| Citation: | Zhou L, Wang YD, Kang JL et al. Observation of polaronic state assisted sub-bandgap saturable absorption. Opto-Electron Adv 8, 240312 (2025). doi: 10.29026/oea.2025.240312 |
Observation of polaronic state assisted sub-bandgap saturable absorption
-
Abstract
In soft-lattice lead-halide perovskites, the polaronic effects involving stabilization of localized charge character by structural deformations and polarizations have an important effect on the properties of functional materials such as the band gap, which has attracted considerable investigations. However, the concept of polaron assisted nonlinear photonics remains largely unexplored, which has a wide range of applications from optoelectronics to telecommunications and quantum technologies. Here, we report the first observation of the polaronic state assisted saturable absorption through sub-bandgap excitation with a redshift exceeding 60 meV. By combining photoluminescence, transient absorption measurements and density functional theory calculations, we explicate that the anomalous nonlinear saturable absorption under sub-bandgap excitation is caused by the transient picosecond timescale polaronic state formed by strong carrier/exciton-phonon coupling effect. The bandgap fluctuation caused by polaron formation can be further tuned through exciton-phonon coupling of perovskites with different Young’s modulus. This suggests that we can design targeted soft lattice lead-halide perovskite with a specific structure to effectively manipulate exciton-phonon coupling and exciton-polaron formation. These findings profoundly expand our understanding of exciton-polaronic nonlinear optics physics and provide an ideal platform for developing actively tunable nonlinear photonics applications.-
Keywords:
- polaron /
- perovskite /
- soft lattice /
- nonlinear optics /
- saturable absorption
-

-
References
[1] Boyd RW, Masters BR. Nonlinear optics, third edition. J Biomed Opt 14, 029902 (2009). doi: 10.1117/1.3115345 [2] Guo QB, Qi XZ, Zhang LS et al. Ultrathin quantum light source with van der Waals NbOCl2 crystal. Nature 613, 53–59 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05393-7 [3] Chang DE, Vuletić V, Lukin MD. Quantum nonlinear optics—photon by photon. Nat Photonics 8, 685–694 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.192 [4] Guo QS, Sekine R, Ledezma L et al. Femtojoule femtosecond all-optical switching in lithium niobate nanophotonics. Nat Photonics 16, 625–631 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41566-022-01044-5 [5] Guo QS, Gutierrez BK, Sekine R et al. Ultrafast mode-locked laser in nanophotonic lithium niobate. Science 382, 708–713 (2023). doi: 10.1126/science.adj5438 [6] Hu YW, Yu MJ, Zhu D et al. On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters. Nature 599, 587–593 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03999-x [7] Cui CH, Zhang L, Fan LR. In situ control of effective Kerr nonlinearity with Pockels integrated photonics. Nat Phys 18, 497–501 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41567-022-01542-x [8] Chen Z, Li JF, Li TZ et al. A CRISPR/Cas12a-empowered surface plasmon resonance platform for rapid and specific diagnosis of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Natl Sci Rev 9, nwac104 (2022). doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac104 [9] Chen Z, Huang H, Deng J et al. Light‐guided genetic scissors based on phosphorene quantum dot. Laser Photonics Rev 18, 2400777 (2024). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202400777 [10] Chen Z, Meng CL, Wang XL et al. Ultrasensitive DNA origami plasmon sensor for accurate detection in circulating tumor DNAs. Laser Photonics Rev 18, 2400035 (2024). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202400035 [11] Bao QL, Zhang H, Wang Y et al. Atomic-layer graphene as a saturable absorber for ultrafast pulsed lasers. Adv Funct Mater 19, 3077–3083 (2009). doi: 10.1002/adfm.200901007 [12] Wang KP, Zhang XY, Kislyakov IM et al. Bacterially synthesized tellurium nanostructures for broadband ultrafast nonlinear optical applications. Nat Commun 10, 3985 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11898-z [13] Dong YC, Chertopalov S, Maleski K et al. Saturable absorption in 2D Ti3C2 MXene thin films for passive photonic diodes. Adv Mater 30, 1705714 (2018). doi: 10.1002/adma.201705714 [14] Zhou L, Kang JL, Dong YL et al. Solvent-stabilized few-layer violet phosphorus and its ultrafast nonlinear optics. Nano Res 16, 5843–5849 (2023). doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-5224-3 [15] Wang YW, Huang GH, Mu HR et al. Ultrafast recovery time and broadband saturable absorption properties of black phosphorus suspension. Appl Phys Lett 107, 091905 (2015). doi: 10.1063/1.4930077 [16] Jiang T, Huang D, Cheng JL et al. Gate-tunable third-order nonlinear optical response of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nat Photonics 12, 430–436 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0175-7 [17] Hong H, Wu CC, Zhao ZX et al. Giant enhancement of optical nonlinearity in two-dimensional materials by multiphoton-excitation resonance energy transfer from quantum dots. Nat Photonics 15, 510–515 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41566-021-00801-2 [18] Wang YD, Wang YW, Lan CY et al. Interfacial charge transfer for enhancing nonlinear saturable absorption in WS2/graphene heterostructure. Adv Sci 11, 2306096 (2024). doi: 10.1002/advs.202306096 [19] Dirnberger F, Quan JM, Bushati R et al. Magneto-optics in a van der Waals magnet tuned by self-hybridized polaritons. Nature 620, 533–537 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06275-2 [20] Tang YX, Zhang YB, Liu QR et al. Interacting plexcitons for designed ultrafast optical nonlinearity in a monolayer semiconductor. Light Sci Appl 11, 94 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00754-3 [21] Gu LX, Zhang LF, Ni RH et al. Giant optical nonlinearity of Fermi polarons in atomically thin semiconductors. Nat Photonics 18, 816–822 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41566-024-01434-x [22] Puppin M, Polishchuk S, Colonna N et al. Evidence of large polarons in photoemission band mapping of the perovskite semiconductor CsPbBr3. Phys Rev Lett 124, 206402 (2020). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.206402 [23] Qian Q, Wan Z, Takenaka H et al. Photocarrier-induced persistent structural polarization in soft-lattice lead halide perovskites. Nat Nanotechnol 18, 357–364 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41565-022-01306-x [24] Yaffe O, Guo YS, Tan LZ et al. Local polar fluctuations in lead halide perovskite crystals. Phys Rev Lett 118, 136001 (2017). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.136001 [25] Tao WJ, Zhang C, Zhou QH et al. Momentarily trapped exciton polaron in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites. Nat Commun 12, 1400 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21721-3 [26] Biswas S, Zhao RY, Alowa F et al. Exciton polaron formation and hot-carrier relaxation in rigid Dion–Jacobson-type two-dimensional perovskites. Nat Mater 23, 937–943 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41563-024-01895-z [27] Guzelturk B, Winkler T, Van de Goor TWJ et al. Visualization of dynamic polaronic strain fields in hybrid lead halide perovskites. Nat Mater 20, 618–623 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-00865-5 [28] Luo TC, Ilyas B, von Hoegen A et al. Time-of-flight detection of terahertz phonon-polariton. Nat Commun 15, 2276 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46515-1 [29] Kim D, Jung HJ, Park IJ et al. Efficient, stable silicon tandem cells enabled by anion-engineered wide-bandgap perovskites. Science 368, 155–160 (2020). doi: 10.1126/science.aba3433 [30] Ren XX, Wang JF, Lin Y et al. Mobile iodides capture for highly photolysis- and reverse-bias-stable perovskite solar cells. Nat Mater 23, 810–817 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41563-024-01876-2 [31] Zhu HM, Fu YP, Meng F et al. Lead halide perovskite nanowire lasers with low lasing thresholds and high quality factors. Nat Mater 14, 636–642 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nmat4271 [32] Chen QS, Wu J, Ou XY et al. All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators. Nature 561, 88–93 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0451-1 [33] Anantharaman SB, Lynch J, Stevens CE et al. Dynamics of self-hybridized exciton–polaritons in 2D halide perovskites. Light Sci Appl 13, 1 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41377-023-01334-9 [34] Gong YY, Yue S, Liang Y et al. Boosting exciton mobility approaching Mott-Ioffe-Regel limit in Ruddlesden−Popper perovskites by anchoring the organic cation. Nat Commun 15, 1893 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45740-y [35] Wu B, Wang AC, Fu J et al. Uncovering the mechanisms of efficient upconversion in two-dimensional perovskites with anti-Stokes shift up to 220 meV. Sci Adv 9, eadi9347 (2023). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi9347 [36] Dai ZB, Lian C, Lafuente-Bartolome J et al. Theory of excitonic polarons: from models to first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 109, 045202 (2024). [37] Miyata K, Meggiolaro D, Trinh MT et al. Large polarons in lead halide perovskites. Sci Adv 3, e1701217 (2017). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701217 [38] Li W, Vasenko AS, Tang JF et al. Anharmonicity extends carrier lifetimes in lead halide perovskites at elevated temperatures. J Phys Chem Lett 10, 6219–6226 (2019). doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b02553 [39] Shao Y, Gao W, Yan HJ et al. Unlocking surface octahedral tilt in two-dimensional Ruddlesden-Popper perovskites. Nat Commun 13, 138 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27747-x [40] Gu T, Scarbrough T, Yang YR et al. Cooperative couplings between octahedral rotations and ferroelectricity in perovskites and related materials. Phys Rev Lett 120, 197602 (2018). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.197602 [41] Zhong YG, Liao K, Du WN et al. Large-scale thin CsPbBr3 single-crystal film grown on sapphire via chemical vapor deposition: toward laser array application. ACS Nano 14, 15605–15615 (2020). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c06380 [42] Mushtaq A, Kushavah D, Ghosh S et al. Nonlinear optical properties of benzylamine lead(II) bromide perovskite microdisks in femtosecond regime. Appl Phys Lett 114, 051902 (2019). doi: 10.1063/1.5082376 [43] Zhang XY, Zhang SF, Xie YF et al. Tailoring the nonlinear optical performance of two-dimensional MoS2 nanofilms via defect engineering. Nanoscale 10, 17924–17932 (2018). doi: 10.1039/C8NR05653F [44] Yamada Y, Kanemitsu Y. Electron-phonon interactions in halide perovskites. NPG Asia Mater 14, 48 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41427-022-00394-4 [45] Wright AD, Verdi C, Milot RL et al. Electron–phonon coupling in hybrid lead halide perovskites. Nat Commun 7, 11755 (2016). doi: 10.1038/ncomms11755 [46] Wang YD, Wang YW, Chen KQ et al. Niobium carbide MXenes with broad-band nonlinear optical response and ultrafast carrier dynamics. ACS Nano 14, 10492–10502 (2020). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c04390 [47] Mushtaq A, Yang XD, Gao J. Unveiling room temperature upconversion photoluminescence in monolayer WSe2. Opt Express 30, 45212–45220 (2022). doi: 10.1364/OE.471027 [48] Roy S, Yang XD, Gao J. Uniaxial strain tuning of upconversion photoluminescence in monolayer WSe2. Adv Photonics Res 5, 2300220 (2024). doi: 10.1002/adpr.202300220 [49] Akizuki N, Aota S, Mouri S et al. Efficient near-infrared up-conversion photoluminescence in carbon nanotubes. Nat Commun 6, 8920 (2015). doi: 10.1038/ncomms9920 [50] Ma YZ, Valkunas L, Dexheimer SL et al. Femtosecond spectroscopy of optical excitations in single-walled carbon nanotubes: evidence for exciton-exciton annihilation. Phys Rev Lett 94, 157402 (2005). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.157402 [51] Wang LL, Liu H, Zhang YH et al. Photoluminescence origin of zero-dimensional Cs4PbBr6 perovskite. ACS Energy Lett 5, 87–99 (2020). doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02275 [52] Thouin F, Valverde-Chávez DA, Quarti C et al. Phonon coherences reveal the polaronic character of excitons in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites. Nat Mater 18, 349–356 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41563-018-0262-7 [53] Giovanni D, Chong WK, Dewi HA et al. Tunable room-temperature spin-selective optical Stark effect in solution-processed layered halide perovskites. Sci Adv 2, e1600477 (2016). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600477 [54] Wu XX, Trinh MT, Zhu XY. Excitonic many-body interactions in two-dimensional lead iodide perovskite quantum wells. J Phys Chem C 119, 14714–14721 (2015). doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b00148 [55] deQuilettes DW, Frohna K, Emin D et al. Charge-carrier recombination in halide perovskites. Chem Rev 119, 11007–11019 (2019). doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00169 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Observation of polaronic state assisted sub-bandgap saturable absorption 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
Polaronic state assisted nonlinear saturable absorption (PSA_SA) picture in LHPs. (a) Schematic diagram of Z-scan. (b) Scheme of transformation from free excitons to exciton-polaron with lattice distortion by dynamic polaronic effect. (c) Schematic diagram of the effect of polaron formation on the band structure of materials, which will cause band energy fluctuations. (d) The valence band maximum (VBM) and conduction band minimum (CBM) at different temperature are extracted according to the molecular dynamics simulation calculation results. (e) The standard variations of the band energy for CBM and VBM at different temperatures. (f) Schematic of SA caused by single photon absorption under up-bandgap excitation in conventional semiconductors. (g) Schematic of PSA_SA under sub-bandgap excitation. CB and VB denote conduction band and valence band respectively.
-
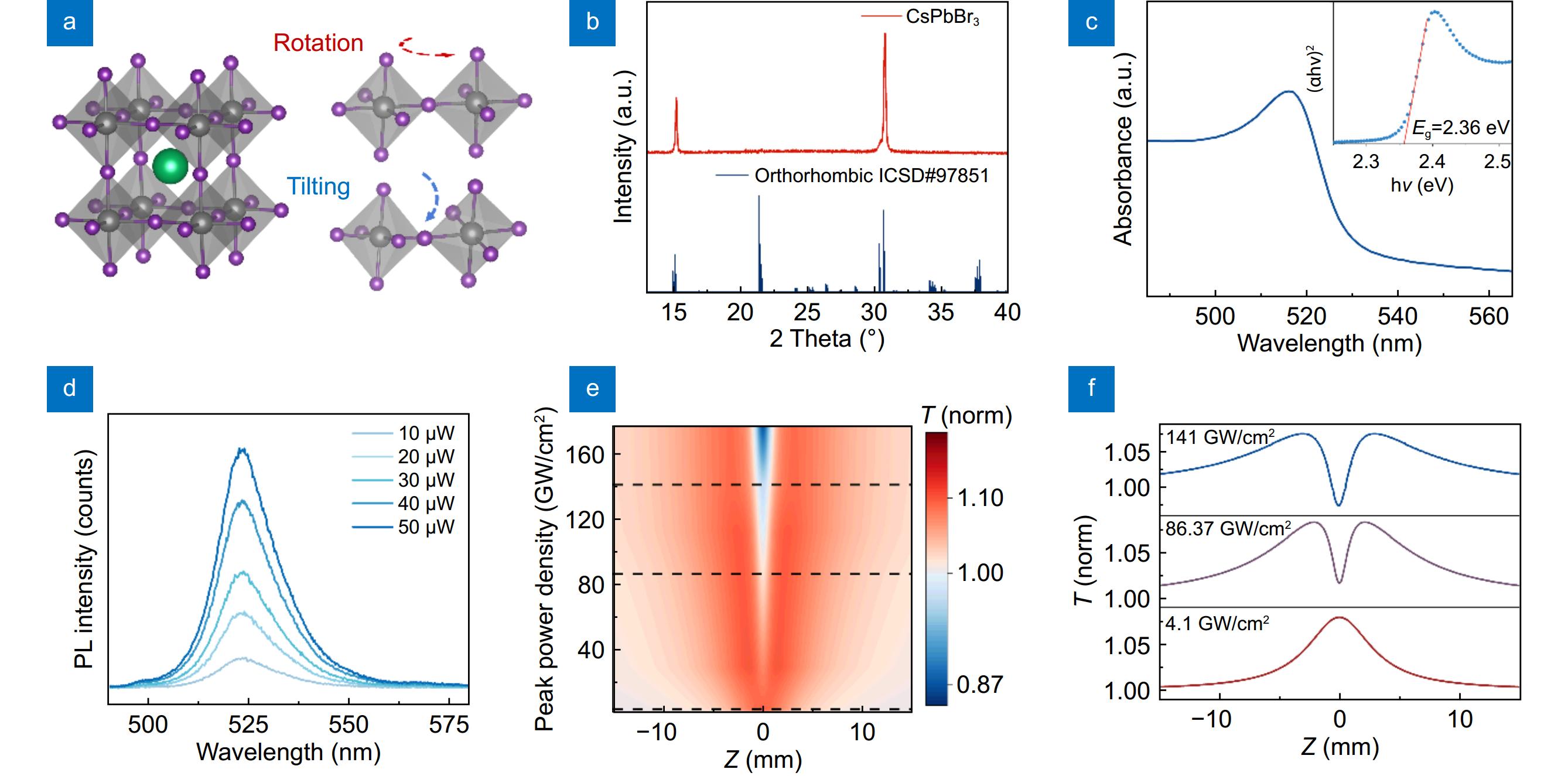
Figure 2.
Structural, linear and nonlinear optical characterizations of CsPbBr3. (a) Crystal structure of CsPbBr3 and associated lattice distortion, where green represents Cs atoms, gray represents Pb atoms, and purple represents Br atoms. (b) XRD pattern of the CsPbBr3 film and the standard card (ICSD-97851). (c) UV-vis absorption spectrum and Tauc plot of CsPbBr3. (d) Steady PL spectra of CsPbBr3 film. (e) The two-dimensional map of transmittance as a function of the scan distance and the excitation peak density under 530 nm laser pulse excitation and (f) the transmittance curves with 3 representative excitation intensities.
-
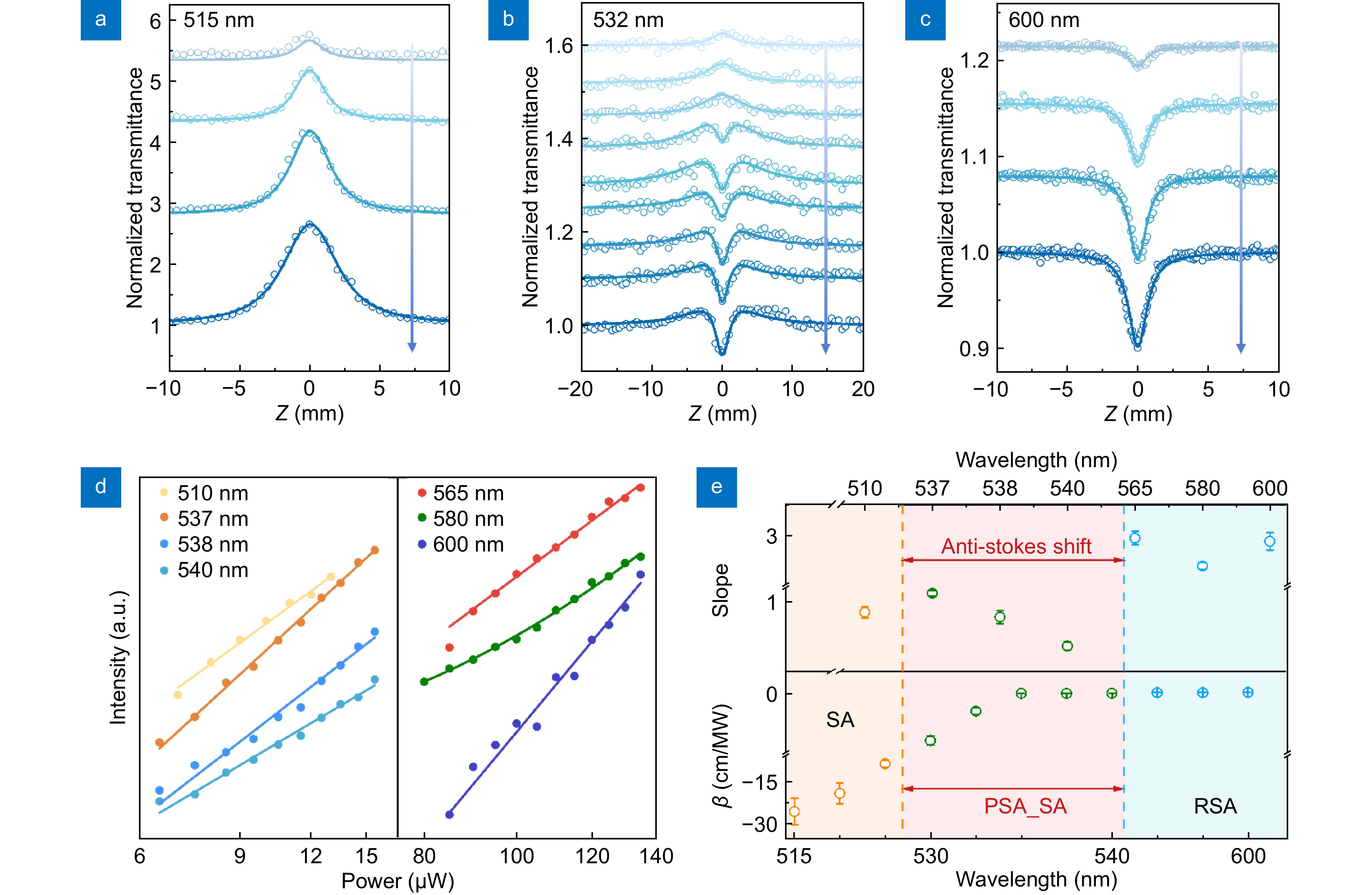
Figure 3.
Z-scan and steady-state PL studies of polaronic state assisted nonlinear saturable absorption (PSA_SA). (a–c) The Z-scan results of CsPbBr3 under different excitation intensity at different wavelengths. The excitation wavelengths are (a) 515 nm (pump intensity: 2.07–4.25 GW/cm2), (b) 532 nm (pump intensity: 3.24–94.86 GW/cm2), and (c) 600 nm (pump intensity: 48.60–215.14 GW/cm2), respectively. From top to bottom, the light intensity increases in turn. (d) Power dependence of the PL intensity at different excitation wavelengths for CsPbBr3. (e) Wavelength dependence of slope (top) and nonlinear absorption coefficient β (bottom) for CsPbBr3. Error bars represent the standard error.
-
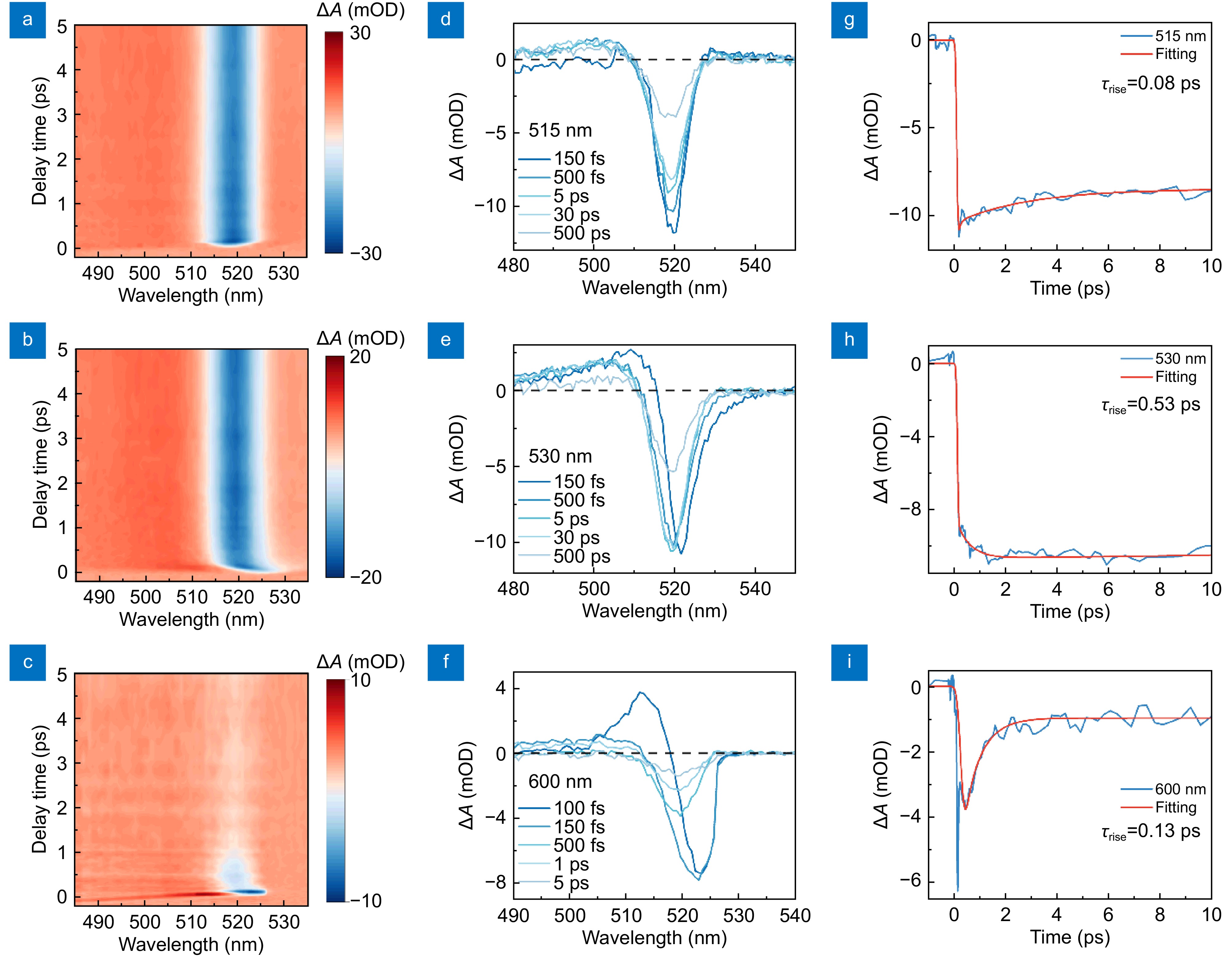
Figure 4.
TA measurements confirming polaronic state assisted nonlinear saturable absorption (PSA_SA). (a–c) Representative pseudocolor TA spectrums at (a) 515 nm, (b) 530 nm and (c) 600 nm excitations, respectively. (d–f) Time-dependent photo-induced changes in absorption (ΔA) which is pumped by (d) 515 nm , (e) 530 nm and (f) 600 nm , respectively. (g–i) Exciton band bleach dynamics monitored at 519 nm for (g) 515 nm , (h) 530 nm, and (i) 600 nm excitations, respectively.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: