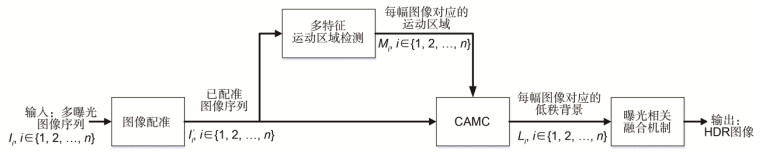
High dynamic range imaging method based on image content adaptive matrix completion
-
摘要:
高动态范围图像合成中容易出现鬼影现象,而传统的矩阵完成算法没有考虑多曝光图像序列的运动特征,导致高动态范围图像中的鬼影未能完全去除。针对这一问题,本文提出一种基于低动态范围图像内容自适应矩阵完成算法以去除高动态范围图像中的鬼影。首先,根据图像的亮度和色度信息,确定低动态范围图像的运动区域;然后根据这一运动先验信息,调整矩阵完成算法过程中的正则化约束强度,从而得到每幅低动态范围图像的背景信息;最后,考虑到不同曝光度的图像在每一区域所包含的细节不同,采用与曝光相关的融合策略合成去鬼影的高动态范围图像。实验分别采用简单背景图像序列和复杂背景图像序列,结果表明,所提出的算法相比于奇异值部分和最小化矩阵完成算法,能取得更好的合成效果,适用于复杂背景下的高动态范围图像合成。
 Abstract:
Abstract:High dynamic range (HDR) imaging usually produces ghosting artifacts, while the traditional matrix completion (MC) method may fail to completely remove the ghosts, without considering the motion characteristics of multi-exposure image. To solve this problem, this paper presents a new HDR imaging method based on content adaptive matrix completion of low dynamic range (LDR) image to remove the ghosts of HDR image. Firstly, according to the image luminance and chrominance information, the LDR image motion area is determined. Then, based on the priori information of motion, the regularization constraint intensity is adjusted in MC process to get each LDR image background information. Finally, a fusion strategy related to multiple exposures is proposed while the difference of details in each image area under different exposures is considered. Regular background sequences and cluttered background sequences are used for experiments. The experimental results demonstrate that, compared with the partial sum minimization of singular values-matrix completion method, the proposed method is more real-time and suitable for cluttered background sequences
-

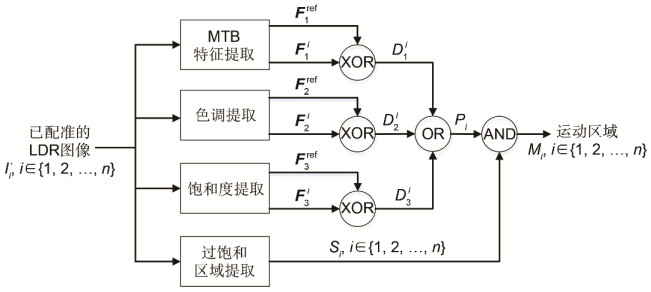
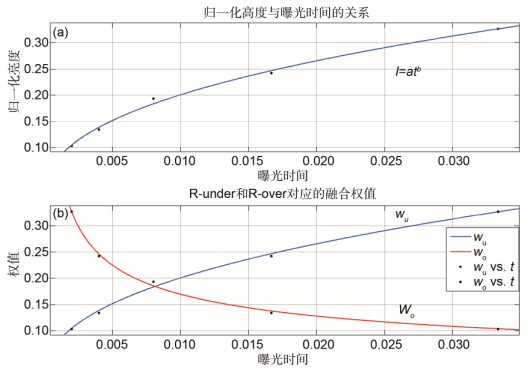
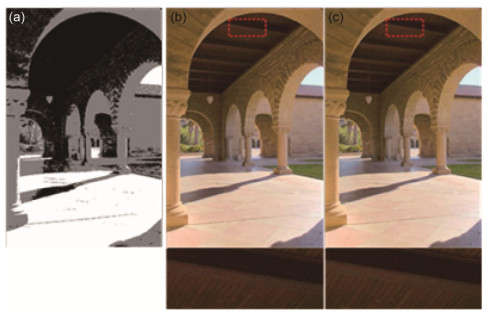
High dynamic range (HDR) image is more consistent with human perception, and is being applied to many fields, such as consumer electronics, remote sensing system, intelligent transportation, security monitoring. So far, HDR imaging has usually produced ghosting artifacts, so there are many researchers carrying out the research about de-ghosting. Some researchers came up with the algorithms which can remove ghosts by detecting moving regions, and other researchers considered the fusion weight distribution to eliminate the artifacts. Recently, the algorithm that models the HDR imaging problem as a rank minimization problem is proposed. It is solved with the idea of matrix completion (MC). However, as no attention was paid to the motion characteristics of multi-exposure image, the traditional MC method could fail to completely remove the ghosts. Therefore, in order to solve this problem, according to the motion information of multi-exposure images and fusion strategy related to exposures, this paper presents a new HDR imaging method based on content adaptive MC of low dynamic range (LDR) image to remove the ghosts of HDR image. Firstly, the motion area of LDR image is obtained based on the luminance and color information of the image with the median threshold bitmap (MTB) features, the hue feature H and color saturation characteristics S. Then, based on the priori information of motion, regularization strength is adjusted in the MC process to obtain the low-rank background information of each LDR image. Finally, a fusion strategy related to multiple exposures is proposed to achieve a ghost-free HDR image, while the difference of details in each image area under different exposures is considered. Regular background sequences and cluttered background sequences are used for experiments. The experimental results demonstrate that, compared with the partial sum minimization of singular values-matrix completion method, the proposed method is more real-time and suitable for cluttered background sequences. The above figure is part of the experimental results, where (e) and (h) are the results of the proposed algorithm of Arch and Forest sequences. Compared with these algorithms, the images synthesized by the proposed algorithm not only have no ghost, but also have richer details. In addition, by calculating the processing speed of several classical algorithms and the proposed algorithm, it is shown that the proposed algorithm can reduce the computational complexity of the overall HDR imaging operation and run more efficiently.
-

-
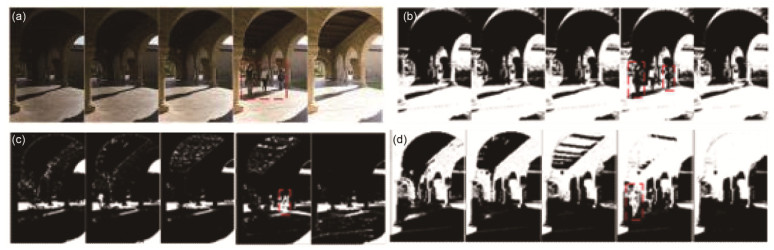
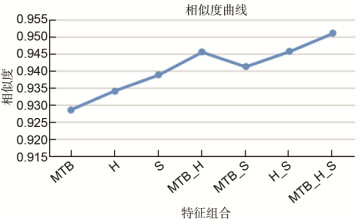
图 6 不同的特征组合对应的运动区域检测结果. (a) MTB特征. (b) H分量. (c) S分量. (d) MTB和H分量. (e) MTB和S分量. (f) H分量和S分量. (g) MTB特征, H分量和S分量. (h) GTM.
Figure 6. Moving region detection results corresponding to different feature combinations. (a) MTB. (b) H component. (c) S component. (d) MTB and H component. (e) MTB and S component. (f) H component and S component. (g) MTB, H component and S component. (h) GTM.
图 10 Arch序列的对比实验. (a) Debevec等[2]. (b) Zhang等[6]. (c) Gallo等[14]. (d) Oh等[19]. (e) Heo等[16]. (f) Zheng等[5]. (g) Hu等[17]. (h) Sen等[18]. (i) Photoshop CS6. (j)本文算法.
Figure 10. Comparison experiments of Arch sequences. (a) Debevec, et al[2]. (b) Zhang, et al[6]. (c) Gallo, et al[14]. (d) Oh, et al[19]. (e) Heo, et al[16]. (f) Zheng, et al[5]. (g) Hu, et al[17]. (h) Sen, et al[18]. (i) Photoshop CS6. (j) The proposed algorithm.
图 11 Forest序列的对比实验. (a) Forest多曝光图像序列. (b) Debevec等[2]. (c) Photoshop CS6. (d) Heo等[16]. (e) Gallo等[13]. (f) Sen等[18]. (g)本文算法.
Figure 11. Comparison experiment of Forest sequence. (a) Forest multi exposure image sequences. (b) Debevec, et al[2]. (c) Photoshop CS6. (d) Heo, et al[16]. (e) Gallo, et al[13]. (f) Sen, et al[18]. (g) The proposed algorithm.
表 1 不同融合策略结果评价.
Table 1. Evaluation of different fusion strategies.
Variance Definition Comentropy PSSV-MC [9] 67.40 4.87 7.58 The proposed 62.01 5.03 7.79 -
[1] Reinhard E, Heidrich W, Debevec P, et al. High dynamic range imaging: acquisition, display and image-based lighting. 2nd ed. [M]. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 2010: 171–183.
[2] Debevec P E, Malik J. Recovering high dynamic range radiance maps from photographs[C]// Proceedings of the 24th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, New York: ACM, 1997: 369–378.
[3] Mitsunaga T, Nayar S K. Radiometric self calibration[C]// Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New York: ACM, 1999: 374–380.
[4] Jacobs K, Loscos C, Ward G. Automatic high dynamic range image generation for dynamic scenes[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2008, 28(2): 84–93. doi: 10.1109/MCG.2008.23
[5] Zheng J H, Li Z G, Zhu Z J, et al. Hybrid patching for a se-quence of differently exposed images with moving objects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 5190–5201. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2283401
[6] Zhang W, Cham W K. Gradient–directed multiexposure composition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 2318–2323. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2170079
[7] Khan E A, Akyuz A O, Reinhard E. Ghost removal in high dynamic range images[C]// IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA: IEEE, 2006: 2005–2008.
[8] Lee C, Li Y L, Monga V. Ghost–free high dynamic range imaging via rank minimization[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(9): 1045–1049. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2323404
[9] Oh T H, Lee J Y, Tai Y W, et al. Robust high dynamic range imaging by rank minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(6): 1219–1232. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2361338
[10] Pece F, Kautz J. Bitmap movement detection: HDR for dynamic scenes[C]// Proceedings of the 2010 Conference on Visual Media Production, Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society, 2010.
[11] Ma K, Li H, Yong H W, et al. Robust multi–exposure image fusion: a structural patch decomposition approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(5): 2519–2532. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2671921
[12] Lee J Y, Matsushita Y, Shi B X, et al. Radiometric calibration by rank minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 144–156. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.66
[13] Hu Y, Zhang D B, Ye J P, et al. Fast and accurate matrix completion via truncated nuclear norm regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(9): 2117–2130. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.271
[14] Gallo O, Gelfand N, Chen W C, et al. Artifact-free high dynamic range imaging[C]// IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, San Francisco CA, USA: IEEE, 2009: 1–7.
[15] [Online]. Available: . http://users.soe.ucsc.edu/orazio/deghost.html.
[16] Heo Y S, Lee K M, Lee S U, et al. Ghost–free high dynamic range imaging[C]// Proceedings of the 10th Asian Conference of Computer Vision (ACCV), New Zealand: Queenstown, 2010: 486–500.
[17] Hu J, Gallo O, Pulli K, et al. HDR deghosting: how to deal with saturation?[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA: IEEE, 2013: 1163–1170.
[18] Sen P, Kalantari N K, Yaesoubi M, et al. Robust patch–based HDR reconstruction of dynamic scenes[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(6): 1–11.
[19] Oh T H, Lee J Y, Kweon I S. High dynamic range imaging by a rank-1 constraint[C]// IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Melbourne, VIC, Australia: IEEE, 2013: 790–794.
[20] Lee Chul. Ghost-free high dynamic range imaging [EB/OL]. . http://cilab.pknu.ac.kr/research/rm_hdr.html.
[21] Karađuzović-Hadžiabdić K, Telalović J H, Mantiuk R K. As-sessment of multi-exposure HDR image deghosting methods[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2017, 63: 1–17. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0097849317300110
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: