| Citation: | Xu BX, Fan XY, Wang S, He ZY. Sub-femtometer-resolution absolute spectroscopy with sweeping electro-optic combs. Opto-Electron Adv 5, 210023 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.210023 |
Sub-femtometer-resolution absolute spectroscopy with sweeping electro-optic combs
-
Abstract
Optical frequency comb with evenly spaced lines over a broad bandwidth has revolutionized the fields of optical metrology and spectroscopy. Here, we propose a fast interleaved dual-comb spectroscopy with sub-femtometer-resolution and absolute frequency, in which two electro-optic frequency combs are swept. Electrically-modulated stabilized laser enables ultrahigh resolution of 0.16 fm (or 20 kHz in optical frequency) and single-shot measurement in 90 ms. Total 20 million points are recorded spanning 3.2 nm (or 400 GHz) bandwidth, corresponding to a spectral sampling rate of 2.5 × 108 points/s under Nyquist-limitation. Besides, considering the trade-off between the measurement time and spectral resolution, a fast single-shot measurement is also realized in 1.6 ms with 8 fm (or 1 MHz) resolution. We demonstrate the 25-averaged result with 30.6 dB spectral measurement signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) by reducing the filter bandwidth in demodulation. The results show great prospect for precise measurement with flexibly fast refresh time, high spectral resolution, and high SNR.-
Keywords:
- dual-comb spectroscopy /
- optical frequency comb /
- interferometry
-

-
References
[1] Hänsch T W. Nobel lecture: Passion for precision. Rev Mod Phys 78, 1297–1309 (2006). doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.78.1297 [2] Diddams S A. The evolving optical frequency comb. J Opt Soc Am B 27, B51–B62 (2010). doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.27.000B51 [3] Jones DJ, Diddams SA, Ranka JK, Stentz A, Windeler RS et al. Carrier-envelope phase control of femtosecond mode-locked lasers and direct optical frequency synthesis. Science 288, 635–639 (2000). doi: 10.1126/science.288.5466.635 [4] Newbury NR. Searching for applications with a fine-tooth comb. Nat Photonics 5, 186–188 (2011). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.38 [5] Picqué N, Hänsch TW. Frequency comb spectroscopy. Nat Photonics 13, 146–157 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0347-5 [6] Diddams SA, Hollberg L, Mbele V. Molecular fingerprinting with the resolved modes of a femtosecond laser frequency comb. Nature 445, 627–630 (2007). doi: 10.1038/nature05524 [7] Mandon J, Guelachvili G, Picqué N. Fourier transform spectroscopy with a laser frequency comb. Nat Photonics 3, 99–102 (2009). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.293 [8] Ycas G, Giorgetta FR, Baumann E, Coddington I, Herman D et al. High-coherence mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy spanning 2.6 to 5.2 µm. Nat Photonics 12, 202–208 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0114-7 [9] Rösch M, Scalari G, Villares G, Bosco L, Beck M et al. On-chip, self-detected terahertz dual-comb source. Appl Phys Lett 108, 171104 (2016). doi: 10.1063/1.4948358 [10] Coddington I, Swann WC, Newbury NR. Coherent multiheterodyne spectroscopy using stabilized optical frequency combs. Phys Rev Lett 100, 013902 (2008). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.013902 [11] Link SM, Maas DJHC, Waldburger D, Keller U. Dual-comb spectroscopy of water vapor with a free-running semiconductor disk laser. Science 356, 1164–1168 (2017). doi: 10.1126/science.aam7424 [12] Hugi A, Villares G, Blaser S, Liu HC, Faist J. Mid-infrared frequency comb based on a quantum cascade laser. Nature 492, 229–233 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nature11620 [13] Meek SA, Hipke A, Guelachvili G, Hänsch TW, Picqué N. Doppler-free Fourier transform spectroscopy. Opt Lett 43, 162–165 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OL.43.000162 [14] Ideguchi T, Bernhardt B, Guelachvili G, Hänsch TW, Picqué N. Raman-induced Kerr-effect dual-comb spectroscopy. Opt Lett 37, 4498–4500 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004498 [15] Ideguchi T, Holzner S, Bernhardt B, Guelachvili G, Picqué N et al. Coherent Raman spectro-imaging with laser frequency combs. Nature 502, 355–358 (2013). doi: 10.1038/nature12607 [16] Hase E, Minamikawa T, Mizuno T, Miyamoto S, Ichikawa R et al. Scan-less confocal phase imaging based on dual-comb microscopy. Optica 5, 634–643 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.000634 [17] Feng PP, Kang JQ, Tan SS, Ren YX, Zhang C et al. Dual-comb spectrally encoded confocal microscopy by electro-optic modulators. Opt Lett 44, 2919–2922 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002919 [18] Zolot AM, Giorgetta FR, Baumann E, Nicholson JW, Swann WC et al. Direct-comb molecular spectroscopy with accurate, resolved comb teeth over 43 THz. Opt Lett 37, 638–640 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OL.37.000638 [19] Ideguchi T, Poisson A, Guelachvili G, Picqué N, Hänsch TW. Adaptive real-time dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat Commun 5, 3375 (2014). doi: 10.1038/ncomms4375 [20] Roy J, Deschênes JD, Potvin S, Genest J. Continuous real-time correction and averaging for frequency comb interferometry. Opt Express 20, 21932–21939 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OE.20.021932 [21] Chen ZJ, Yan M, Hänsch TW, Picqué N. A phase-stable dual-comb interferometer. Nat Commun 9, 3035 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05509-6 [22] Long DA, Fleisher AJ, Douglass KO, Maxwell SE, Bielska K et al. Multiheterodyne spectroscopy with optical frequency combs generated from a continuous-wave laser. Opt Lett 39, 2688–2690 (2014). doi: 10.1364/OL.39.002688 [23] Martín-Mateos P, Jerez B, Acedo P. Dual electro-optic optical frequency combs for multiheterodyne molecular dispersion spectroscopy. Opt Express 23, 21149–21158 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OE.23.021149 [24] Millot G, Pitois S, Yan M, Hovhannisyan T, Bendahmane A et al. Frequency-agile dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat Photonics 10, 27–30 (2016). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.250 [25] Durán V, Andrekson PA, Torres-Company V. Electro-optic dual-comb interferometry over 40 nm bandwidth. Opt Lett 41, 4190–4193 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OL.41.004190 [26] Yan M, Luo PL, Iwakuni K, Millot G, Hänsch TW et al. Mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy with electro-optic modulators. Light:Sci Appl 6, e17076 (2017). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2017.76 [27] Fdil K, Michaud-Belleau V, Hébert NB, Guay P, Fleisher AJ et al. Dual electro-optic frequency comb spectroscopy using pseudo-random modulation. Opt Lett 44, 4415–4418 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OL.44.004415 [28] Wang S, Fan XY, Xu BX, He ZY. Fast MHz spectral-resolution dual-comb spectroscopy with electro-optic modulators. Opt Lett 44, 65–68 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OL.44.000065 [29] Xu BX, Fan XY, Wang S, He ZY. Broadband and high-resolution electro-optic dual-comb interferometer with frequency agility. Opt Express 27, 9266–9275 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.009266 [30] Sakamoto T, Kawanishi T, Izutsu M. Asymptotic formalism for ultraflat optical frequency comb generation using a Mach-Zehnder modulator. Opt Lett 32, 1515–1517 (2007). doi: 10.1364/OL.32.001515 [31] Wu R, Supradeepa VR, Long CM, Leaird DE, Weiner AM. Generation of very flat optical frequency combs from continuous-wave lasers using cascaded intensity and phase modulators driven by tailored radio frequency waveforms. Opt Lett 35, 3234–3236 (2010). doi: 10.1364/OL.35.003234 [32] Beha K, Cole DC, Del’haye P, Coillet A, Diddams SA et al. Electronic synthesis of light. Optica 4, 406–411 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000406 [33] Bao Y, Yi XW, Li ZH, Chen QM, Li JP et al. A digitally generated ultrafine optical frequency comb for spectral measurements with 0.01-pm resolution and 0.7-µs response time. Light Sci Appl 4, e300 (2015). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2015.73 [34] Long DA, Reschovsky BJ. Electro-optic frequency combs generated via direct digital synthesis applied to sub-Doppler spectroscopy. OSA Continuum 2, 3576–3583 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OSAC.2.003576 [35] Jacquet P, Mandon J, Bernhardt B, Holzwarth R, Guelachvili G et al. Frequency comb Fourier transform spectroscopy with KHz optical resolution. In Fourier Transform Spectroscopy 2009 (Optical Society of America, 2009); https://doi.org/10.1364/FTS.2009.FMB2. [36] Baumann E, Giorgetta FR, Swann WC, Zolot AM, Coddington I et al. Spectroscopy of the methane ν3 band with an accurate midinfrared coherent dual-comb spectrometer. Phys Rev A 84, 062513 (2011). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.84.062513 [37] Villares G, Hugi A, Blaser S, Faist J. Dual-comb spectroscopy based on quantum-cascade-laser frequency combs. Nat Commun 5, 5192 (2014). doi: 10.1038/ncomms6192 [38] Yu MJ, Okawachi Y, Griffith AG, Lipson M, Gaeta AL. Microresonator-based high-resolution gas spectroscopy. Opt Lett 42, 4442–4445 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OL.42.004442 [39] Nishikawa T, Oohara A, Uda S, Ishizawa A, Hitachi K et al. Automatic interpolation of 25 GHz mode spacing in dual EOM comb spectroscopy. In 2019 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics 1–2 (IEEE, 2019);http://doi.org/10.1364/CLEO_SI.2019.SF1I.3. [40] Hashimoto K, Ideguchi T. Phase-controlled fourier-transform spectroscopy. Nat Commun 9, 4448 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06956-x [41] Ahn TJ, Kim DY. Analysis of nonlinear frequency sweep in high-speed tunable laser sources using a self-homodyne measurement and Hilbert transformation. Appl Opt 46, 2394–2400 (2007). doi: 10.1364/AO.46.002394 [42] Long DA, Fleisher AJ, Plusquellic DF, Hodges JT. Multiplexed sub-Doppler spectroscopy with an optical frequency comb. Phys Rev A 94, 061801 (2016). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.94.061801 [43] Wei F, Lu B, Wang J, Xu D, Pan ZQ et al. Precision and broadband frequency swept laser source based on high-order modulation-sideband injection-locking. Opt Express 23, 4970–4980 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OE.23.004970 -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
The schematic to show the operation principle of proposed EO-DCS with real-time interleaved spectrum. CW laser: continuous-wave laser; EOFCG: electro-optic frequency comb generation; DUT: device under test; RF: radio frequency; FFT: fast Fourier transformation.
-
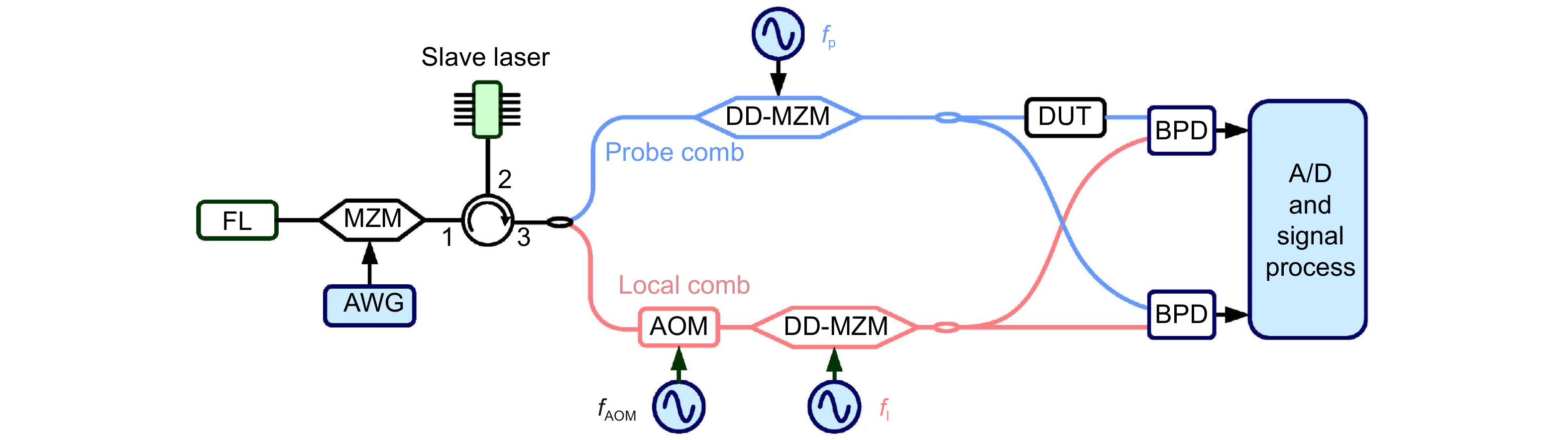
Figure 2.
Experimental setup of the proposed EO-DCS system. FL: fiber laser; MZM: Mach-Zehnder modulator; AWG: arbitrary waveform generator; AOM: acousto-optic modulator; DDMZM: dual-drive Mach-Zehnder modulator; DUT: device under test; BPD: balanced photodetector.
-
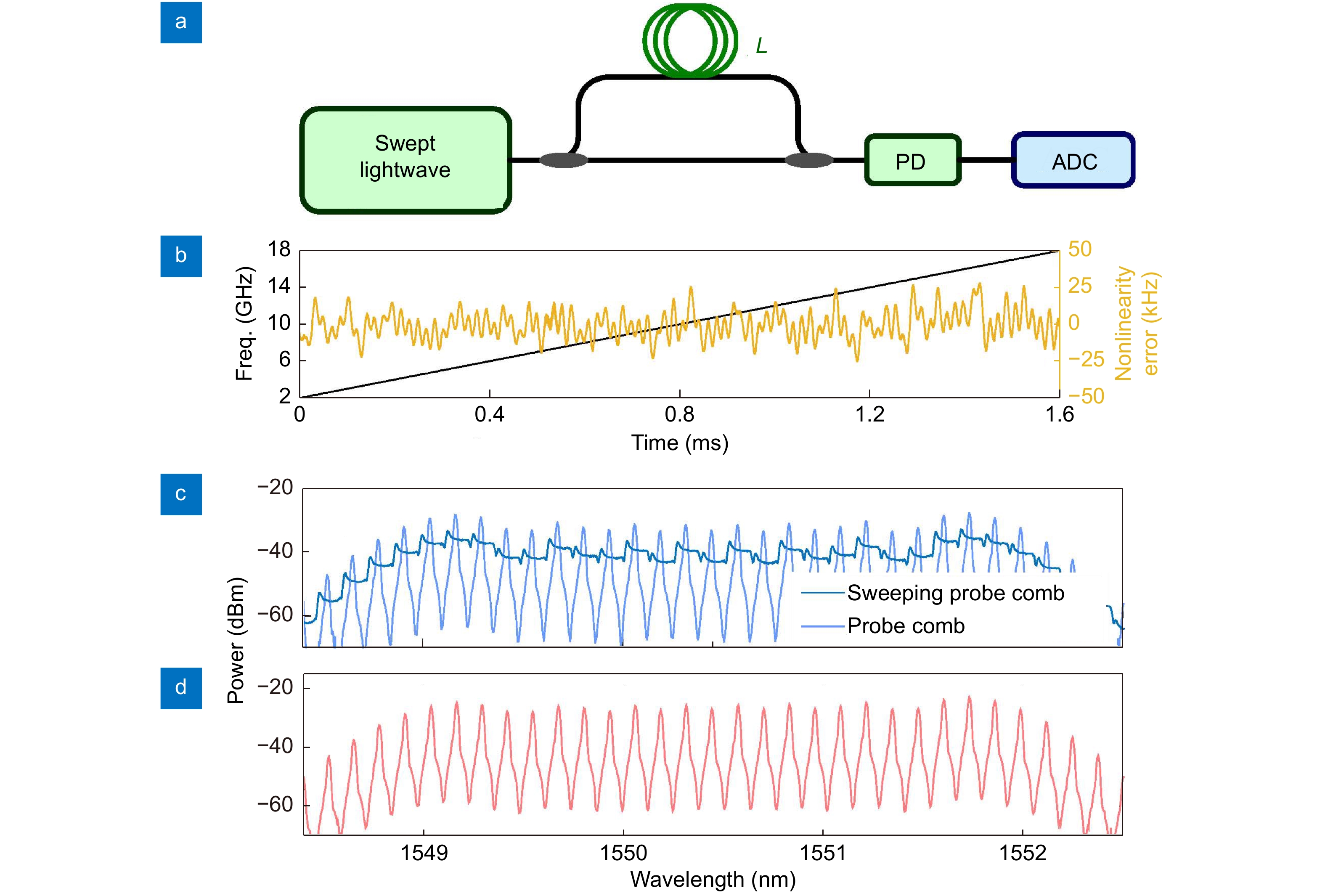
Figure 3.
(a) Experiment setup of swept lightwave characterization. (b) Sweep range and nonlinear error of the ultra-linearly swept optical source measured by using an unbalanced Mach-Zehnder interferometer. (c) Optical spectrum of the probe comb with a stabilized optical source and a linearly-swept optical source. (d) Optical spectrum of the local comb with a stabilized optical source.
-
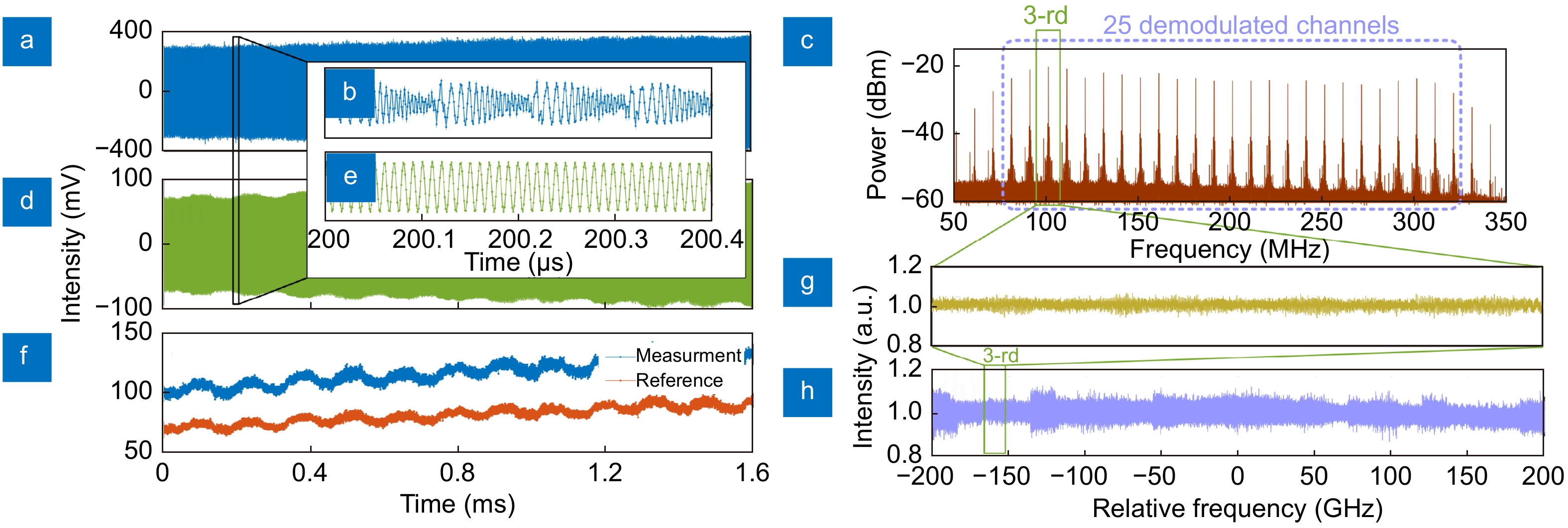
Figure 4.
(a) Temporal waveform of dual-comb interferometer recorded in 1.6 ms with a sampling rate of 1 GS/s. (b) Zoom-in figure of (a) in 0.4 µs. (c) Electrical spectrum of reference branch containing total 25 lines centered at about 200 MHz. (d) Temporal waveform and (e) zoom-in figure of the 3-rd channel obtained by digital filtering. (f) Envelopes of the 3-rd channel for measurement and reference branches obtained by digital Hilbert transformation. Demodulated spectrum without DUT at 1 MHz spectral resolution for (g) the 3-rd channel in 16 GHz bandwidth and (h) all channels covering 400 GHz bandwidth, in which the standard deviation is calculated to be 2.316 %.
-
Figure 5.
(a) Reflectance spectrum measured in 1.6 ms with 1 MHz resolution. (b) Experimental setup of the fiber F-P cavity with 3 GHz FSR. (c) Measurement results of the deepest resonance with 17 MHz FWHM by using proposed method and ultra-fine EOFC. (d) Experimental setup of UFEOFC-based high resolution spectroscopy for comparison.
-
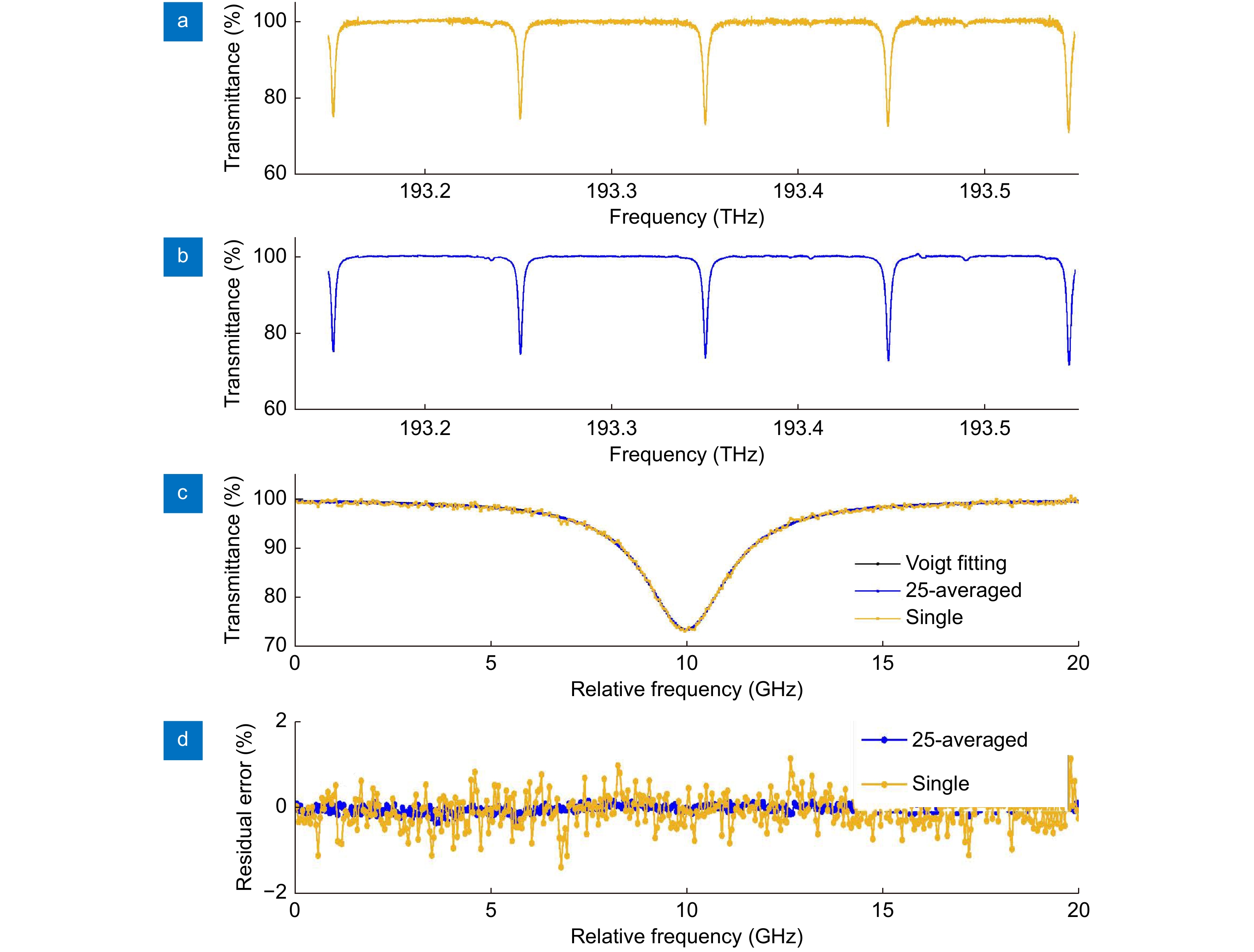
Figure 6.
Spectra of H13CN gas cell obtained by (a) single-shot measurement and (b) 25 times averaged measurement, containing the absorption lines of P9-13 in the 2v3 band. (c) Measurement results and Voigt fitting curve of the P11 line. (d) Residual errors between the measurement results and fitting curve, and the standard deviations are calculated to be 0.378% and 0.087% for the single-shot measurement and 25-averaged measurement. The spectral resolution is 50 MHz by reducing the filter bandwidth to 200 kHz.
-
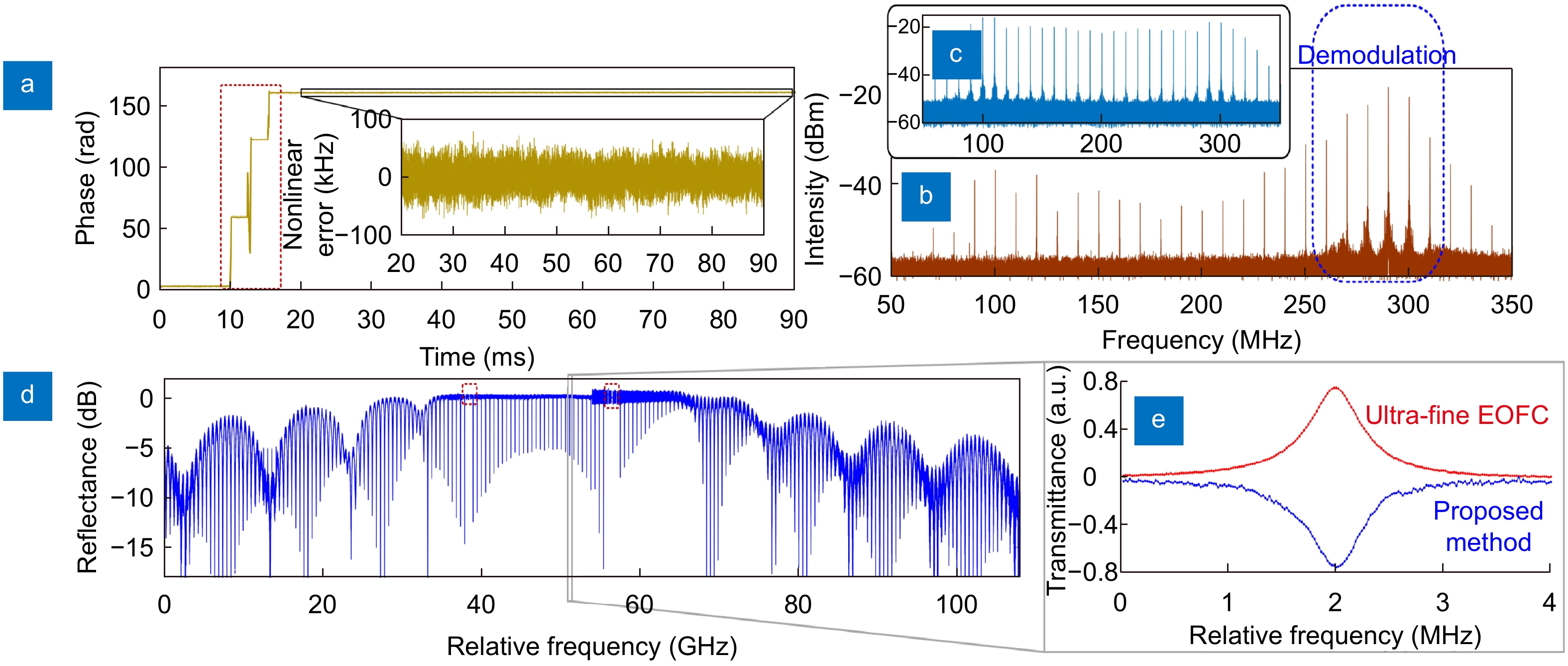
Figure 7.
(a) Unwrapped phase and nonlinear error of the swept optical source with 18 GHz sweep range and 90 ms sweep time. Electrical spectrum of (b) measurement branch and (c) reference branch, in which six lines circled are demodulated. (d) Demodulated reflectance spectrum of a fiber F-P cavity with 20 kHz spectral resolution. The points during the phase hopping circled in red are removed. (e) A resonance with 600 kHz FWHM measured by using the proposed method and UFEOFC.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: