| Citation: | Liu B, Yu Y, Chen Z, Han W Q. True random coded photon counting Lidar. Opto-Electron Adv 3, 190044 (2020). doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.190044 |
-
Abstract
A true random coded photon counting Lidar system is proposed in this paper, in which a single photon detector acts as the true random sequence signal generator instead of the traditional function generator. Compared with the traditional pseudo-random coded method, the true random coded method not only improves the anti-crosstalk capability of the system, but more importantly, it effectively overcomes the adverse effect of the detector's dead time on the ranging performance. The experiment results show that the ranging performance of the true random coded method is obviously better than that of the pseudo-random coded method. As a result, a three-dimensional scanning imaging of a model car is completed by the true random coded method.-
Keywords:
- Lidar /
- photon counting /
- true random coded /
- pseudo-random coded
-

-
References
[1] McCarthy A, Collins R J, Krichel N J, Fernández V, Wallace A M et al. Long-range time-of-flight scanning sensor based on high-speed time-correlated single-photon counting. Appl Opt 48, 6241-6251 (2009). doi: 10.1364/AO.48.006241 [2] Albota M A, Heinrichs R M, Kocher D G, Marino R M, Fouche D G et al. Three-dimensional imaging laser radar with a photon-counting avalanche photodiode array and microchip laser. Appl Opt 41, 7671-7678 (2002). doi: 10.1364/AO.41.007671 [3] Degnan J, Wells D, Machan R, Leventhal E. Second generation airborne 3D imaging lidars based on photon counting. Proc SPIE 6771, 67710N (2007). doi: 10.1117/12.732086 [4] Degnan J J. Scanning, multibeam, single photon lidars for rapid, large scale, high resolution, topographic and bathymetric mapping. Remote Sens 8, 958 (2016). doi: 10.3390/rs8110958 [5] Takeuchi N, Sugimoto N, Baba H, Sakurai K. Random modulation CW lidar. Appl Opt 22, 1382-1386 (1983). doi: 10.1364/AO.22.001382 [6] Sun X L, Abshire J B, Krainak M A, Hasselbrack W B. Photon counting pseudorandom noise code laser altimeters. Proc SPIE 6771, 677100 (2007). doi: 10.1117/12.735453 [7] Hiskett P A, Parry C S, McCarthy A, Buller G S. A photon-counting time-of-flight ranging technique developed for the avoidance of range ambiguity at gigahertz clock rates. Opt Express 16, 13685-13698 (2008). doi: 10.1364/OE.16.013685 [8] Krichel N J, McCarthy A, Buller G S. Resolving range ambiguity in a photon counting depth imager operating at kilometer distances. Opt Express 18, 9192-9206 (2010). doi: 10.1364/OE.18.009192 [9] Rieger P, Ullrich A. A novel range ambiguity resolution technique applying pulse-position modulation in time-of-flight ranging applications. Proc SPIE 8379, 83790R (2012). doi: 10.1117/12.919140 [10] Zhang Y F, He Y, Yang F, Luo Y, Chen W B. Three-dimensional imaging Lidar system based on high speed pseudorandom modulation and photon counting. Chin Opt Lett 14, 111101 (2016). doi: 10.3788/COL201614.111101 [11] Yang F, Zhang X, He Y, Chen W B. High speed pseudorandom Modulation fiber laser ranging system. Chin Opt Lett 12, 082801 (2014). doi: 10.3788/COL201412.082801 [12] Zhang Q, Soon H W, Tian H T, Fernando S, Ha Y J et al. Pseudo-random single photon counting for time-resolved optical measurement. Opt Express 16, 13233-13239 (2008). doi: 10.1364/OE.16.013233 [13] Zhang Q, Chen L, Chen N G. Pseudo-random single photon counting: a high-speed implementation. Biomed Opt Express 1, 41-46 (2010). doi: 10.1364/BOE.1.000041 [14] Zhang F, Du P F, Liu Q, Gong M L, Fu X. Adaptive strategy for CPPM single-photon collision avoidance LIDAR against dynamic crosstalk. Opt Express 25, 12237-12250 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OE.25.012237 -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
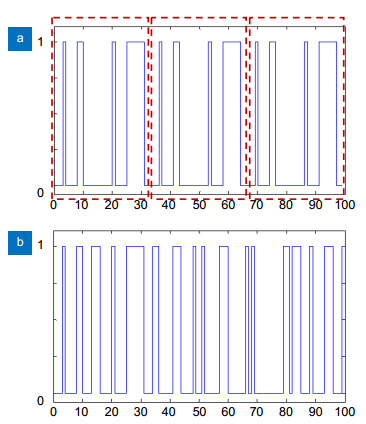
Figure 1.
(a) Pseudo-random sequence and (b) true random sequence.
-
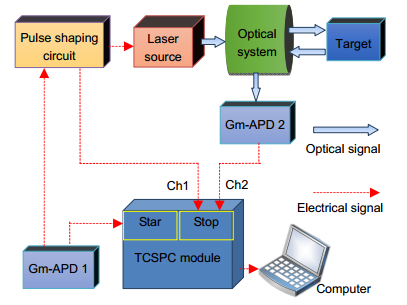
Figure 2.
True random coded photon counting Lidar system.
-
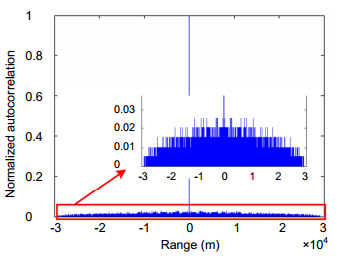
Figure 3.
Normalized auto-correlation function of the true random sequence
-
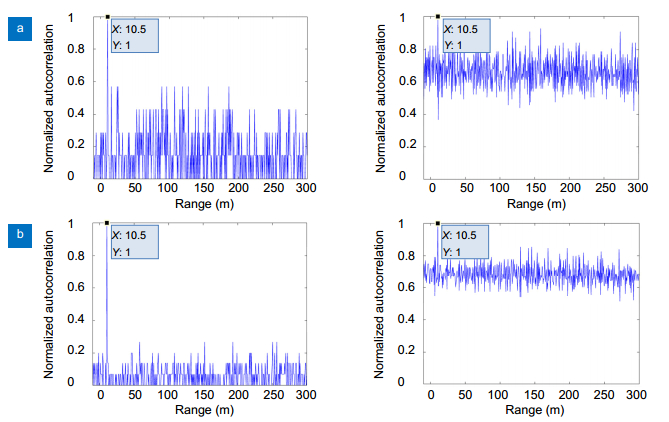
Figure 4.
Normalized auto-correlation range images with two different echo photons number for the true random coded method and the pseudo-random coded method.
-
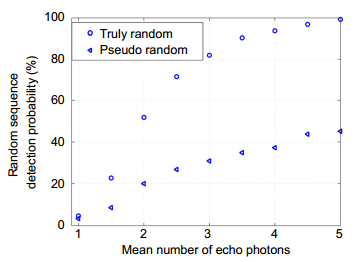
Figure 5.
The detection probability statistical results of the true random coded method and the pseudo-random coded method at different mean echo photons number.
-
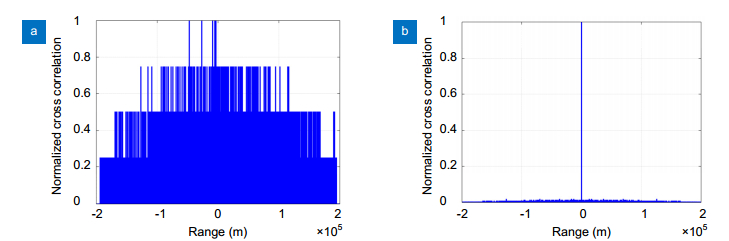
Figure 6.
Normalized cross-correlation range images for the true random sequence (a) and the sparse pseudo-random sequence (b).
-
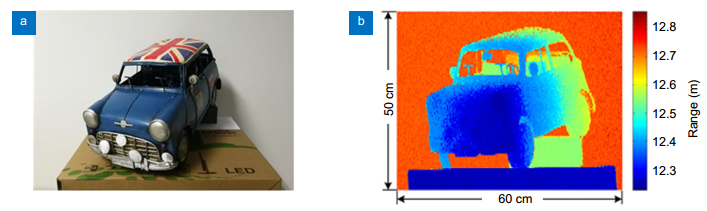
Figure 7.
(a) The picture of the model car and (b) three-dimensional scanning imaging of the model car.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: