| Citation: | Abraham E, Zhou JX, Liu ZW. Speckle structured illumination endoscopy with enhanced resolution at wide field of view and depth of field. Opto-Electron Adv 6, 220163 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.220163 |
Speckle structured illumination endoscopy with enhanced resolution at wide field of view and depth of field
-
Abstract
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is one of the most widely applied wide field super resolution imaging techniques with high temporal resolution and low phototoxicity. The spatial resolution of SIM is typically limited to two times of the diffraction limit and the depth of field is small. In this work, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a low cost, easy to implement, novel technique called speckle structured illumination endoscopy (SSIE) to enhance the resolution of a wide field endoscope with large depth of field. Here, speckle patterns are used to excite objects on the sample which is then followed by a blind-SIM algorithm for super resolution image reconstruction. Our approach is insensitive to the 3D morphology of the specimen, or the deformation of illuminations used. It greatly simplifies the experimental setup as there are no calibration protocols and no stringent control of illumination patterns nor focusing optics. We demonstrate that the SSIE can enhance the resolution 2–4.5 times that of a standard white light endoscopic (WLE) system. The SSIE presents a unique route to super resolution in endoscopic imaging at wide field of view and depth of field, which might be beneficial to the practice of clinical endoscopy. -

-
References
[1] Lopez-Ceron M, van den Broek FJC, Mathus-Vliegen EM, Boparai KS, van Eeden S et al. The role of high-resolution endoscopy and narrow-band imaging in the evaluation of upper GI neoplasia in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc 77, 542–550 (2013). doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.11.033 [2] Anagnostopoulos GK, Yao K, Kaye P, Fogden E, Fortun P et al. High-resolution magnification endoscopy can reliably identify normal gastric mucosa, Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis, and gastric atrophy. Endoscopy 39, 202–207 (2007). doi: 10.1055/s-2006-945056 [3] Bruno MJ. Magnification endoscopy, high resolution endoscopy, and chromoscopy; towards a better optical diagnosis. Gut 52, iv7–iv11 (2003). doi: 10.1136/gut.52.1.7 [4] Rust MJ, Bates M, Zhuang XW. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat Methods 3, 793–796 (2006). doi: 10.1038/nmeth929 [5] Hess ST, Girirajan TPK, Mason MD. Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence photoactivation localization microscopy. Biophys J 91, 4258–4272 (2006). doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.091116 [6] Hell SW, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt Lett 19, 780–782 (1994). doi: 10.1364/OL.19.000780 [7] Gustafsson MGL. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J Microsc 198, 82–87 (2000). doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.2000.00710.x [8] Heintzmann R, Jovin TM, Cremer C. Saturated patterned excitation microscopy: a concept for optical resolution improvement. J Opt Soc Am A 19, 1599–1609 (2002). doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.19.001599 [9] Lee YU, Zhao JX, Ma Q, Khorashad LK, Posner C et al. Metamaterial assisted illumination nanoscopy via random super-resolution speckles. Nat Commun 12, 1559 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21835-8 [10] Liu ZW. Plasmonics and metamaterials based super-resolution imaging (Conference Presentation). Proc SPIE 10194, 101940M (2017). doi: 10.1117/12.2263385 [11] Wei FF, Liu ZW. Plasmonic structured illumination microscopy. Nano Lett 10, 2531–2536 (2010). doi: 10.1021/nl1011068 [12] Fernández-Domínguez AI, Liu ZW, Pendry JB. Coherent four-fold super-resolution imaging with composite photonic–plasmonic structured illumination. ACS Photonics 2, 341–348 (2015). doi: 10.1021/ph500342g [13] Goetz M, Watson A, Kiesslich R. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in gastrointestinal diseases. J Biophotonics 4, 498–508 (2011). doi: 10.1002/jbio.201100022 [14] Jabbour JM, Saldua MA, Bixler JN, Maitland KC. Confocal endomicroscopy: instrumentation and medical applications. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 378–397 (2012). doi: 10.1007/s10439-011-0426-y [15] Elliott AD. Confocal microscopy: principles and modern practices. Curr Protoc Cytom 92, e68 (2020). doi: 10.1002/cpcy.68 [16] Ilie MA, Caruntu C, Lupu M, Lixandru D, Tampa M et al. Current and future applications of confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging in skin oncology. Oncol Lett 17, 4102–4111 (2019). doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10066 [17] Meining A, Saltzman JR, Travis AC. Confocal laser endomicroscopy and endocytoscopy (2020). https://www.uptodate.com/contents/confocal-laser-endomicroscopy-and-endocytoscopy [18] Chang Tou Pin et al. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy: an evaluation of its role towards real-time, in vivo, in situ intraoperative applications. Imperial College London (2016). [19] Wijsmuller AR, Ghnassia JP, Varatharajah S, Schaeffer M, Leroy J et al. Prospective trial on probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy for the identification of the distal limit in rectal adenocarcinoma. Surg Innov 25, 313–322 (2018). doi: 10.1177/1553350618773011 [20] Singh H, Schiff GD, Grabe ML, Igho O, Thompson MJ. The global burden of diagnostic errors in primary care. BMJ Qual Saf 26, 484–494 (2016). doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2016-005401 [21] Kurniawan N, Keuchel M. Flexible gastro-intestinal endoscopy clinical challenges and technical achievements. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 15, 168–179 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2017.01.004 [22] Moore LE. The advantages and disadvantages of endoscopy. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract 18, 250–253 (2003). doi: 10.1016/S1096-2867(03)00071-9 [23] Banerjee R, Reddy DN. Advances in endoscopic imaging: advantages and limitations. J Dig Endosc 3, 7–12 (2012). doi: 10.4103/0976-5042.95023 [24] ASGE Technology Committee, Chauhan SS, Dayyeh BKA, Bhat YM, Gottlieb KT et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 80, 928–938 (2014). doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.06.021 [25] Mudry E, Belkebir K, Girard J, Savatier J, Le Moal E et al. Structured illumination microscopy using unknown speckle patterns. Nat Photonics 6, 312–315 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.83 [26] Yeh LH, Chowdhury S, Repina NA, Waller L. Speckle-structured illumination for 3D phase and fluorescence computational microscopy. Biomed Opt Express 10, 3635–3653 (2019). doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.003635 [27] Yeh LH, Chowdhury S, Waller L. Computational structured illumination for high-content fluorescence and phase microscopy. Biomed Opt Express 10, 1978–1998 (2019). doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.001978 [28] Ponsetto JL, Wei FF, Liu ZW. Localized plasmon assisted structured illumination microscopy for wide-field high-speed dispersion-independent super resolution imaging. Nanoscale 6, 5807–5812 (2014). doi: 10.1039/C4NR00443D [29] Min JH, Jang J, Keum D, Ryu SW, Choi C et al. Fluorescent microscopy beyond diffraction limits using speckle illumination and joint support recovery. Sci Rep 3, 2075 (2013). doi: 10.1038/srep02075 [30] Kim M, Park C, Rodriguez C, Park Y, Cho YH. Superresolution imaging with optical fluctuation using speckle patterns illumination. Sci Rep 5, 16525 (2015). doi: 10.1038/srep16525 [31] Ayuk R, Giovannini H, Jost A, Mudry E, Girard J et al. Structured illumination fluorescence microscopy with distorted excitations using a filtered blind-SIM algorithm. Opt Lett 38, 4723–4726 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OL.38.004723 [32] Hoffman ZR, DiMarzio CA. Structured illumination microscopy using random intensity incoherent reflectance. J Biomed Opt 18, 061216 (2013). doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.6.061216 [33] Chaigne T, Gateau J, Allain M, Katz O, Gigan S et al. Super-resolution photoacoustic fluctuation imaging with multiple speckle illumination. Optica 3, 54–57 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000054 [34] García J, Zalevsky Z, Fixler D. Synthetic aperture super resolution by speckle pattern projection. Opt Express 13, 6073–6078 (2005). doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.006073 [35] Clancy NT, Li R, Rogers K, Driscoll P, Excel P et al. Development and evaluation of a light-emitting diode endoscopic light source, advanced biomedical and clinical diagnostic systems. Proc SPIE 8214, 82140R (2012). doi: 10.1117/12.909331 [36] ASGE Technology Committee, Varadarajulu S, Banerjee S, Barth BA, Desilets DJ et al. GI endoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc 74, 1–6.e6 (2011). doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.061 [37] Waddington DEJ, Hindley N, Koonjoo N, Chiu C, Reynolds T et al. On real-time image reconstruction with neural networks for MRI-guided radiotherapy. arXiv: 2202.05267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2202.05267 [38] Wu DF, Kim K, Li QZ. Computationally efficient deep neural network for computed tomography image reconstruction. Med Phys 46, 4763–4776 (2019). doi: 10.1002/mp.13627 [39] Paderno A, Gennarini F, Sordi A, Montenegro C, Lancini D et al. Artificial intelligence in clinical endoscopy: Insights in the field of videomics. Front Surg 9, 933297 (2022). doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.933297 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Speckle structured illumination endoscopy with enhanced resolution at wide field of view and depth of field 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
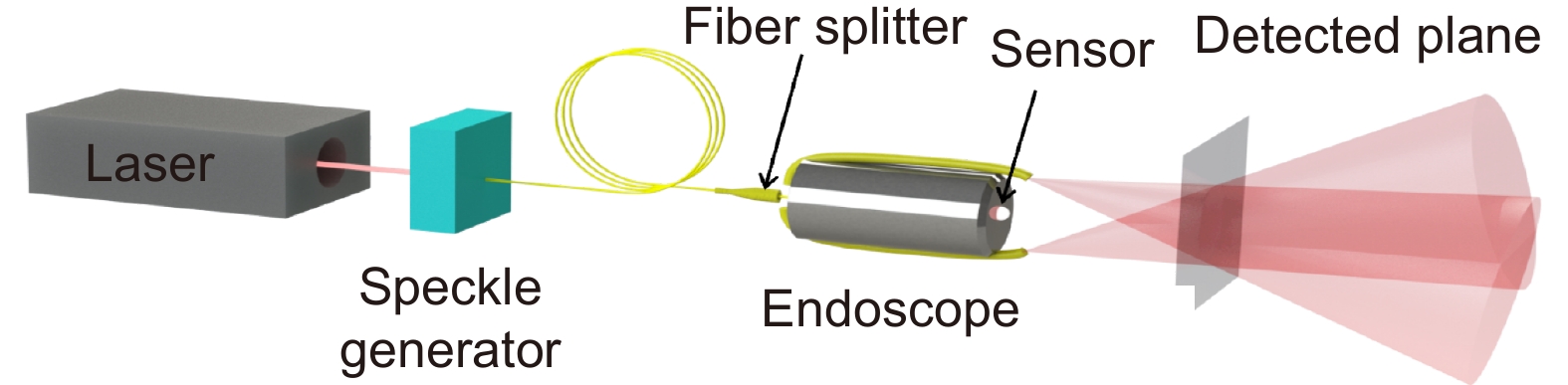
Figure 1.
Schematic of SSIE. A continuous wave laser is routed through two multimode fibers via speckle generator onto the object. The intrinsic image sensor of the endoscope is used to collect images.
-
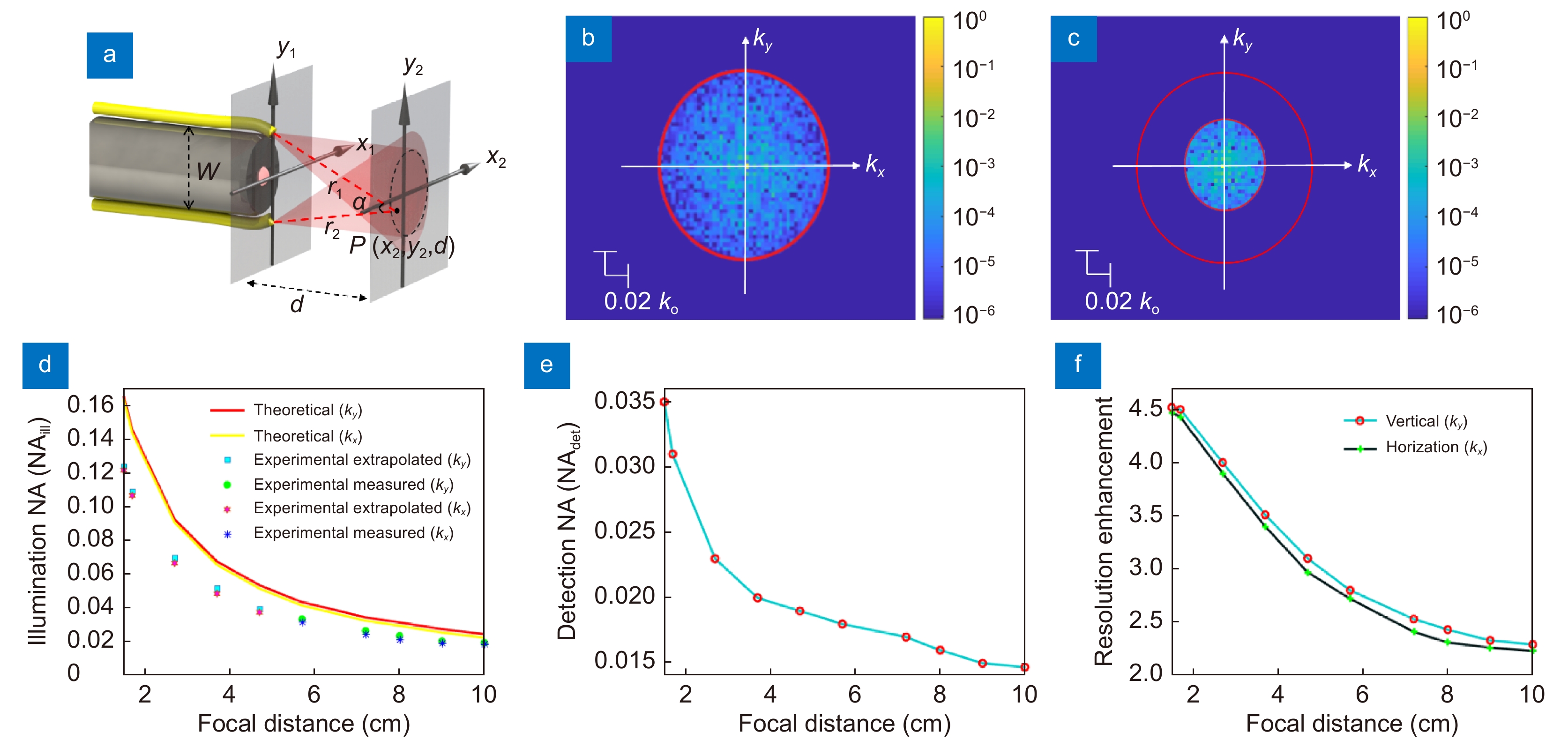
Figure 2.
Characterization of the speckle patterns and the estimated resolution enhancement of SSIE compared to traditional WLE. (a) Schematic of the endoscope with illumination projected at distance d. The field of view should be covered by light from both fibers. (b, c) Numerical simulated Fourier spectra of the speckle patterns at d=3.7 cm and d=7.2 cm, respectively. (d) Theoretical and experimental illumination NA (
NAill) for various distances d from 1.5 to 10 cm. Focal distance 5.7–10 cm (measured); 1.5–5.7 cm (extrapolation was performed with a power trendline as an exponential curve). (e) Experimentally detected NA ( NAdet) for different focal distance d. (f) Estimated SSIE resolution enhancement factor compared to traditional WLE at various focal distances. -
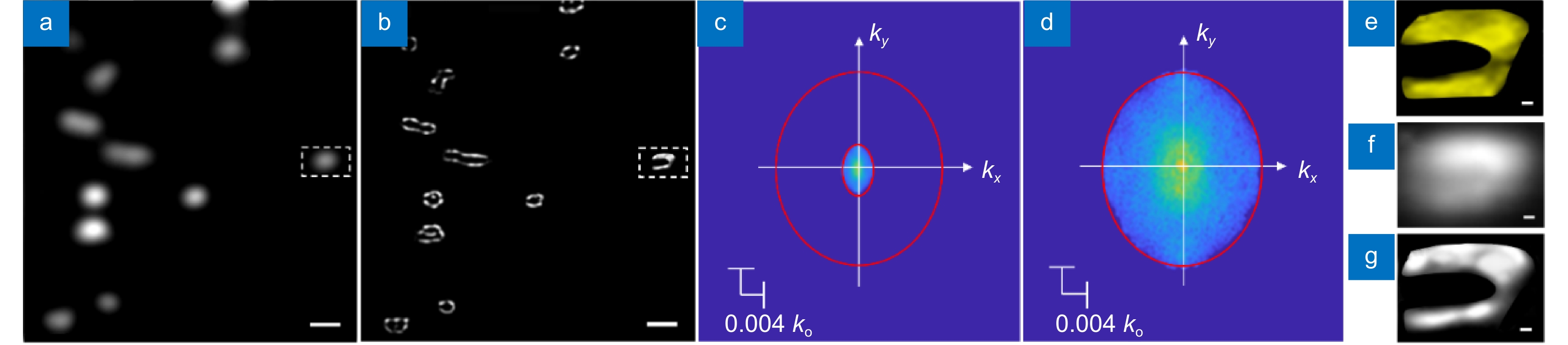
Figure 3.
Experimental demonstration of SSIE at 3.7 cm. (a) Diffraction limited endoscopic image of the drop casted stains. (b) SSIE image of the same area in (a). Scale bars in (a-b) are 800 μm. (c–d) Fourier spectra of the images in (a) and (b), respectively. (e–g) Zoom in view of the ground truth, diffraction limited endoscopic image, and SSIE image of the marked area in (a) and (b). Scale bars in (e–g) are 100 μm.
-
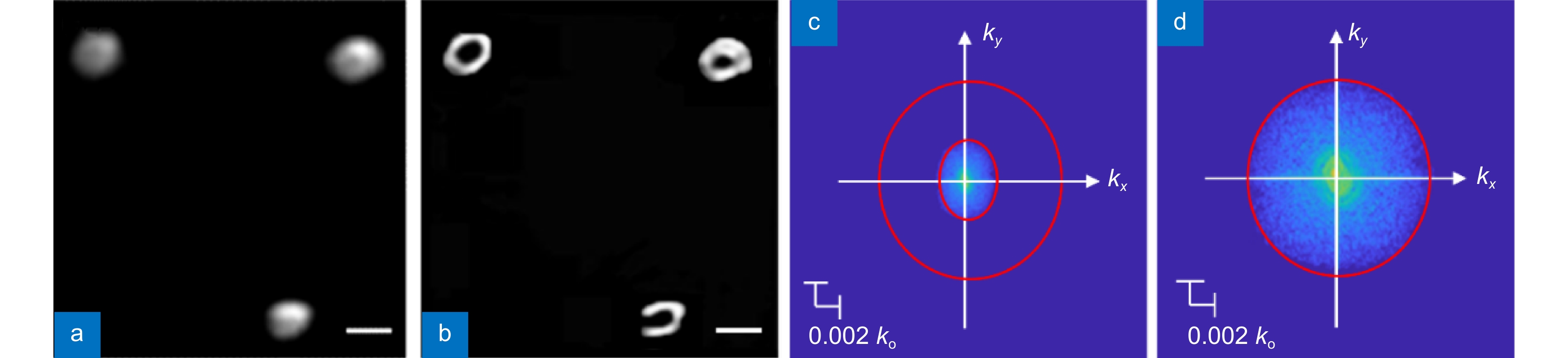
Figure 4.
Experimental demonstration of SSIE at 7.2 cm. Diffraction limited endoscopic image (a) and SSIE super resolution image (b) of a fluorescent object. Scale bars in (a, b) are 600 um. (c, d) Fourier spectra of the images in (a) and (b), respectively.
-
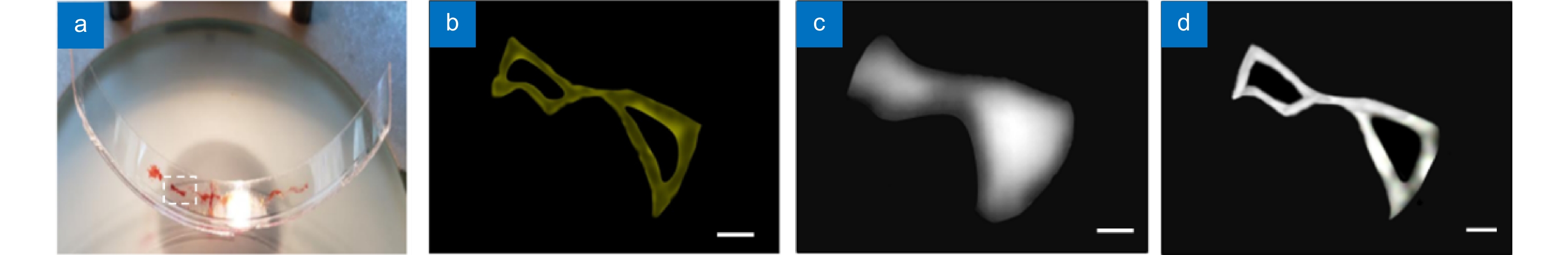
Figure 5.
Experimental demonstrations of SSIE on curved surface with large depth of field. (a) Photograph of a drop casted rhodamine dye sample on a curved glass surface. (b) A zoom-in review of the marked area in (a) obtained from a stereo microscope. This can be considered as the ground truth of the object. Diffraction limited endoscopic image (c) and the SSIE image (d) of the same object shown in (b). Scale bars in (b–d) are 700 μm.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: