Infrared dim and small target background suppression based on improved gradient inverse weighting filter
-
摘要:
红外弱小目标易淹没在复杂的起伏背景中,为了提高后续目标的检测能力,往往需要通过抑制背景来增强目标信号。传统梯度倒数加权滤波对背景边缘缺乏稳健的适应性,本文提出了改进的梯度倒数加权滤波算法,即通过建立背景局部区域相关函数,利用背景局部统计特性自适应调整滤波参数,能较好地适应剧烈变化的背景,提高背景抑制能力。实验表明,改进的梯度倒数滤波器能对图像背景进行有效的抑制,总体性能优于其他背景抑制方法。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Dim and small infrared target easily flooded in complicated background. In order to improve the ability of target detection, the background is often suppressed to enhance the target signal. Referring to the lack of robust adaptability of the gradient inverse weighted filtering for background edges, an improved gradient inverse weighting filtering algorithm is proposed through the establishment of background local correlation function. The use of background local statistical characteristics of adaptive filter parameters, can better adapt to the drastic change in the background, and improve the ability to suppress background suppression algorithm. Experimental results show that the improved gradient inverse weighted filtering could effectively suppress the background of images, presenting a superior overall performance to other background suppression methods.
-

Abstract: Because the distance between the infrared imaging system and the target is usually far away, the background in the infrared image often contains clouds, clutter, and infrared correction caused by uneven undulation or stripes as well as all kinds of noise. At the same time, the small target of image in the pixel is less, and the lack of shape and texture information, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is low, easily submerged in the complex background, which makes the detection and tracking of infrared dim and small target difficult. In order to improve the abilities of detection and tracking of infrared dim and small targets, it is necessary to effectively suppress the complex background in infrared images. The background prediction is a valid complex background suppression method. By dividing the original image from the predicted background, a differential image is obtained, and the difference image can sufficiently suppress the complex background and the target is effectively preserved.
At present, the commonly used background prediction algorithms include low-pass filtering, median filtering, morphological filtering, two-dimensional least mean square error filtering (TDLMS), mixed of Gaussian, background prediction based on pixel estimation method, and so on. The above background prediction methods are effective for the background of stable or slowly changing, but they are ineffective for the large span background. In view of the shortcomings of the above methods, considering the ability of gradient inverse weighting filter has the advantages of good detail preserving and strong clutter resistance, it is introduced into the paper for background suppression. However, because its key parameters cannot be adjusted in real time according to local clutter, in order to enhance its adaptability, this paper proposes an improved gradient inverse weighting filtering algorithm through the establishment of clutter local correlation function. The use of background of the local statistical characteristics of adaptive filter parameters, can better adapt to the drastic change in the clutter, and improve the ability to suppress clutter suppression algorithm.
For evaluation of background prediction result, three performance indices are used in this study, mean squared error (MSE), structural similarity (SSIM) and local signal-to-noise ratio gain (GSNR), to evaluate the effect of image background prediction. By comparing and analyzing these three indexes, MSE, SSIM and GSNR, it could be seen that the improved gradient inverse weighted filtering could effectively suppress the complex background of images, presenting a superior overall performance to other background suppression methods.
-

-
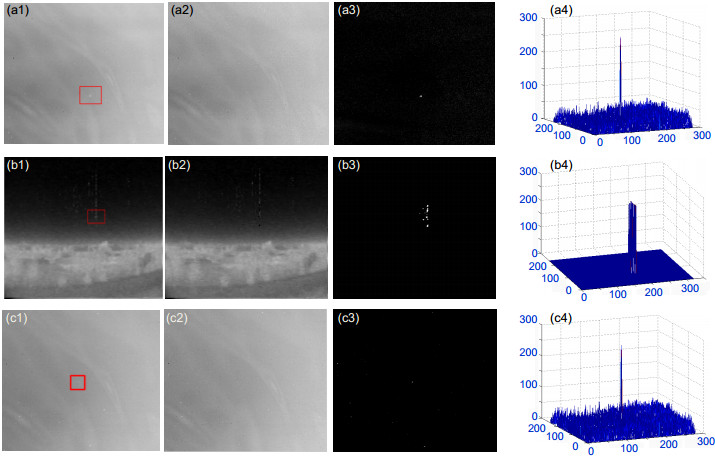
图 1 本文算法对不同场景红外图像的背景抑制. (a1)~(a4)从左到右分别是场景A的原图(a1)、获取的背景图(a2)、差分图(a3)及差分图对应的三维图(a4). (b1)~(b4)从左到右分别是场景B的原图(b1)、获取的背景图(b2)、差分图(b3)及差分图对应的三维图(b4). (c1)~(c4)从左到右分别是场景C的原图(c1)、获取的背景图(c2)、差分图(c3)及差分图对应的三维图(c4).
Figure 1. The results of background suppression via the proposed algorithm for different infrared images. (a1)~(a4) From left to right are original images of scene A (a1), the background map (a2), the differential graph (a3) and the corresponding 3D map (a4). (b1)~(b4) From left to right are original images of scene B (b1), the background map (b2), the differential graph (b3) and the corresponding 3D map (b4). (c1)~(c4) From left to right are original images of scene C (c1), the background map (c2), the differential graph (c3) and the corresponding 3D map (c4).
表 1 6帧图像的信噪比情况.
Table 1. Different SNR of images.
帧数 1 2 3 4 5 6 信噪比 2.25 1.96 2.14 2.02 1.91 2.21 表 2 各背景预测法MSE值比较.
Table 2. Comparison of MSE derived by several background prediction methods.
表 3 各背景预测方法SSIM值比较.
Table 3. Comparison of SSIM derived by several background prediction methods.
-
[1] Li Hong, Wei Yantao, Li Luoqing, et al. Infrared moving target detection and tracking based on tensor locality preserving projection[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2010, 53(2): 77–83. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1350449509001273
[2] 肖宁, 李爱军.多特征差异决策耦合Top-Hat变换的红外目标检测[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12): 110–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.018
Xiao Ning, Li Aijun. Infrared target detection with multiple feature difference decision coupled Top-Hat transform [J]. Opto Electronics Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 110–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.018
[3] Bai Xiangzhi, Zhou Fugen. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(6): 2145–2156. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.12.023
[4] 盛文, 邓斌, 柳健.一种基于多尺度距离像的红外小目标检测方法[J].电子学报, 2002, 30(1): 42–45. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dianzixb200201011.aspx
Sheng Wen, Deng Bin, Liu Jian. Multi-resolution distance map based small target detection in infrared image[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2002, 30(1): 42–45. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dianzixb200201011.aspx
[5] Braga-Neto U M, Choudhury M, Goutsias J. Automatic target detection and tracking in forward-looking infrared image sequences using morphological connected operators[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2004, 13(4): 802–813. doi: 10.1117/1.1789982
[6] Bae T W, Kim Y C, Ahn S H, et al. An efficient two dimensional least mean square (tdlms) based on block statistics for small target detection[J]. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2009, 30(10): 1092–1101. doi: 10.1007/s10762-009-9530-6
[7] Sobral A, Vacavant A. A comprehensive review of background subtraction algorithms evaluated with synthetic and real videos[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2014, 122: 4–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2013.12.005
[8] Hofmann M, Tiefenbacher P, Rigoll G. Background segmentation with feedback: the pixel-based adaptive segmented[C]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Providence, RI, USA, 2012: 38–43.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.364.4347&rep=rep1&type=pdf [9] Arnich O, Van Droogenbroeck M. Vibe: a universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(6): 1709–1724. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2101613
[10] 苗晓孔, 王春平.改进Sobel算子的单帧红外弱小目标检测[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12): 119–125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.019
Miao Xiaokong, Wang Chunping. Detection of dim targets in single frame by using improved Sobel[J]. Opto-Electronics Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 119–125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.019
[11] 王艳华, 刘伟宁.基于各向异性扩散的弱小目标增强算法[J].光电工程, 2008, 35(6): 15–19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdgc200806004
Wang Yanhua, Liu Weining. Dim target enhancement algorithm for low-contrast image based on anisotropic diffusion[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2008, 35(6): 15–19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdgc200806004
[12] 李正周, 董能力, 金钢, 等.基于自适应滤波的强起伏背景下弱小目标检测[J].仪器仪表学报, 2004, 25(S1): 663–665. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYF200408001283.htm
Li Zhengzhou, Dong Nengli, Jin Gang, et al. Dim small target detection in strong undulant clutter background based on adaptive filter[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2004, 25(S1): 663–665. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYF200408001283.htm
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载:




