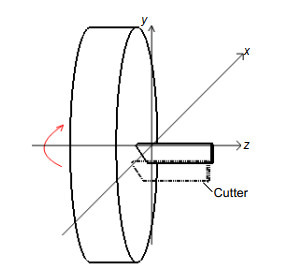
Research on the calculation method of the ultra-precision turning trajectory of large-vector high-convex cylinders
-
摘要:
阵列微结构光学元件广泛用于各种光束匀化场合,而常规的加工方法难以满足大矢高凸柱面阵列的精度要求。本文采用超精密车削成型法,分析了影响金刚石车削的主要因素,设计了顺序搜索法和二分搜索法寻找车削轨迹,并对比了两种方法的优缺点,结合Matlab软件用二分搜索法成功找到车削轨迹及数控程序,并在超精密车床上进行了车削实验,得到了表面轮廓误差在135 nm的大矢高阵列微结构。证明了二分搜索法能够准确获得车削轨迹,并且此法可同时适用于球面轮廓和非球面轮廓,具有重要的工程应用价值。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Array microstructure optical elements are widely used in various beam homogenization occasions, but conventional processing methods cannot meet the accuracy requirements of large-sagittal convex cylindrical arrays. In this paper, the ultra-precision turning forming method is used to analyze the main factors affecting diamond turning, the sequential search method and the binary search method are designed to find the turning track, and the advantages and disadvantages of the two methods are compared. Furthermore, the binary search method is successfully found by combining the Matlab software turning trajectory and the numerical control program. As proof-of-concept demonstrations, turning experiments are carried on an ultra-precision lathe, and a large-vector high-array microstructure with a surface profile error of 135 nm is obtained. It proves that the force binary search method can accurately obtain the turning trajectory, and this method can be applied to both spherical and aspherical contours, showing important engineering application value.
-

Overview: Array microstructured optical elements are widely used in various beam homogenization occasions, with complex structures and extremely high surface shape accuracy requirements. The microstructures of large-sag high-convex cylindrical arrays have the characteristics of high sagittal height, large diameter, small seam, and high surface shape accuracy. It is often difficult for conventional processing methods to meet the accuracy requirements. As a ultra-precision turning forming method, the diamond tip has a micron-level structure, and the processing accuracy is not limited by the height of the microstructure, which is a very potential method for processing the microstructure of the large array of high convex cylindrical arrays.
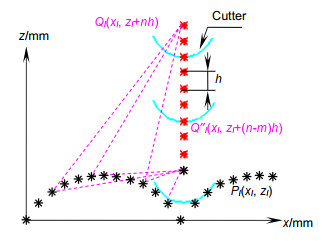
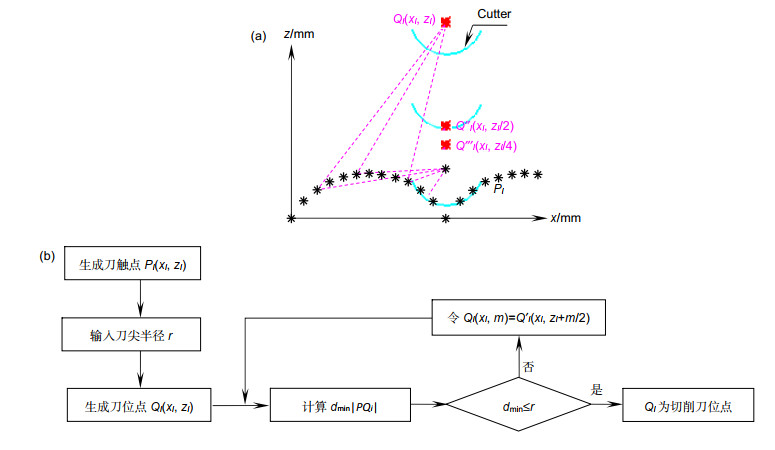
How to ensure the machining accuracy is an important problem that needs to be solved in ultra-precision turning. This paper analyzes the main factors that affect diamond turning-turning trajectories. Increasing the turning trajectory accuracy can improve the turning surface accuracy and obtain a good machining surface shape. This article analyzes and compares two methods, namely sequential search method and binary search method, to find the best turning trajectory, and each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The sequential search method can obtain a high-precision turning trajectory, but the calculation amount will gradually increase as the stepping distance decreases, which leads to lower efficiency. The binary search method can quickly obtain the turning trajectory, and the calculation amount is relatively small. So the calculation time is short, which greatly improves the turning efficiency. Combined with actual production applications, improving efficiency is one of the important issues that need to be considered. Therefore, this paper chooses the binary search method to find the turning contour trajectory.
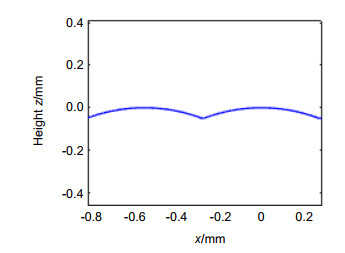
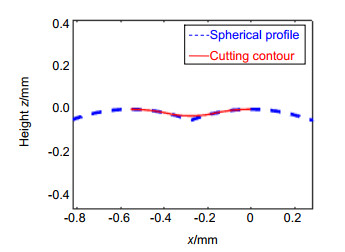
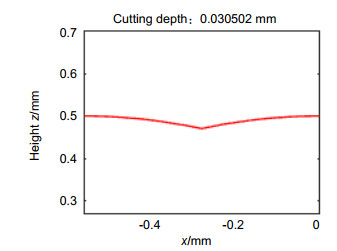
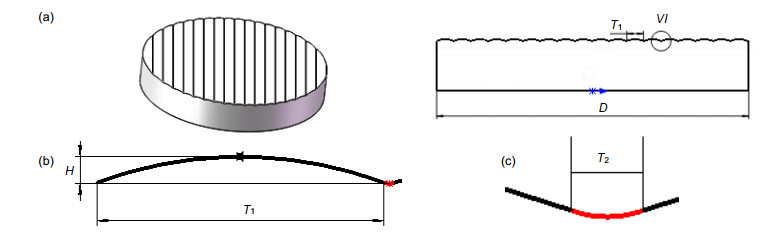
The binary search method can be used to find the turning trajectories of both spherical and aspherical contours. Combined with laboratory conditions, the experiment took the spherical contour as an example, and the spherical turning trajectory was successfully generated through numerical control programs. Furthermore, turning experiments on ultra-precision turning machine tools were carried out, with the turning results being analyzed using the least square method. The original curve is compared with the fitted curve, and the difference curve is obtained. It is found that the contour error of the workpiece after processing is 135 nm, and the expected surface shape and good surface contour error are basically obtained. This article provides a theoretical basis for how to find the turning trajectory of the large-vector convex cylindrical array microstructure, and has important practical application value.
-

-
表 1 实验车削参数
Table 1. Experimental turning parameters
实验参数 实验参数值 主轴转速/(r/mm) 500 进给速度/(mm/min) 3 刀具半径R/mm 0.5 曲线T1宽度/mm 0.534 接缝宽度T2/mm 0.02 切削周期数 10 -
[1] 范占斌. 圆柱表面微结构超精密加工关键技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2014.
Fan Z B. Research on key technology in ultra-precision turning processing of microstructure on cylindrical surface[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-90002-1016921217.htm [2] 刘鑫, 张满, 史立芳, 等. 一种大F数微透镜阵列的制备方法[J]. 光子学报, 2017, 46(2): 0222004. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB201702005.htm
Liu X, Zhang M, Shi L F, et al. Fabrication method for the microlens array of high F-number[J]. Acta Photon Sini, 2017, 46(2): 0222004. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB201702005.htm
[3] 徐礼威. 微透镜阵列超精密切削加工技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.
Xu L W. Research on ultra-precision turning technology of microlens array[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1015980583.htm [4] 田霏, 刘现磊, 张效栋, 等. 微透镜阵列加工误差对光学性能的影响[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(2): 0222002. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201602025.htm
Tian F, Liu X L, Zhang X D, et al. Influence of manufacture error on optical performance of micro lens array[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2016, 36(2): 0222002. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201602025.htm
[5] 肖艳芬, 朱菁, 杨宝喜, 等. 用于光刻机照明均匀化的微柱面镜阵列设计[J]. 中国激光, 2013, 40(2): 0216001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201302040.htm
Xiao Y F, Zhu J, Yang B X, et al. Design of micro-cylindrical-lens array used for illumination uniformization in lithography systems[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2013, 40(2): 0216001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201302040.htm
[6] 王灏, 董连和, 朱国栋, 等. 车削掩模的石英非球面微透镜阵列制作方法[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(4): 170671. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170671
Wang H, Dong L H, Zhu G D, et al. Fabrication method of quartz aspheric microlens array for turning mask[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(4): 170671. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170671
[7] 张为国, 董小春, 杜春雷. 微透镜列阵成像光刻技术[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2010, 39(3): 469-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2010.03.019
Zhang W G, Dong X C, Du C L. Microlens array imaging-based photolithography technique[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2010, 39(3): 469-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2010.03.019
[8] 史立芳, 叶玉堂, 邓启凌, 等. 制备人工复眼结构的方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(9): 2462-2466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.09.030
Shi L F, Ye Y T, Deng Q L, et al. Method to fabricate artificial compound eye[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2013, 42(9): 2462-2466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.09.030
[9] Chakrabarti M, Dam-Hansen C, Stubager J, et al. Replication of optical microlens array using photoresist coated molds[J]. Opt Express, 2016, 24(9): 9528-9540. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.009528
[10] Zhou W C, Zhang L, Yi A Y. Design and fabrication of a compound-eye system using precision molded chalcogenide glass freeform microlens arrays[J]. Optik, 2018, 171: 294-303. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.06.033
[11] Mukaida M, Yan J W. Ductile machining of single-crystal silicon for microlens arrays by ultraprecision diamond turning using a slow tool servo[J]. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2017, 115: 2-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.11.004
[12] 史成勇. 仿生曲面复眼系统设计及其图像处理研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2017.
Shi C Y. Research on the design and image process of bioinspired spherical compound eve imaging system[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/Y3353261 [13] 张雄, 宋乐, 张姗姗, 等. 仿生复眼系统标定及测量方法研究[J]. 光电工程, 2014, 41(3): 35-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.03.006
Zhang X, Song L, Zhang S S, et al. The method for the calibration and measurement of bionic compound-eye system[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2014, 41(3): 35-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.03.006
[14] 李荣彬, 杜雪, 张志辉, 等. 光学微结构的超精密加工技术[J]. 纳米技术与精密工程, 2003, 1(1): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMJM200301014.htm
Li R B, Du X, Zhang Z H, et al. Ultra-precision machining of optical microstructures[J]. Nanotechnol Prec Eng, 2003, 1(1): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMJM200301014.htm
[15] 朱登超. 光学微结构快速车削工艺研究与精度分析[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2010.
Zhu D C. Technology study and accuracy analysis of optical microstructures manufactured by fast tool servo[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2010.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-1011279580.htm [16] 张效栋, 王志诚, 曾臻, 等. 微透镜阵列超精密切削正弦过渡路径优化设计[J]. 纳米技术与精密工程, 2017, 15(4): 239-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMJM201704001.htm
Zhang X D, Wang Z C, Zeng Z, et al. Optimized design of sine-transition cutting path for microlens array in ultra-precision cutting[J]. Nanotechnol Prec Eng, 2017, 15(4): 239-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMJM201704001.htm
[17] 黄昆涛, 房丰洲, 宫虎. 超精密车削表面微观形貌对光学特性的影响[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2013, 21(1): 101-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201301017.htm
Huang K T, Fang F Z, Gong H. Effect of surface microscopic topology generated by ultra-precision turning on optical characteristics[J]. Opt Prec Eng, 2013, 21(1): 101-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201301017.htm
[18] 何成奎, 张平, 李东, 等. 超精密车削表面质量影响因素及发展趋势研究[J]. 装备制造技术, 2017(11): 12-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJX201711005.htm
He C K, Zhang P, Li D, et al. Research on influencing factors and development trend of surface quality in ultra precision turning[J]. Equip Manuf Technol, 2017(11): 12-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJX201711005.htm
[19] 张效栋, 房丰洲, 程颖. 自由曲面超精密车削加工路径优化设计[J]. 天津大学学报, 2009, 42(3): 278-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX200903018.htm
Zhang X D, Fang F Z, Cheng Y. Optimized design of cutting path for freeform surface in ultra-precision turning[J]. J Tianjin Univ, 2009, 42(3): 278-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX200903018.htm
[20] 王毅, 余景池. 超精密车削金刚石刀具刃口误差的高精度补偿[J]. 光电工程, 2011, 38(1): 98-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2011.01.019
Wang Y, Yu J C. Compensation for error of diamond tool's cutting edge in single diamond turning[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2011, 38(1): 98-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2011.01.019
[21] 于慧娟. 光学自由曲面单点金刚石超精密车削理论与技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015.
Yu H J. Theoretical and technological research on optical freeform surface of single point diamond ultra-precision turning[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1015598327.htm -


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: