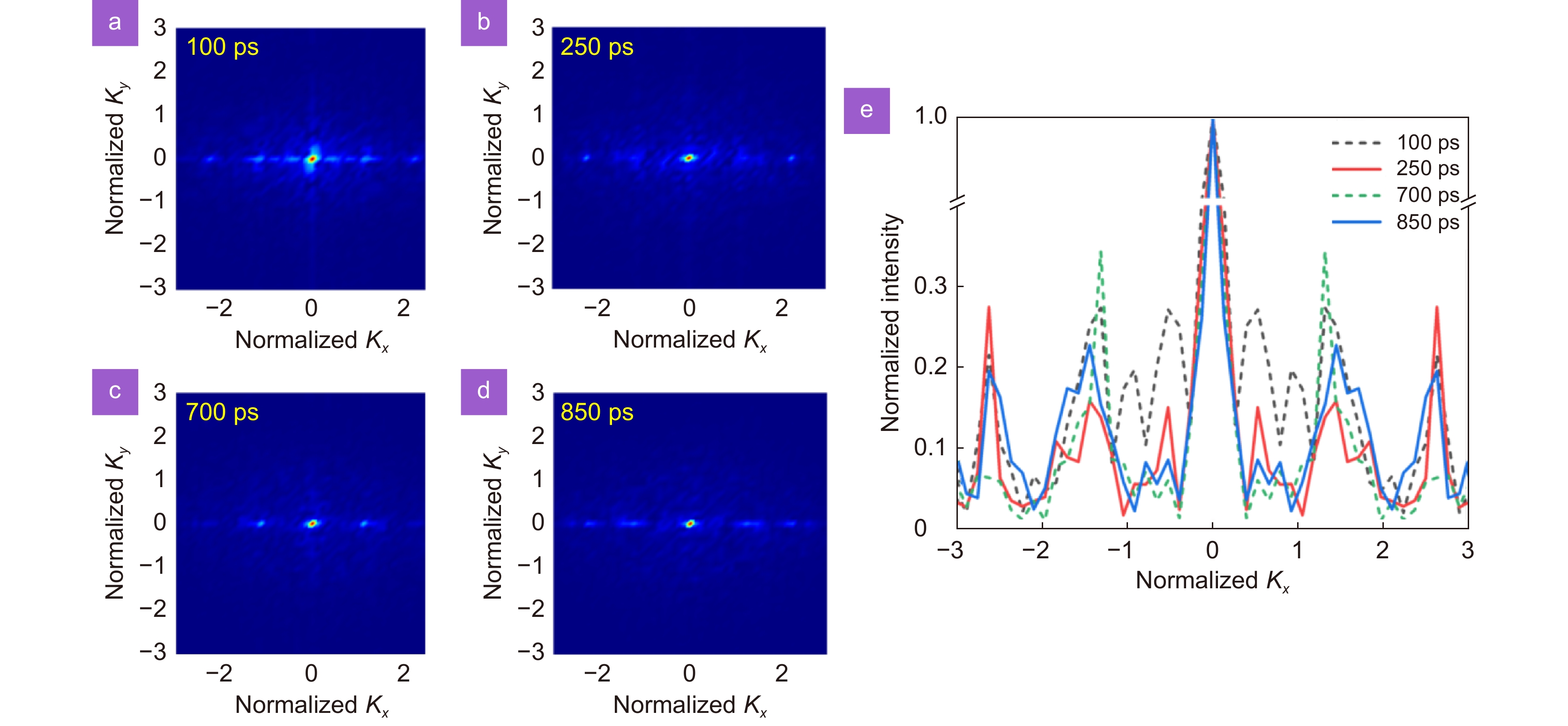
Two-dimensional FT images of the surface nanostructures shown in Fig. 4 at different delay times. (a) 100 ps, (b) 250 ps, (c) 700 ps, and (d) 850 ps, respectively. (e) The FT spectra in the x-direction of Ky=0.
-
Figure 6.
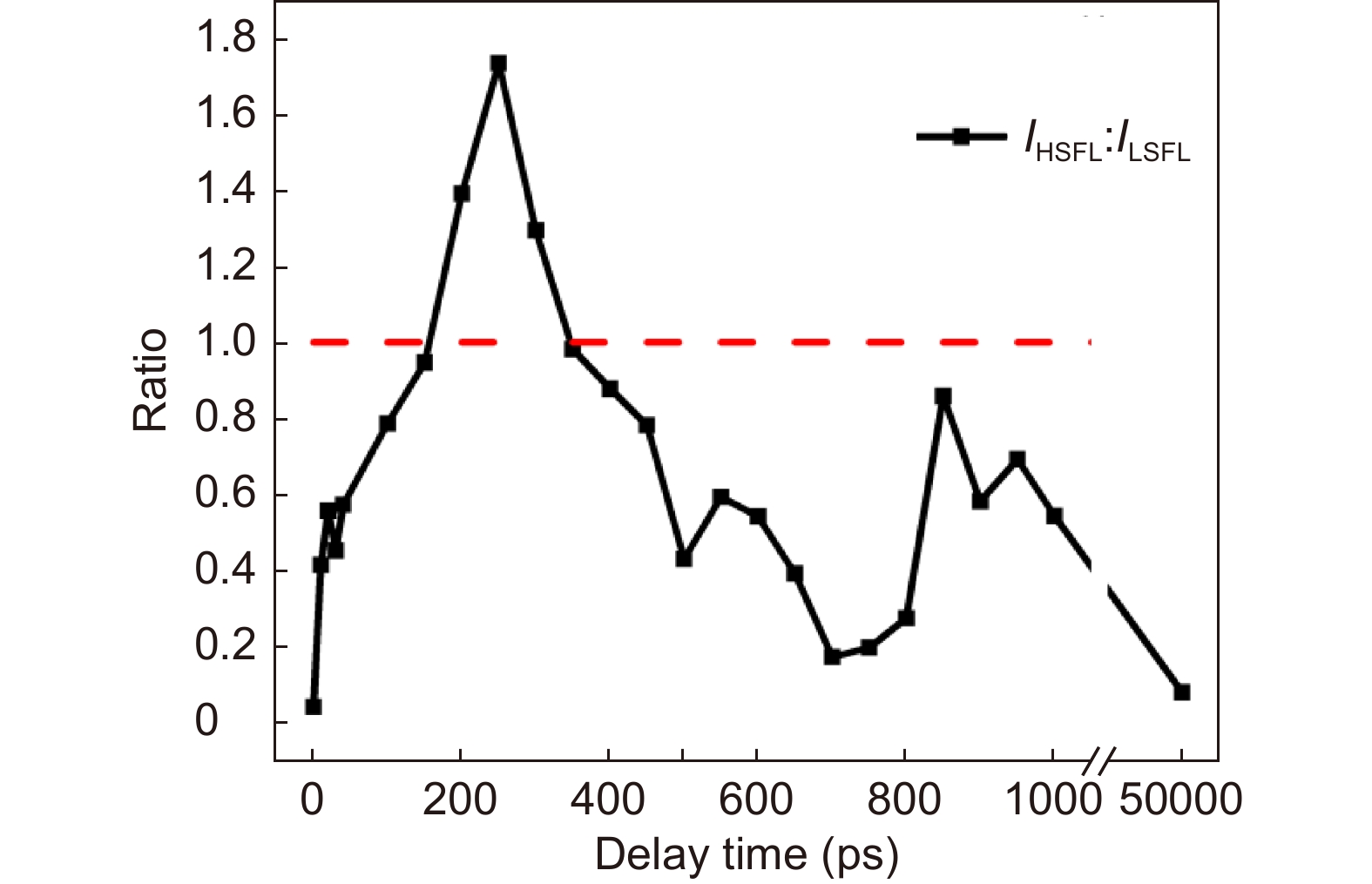
The delay time dependence of the peak intensity ratio of HSFL to LSFL corresponding to the FT images.
-
Figure 7.
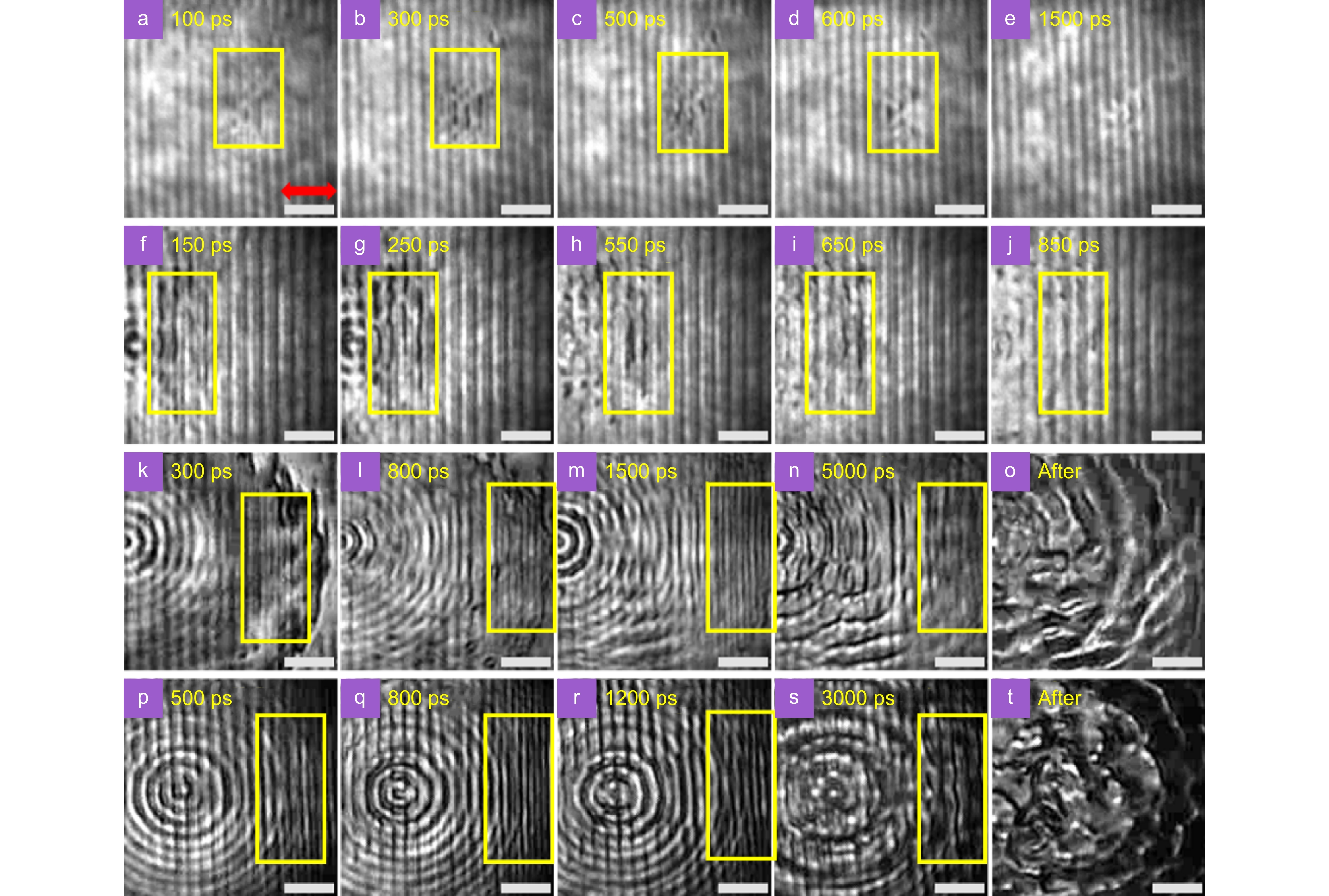
Optical micrographs of the silicon surface with pre-fabricated LSFL at different delay times after irradiation by a single laser pulse with different fluences. (a–e) Laser fluence is 0.44 J/cm2, (f–j) is 0.59 J/cm2, (k–o) is 1.76 J/cm2, and (p–t) is 3.53 J/cm2. The red horizontal double arrow shows the laser polarization direction. The gray scale in all figures is 3 microns.
-
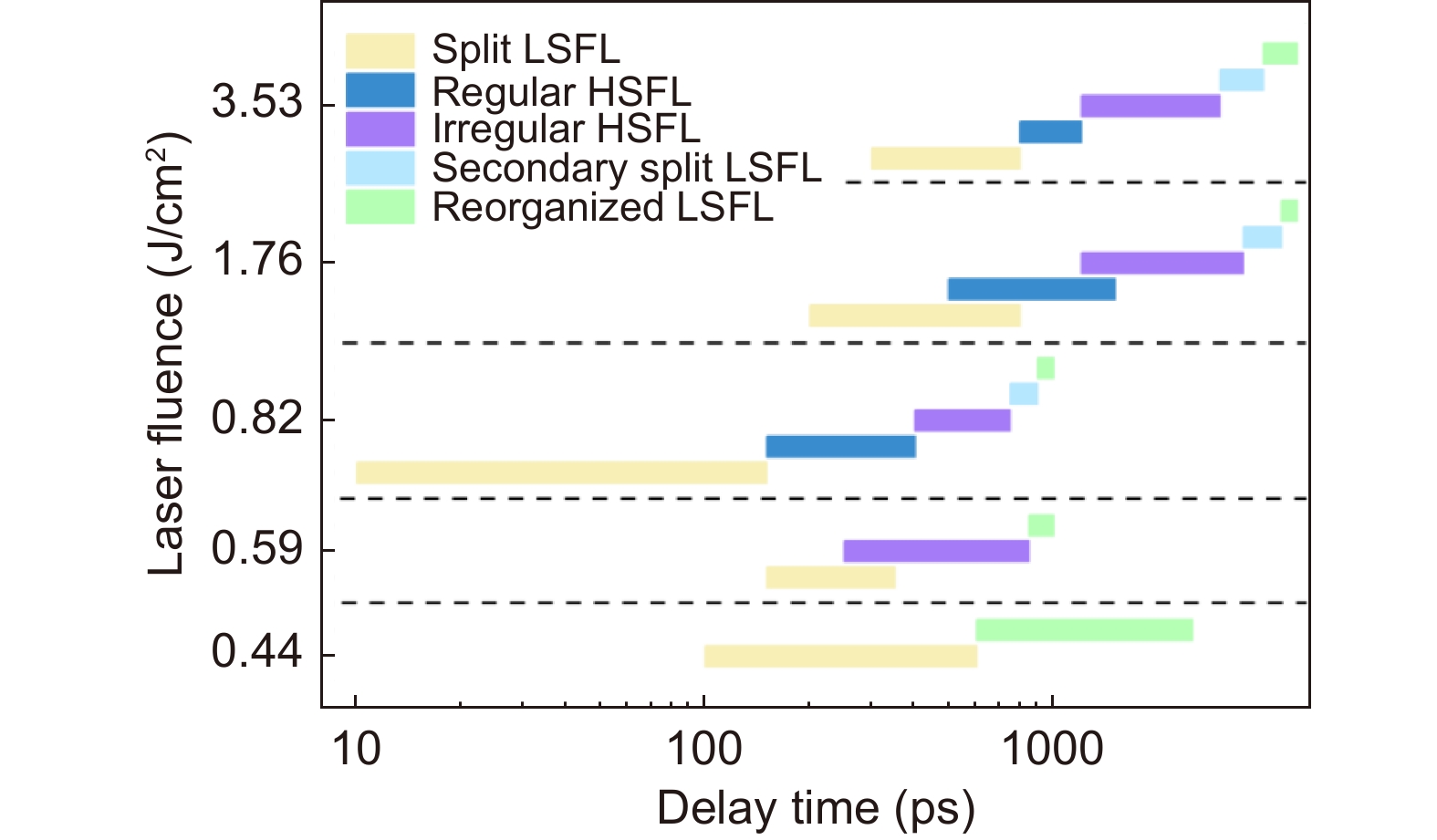
Figure 8.
Evolution of surface morphology with delay time under single pulse irradiation with different laser fluences. LSFL was pre-fabricated prior to irradiation by a single pulse.
-
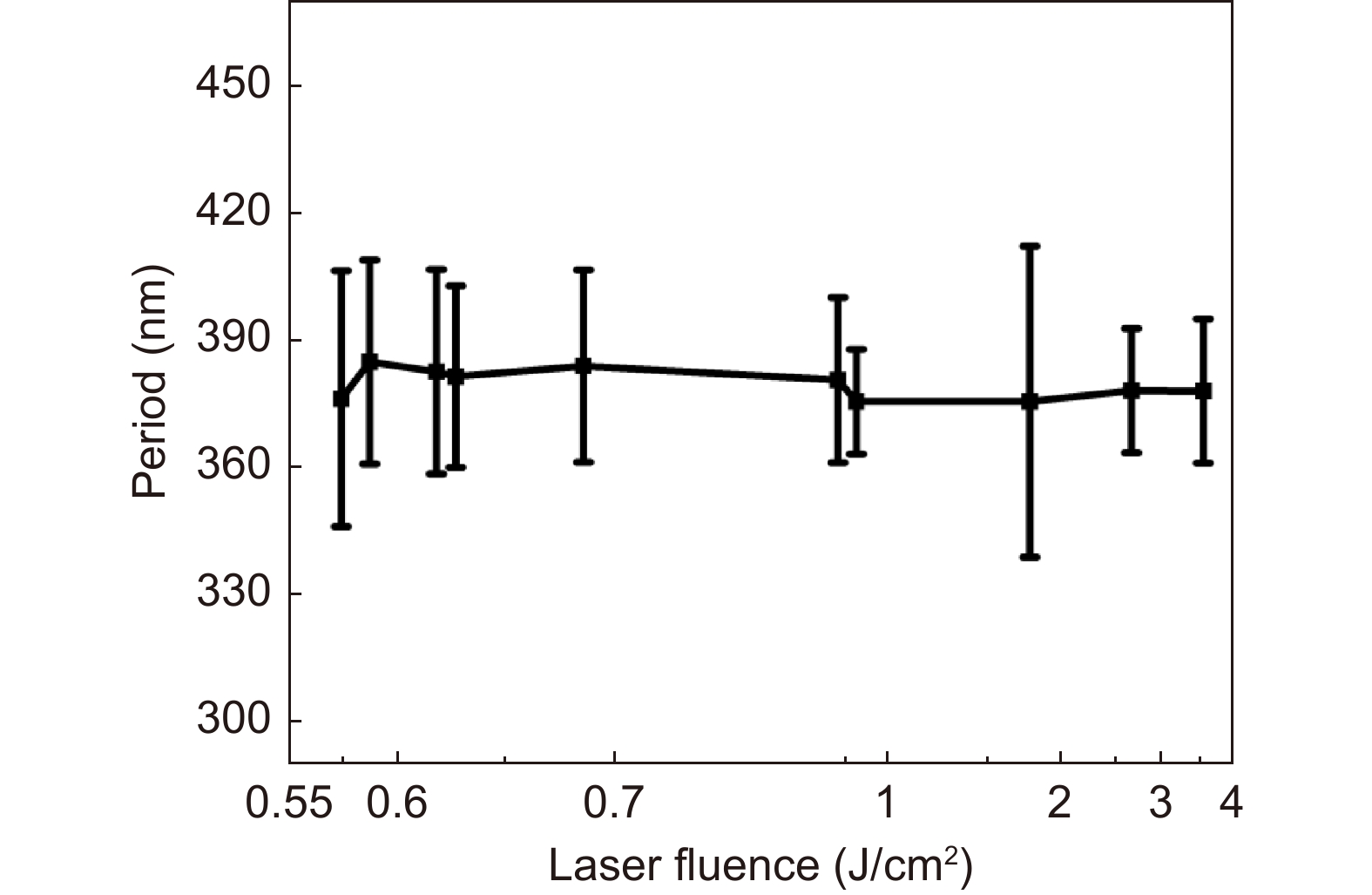
Figure 9.
The laser fluence dependence of the period of uniform and clear HSFL under femtosecond laser irradiation.
-
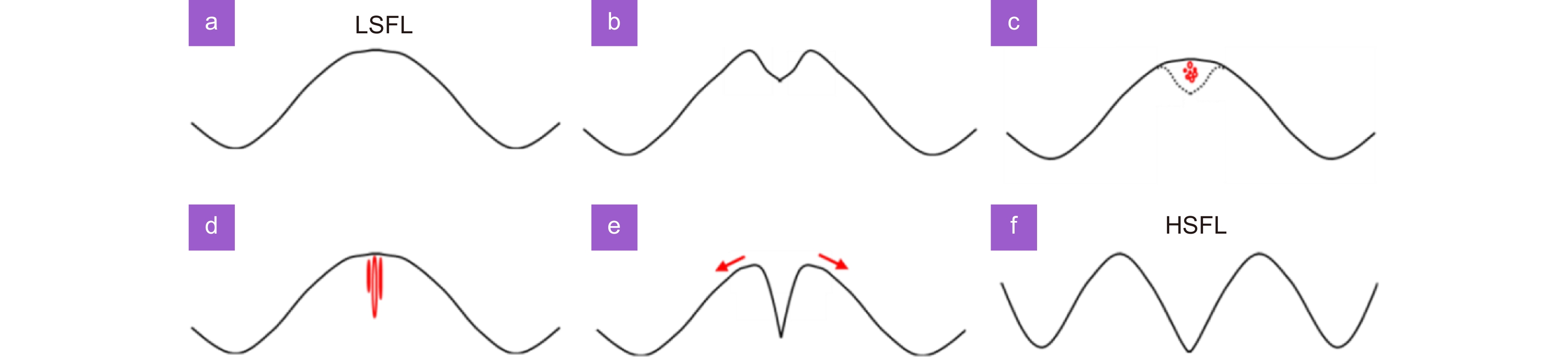
Figure 10.
(a–c) Schematic diagram of the formation process of submerged nanocavities during LSFL prefabrication. (d–f) Schematic diagram of the formation of uniform HSFL.
-
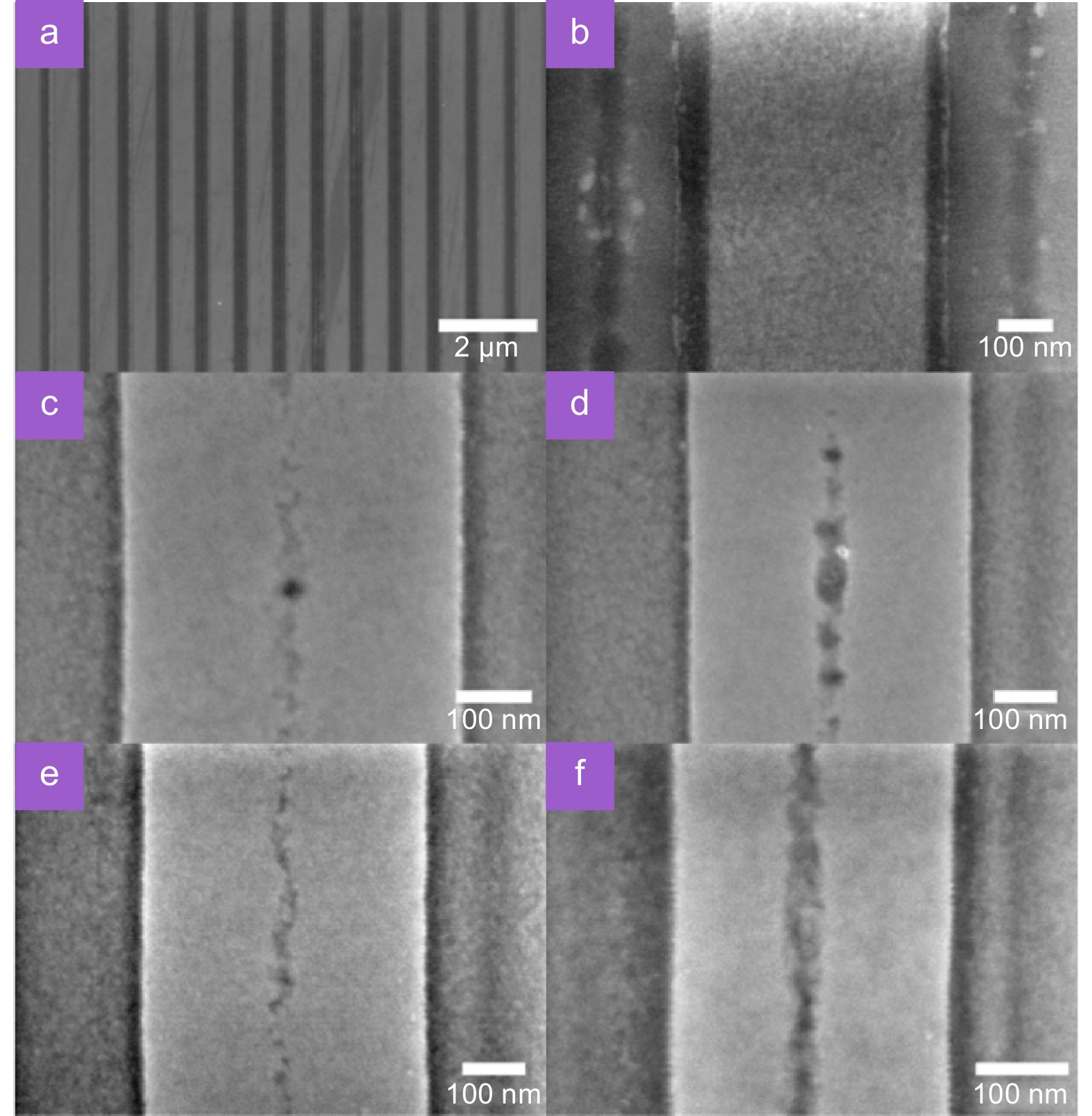
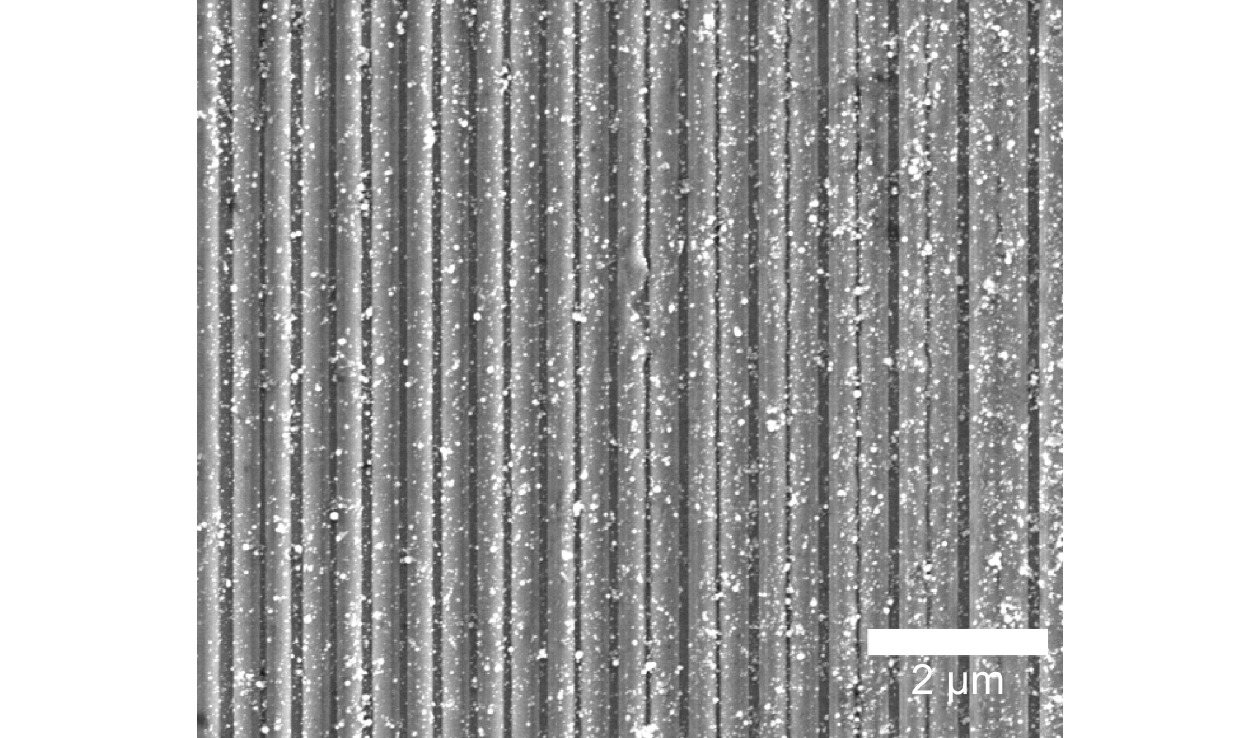
Figure 11.
SEM images of the LSFL prefabricated on a silicon surface by direct writing with dual-beam interference, where a single-beam laser with a fluence of 0.13 J/cm2 and a scanning speed of 2 mm/s. (a–b) Before etched, and (c–f) after etched with HF solution.
-
Figure 12.
SEM image of silicon surface by direct writing with dual-beam interference, where a single-beam laser with a fluence of 0.24 J/cm2 and a scanning speed of 2.0 mm/s. The sample was not corroded with HF solution.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: