-
摘要:
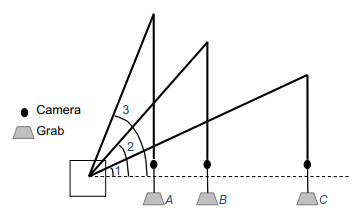
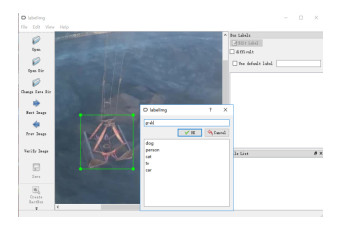
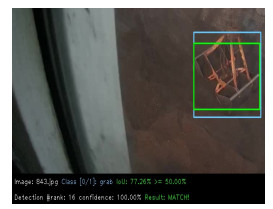
在港口门机抓斗装卸干散货的作业过程中,人眼观察无法精确判断抓斗所在位置,会带来工作效率低下及安全性等问题。为解决该问题首次提出了一种基于深度学习的门机抓斗检测方法。利用改进的深度卷积神经网络YOLOv3-tiny对抓斗数据集进行训练及测试,进而学习其内部特征表示。实验结果表明,基于深度学习的门机抓斗检测方法可实现门机抓斗检测速度每秒45帧,召回率高达95.78%,在很好满足检测实时性与准确性的同时,提高了工业现场作业的安全性及效率。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to solve the problems of low work efficiency and safety caused by the inability of human eyes to accurately determine the position of the grab during the loading and unloading of dry bulk cargo by portal crane, a method of grab detection based on deep learning is proposed for the first time. The improved deep convolution neural network (YOLOv3-tiny) is used to train and test on the data set of grab, and then to learn its internal feature representation. The experimental results show that the detection method based on deep learning can achieve a detection speed of 45 frames per second and a recall rate of 95.78%. It can meet the real-time and accuracy of detection, and improve the safety and efficiency of work in the industrial field.
-
Key words:
- grab detection /
- deep learning /
- YOLOv3-tiny /
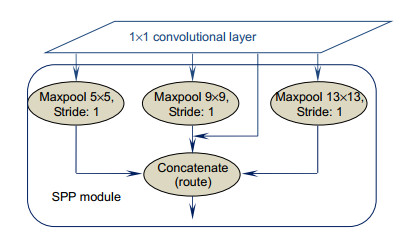
- SPP /
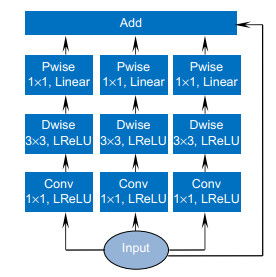
- inverted residual group /
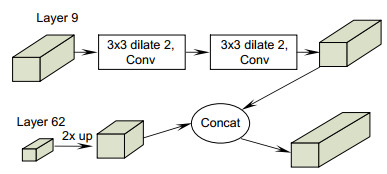
- dilated convolution
-

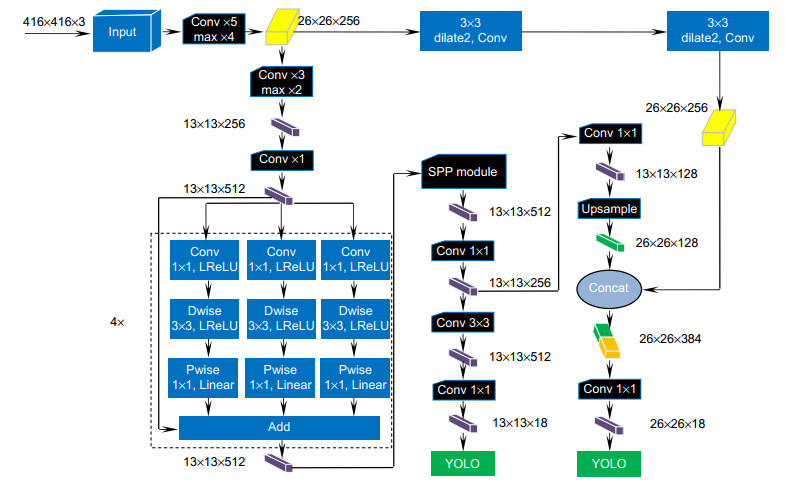
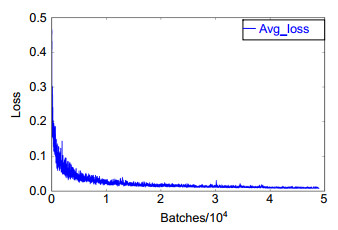
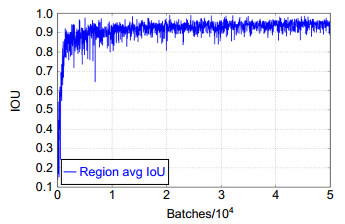
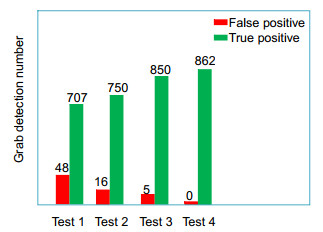
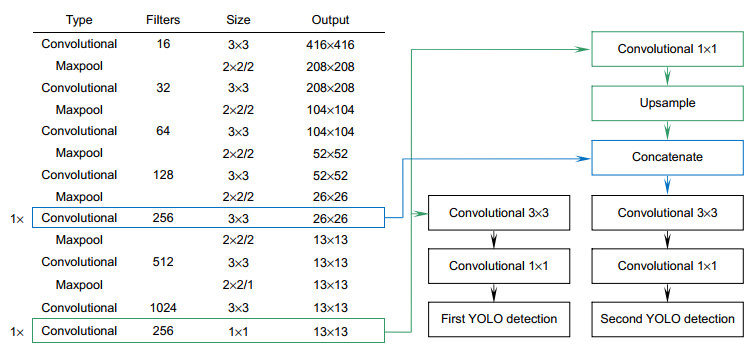
Overview: In recent years, with the vigorous development of the port industry, the port throughput is increasing, and the demand for loading and unloading dry bulk cargo is also increasing. At present, the method adopted is mainly man-made operation. The driver sits in the cab of the gantry crane, and observes whether the grab reaches the proper position to grab or release the dry bulk by naked eyes, and judges when to lower or raise the steel wire rope on the grab. Then there will be the following problems: first, because the human eyes are far away from the goods, the wire rope is easy to be over released when the driver releases the grab. A few seconds are wasted in one operation cycle, and a lot of time is wasted and a lot of idle work is produced in multiple operation cycles. Second, the driver's long-term operation will lead to eyestrain, which will lead to misjudgment and over the release. It is not conducive to the development of the enterprise, because, in addition to time-consuming and labor-consuming, it will increase the input cost of the company. So how to accurately detect the position of grab and make it more efficient to load and unload cargo has become an urgent problem for the port industry. In order to solve the problems of low work efficiency and safety caused by the inability of human eyes to accurately determine the position of the grab during the loading and unloading of dry bulk cargo by portal crane, a method of grab detection based on deep learning is proposed for the first time. The improved deep convolution neural network (YOLOv3-tiny) is used to train and test on the data set of grab, and then to learn its internal feature representation. The experimental results show that the detection method based on deep learning can achieve a detection speed of 45 frames per second, a recall rate of 95.78%, and a false detection rate of 0. Although the accuracy of detection is lower than Faster RCNN, the detection speed is 225 times faster than Faster RCNN. Compared with the original model YOLOv3-tiny, the detection speed of the improved network model in this paper is slightly reduced, but the detection accuracy has been greatly improved. Through the contrast test, we can see that the YOLOv3 network model is not as good as the improved network in the two indicators of mAP and FPS. Therefore, for the real-time detection task of gantry crane grab, the improved model in this paper performs better. It can meet the real-time and accuracy of detection, and improve the safety and efficiency of work in the industrial field.
-

-
表 1 网络参数表
Table 1. The table of network parameter
参数名 学习率 迭代次数 批量大小 动量 权重衰减 旋转角度 饱和度 曝光量 色调 抖动因子 参数值 0.001 50000 60 0.9 0.0005 3 1.5 1.5 0.1 0.3 表 2 实验结果对比表
Table 2. Comparison table of experimental results
Model Precision/% Recall/% Time/s mAP/% YOLOv3-tiny 93.64 78.56 5.203 78.57 YOLOv3-tiny-SPP 97.91 83.33 5.982 86.03 YOLOv3-tiny-group 99.42 94.44 6.953 95.71 YOLOv3-tiny-new 100 95.78 6.959 96.25 表 3 性能对比表
Table 3. Comparison table of performance
Model FPS mAP/% YOLOv3-tiny 66 78.57 YOLOv3 23 94.91 YOLOv3-tiny-new 45 96.25 Faster RCNN 0.2 97.31 -
[1] 陈英明. 中国港口现状及未来走势[J]. 中国水运, 2019(6): 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHOG201906004.htm
Chen Y M. Current situation and future trend of Chinese ports[J]. China Water Transp, 2019(6): 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHOG201906004.htm
[2] 邢小健. 对国内港口散货装卸行业的一些思考[J]. 起重运输机械, 2019(10): 1. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QZJJ201910001.htm
Xing X J. Some thoughts on bulk cargo handling industry of domestic port[J]. Hoist Con Mach, 2019(10): 1. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QZJJ201910001.htm
[3] 季本山. 现代门机抓斗控制程序的设计[J]. 南通航运职业技术学院学报, 2012, 11(4): 76–79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NTHY201204023.htm
Ji B S. A study on the design of grab bucket control program[J]. J Nantong Vocational Tech Shipping Coll, 2012, 11(4): 76–79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NTHY201204023.htm
[4] 姚筑宇. 基于深度学习的目标检测研究与应用[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2019.
Yao Z Y. Research on the application of object detection technology based on deep learning algorithm[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019.
[5] Manana M, Tu C L, Owolawi P A. A survey on vehicle detection based on convolution neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications, 2017: 1751–1755.
[6] 戴伟聪, 金龙旭, 李国宁, 等. 遥感图像中飞机的改进YOLOv3实时检测算法[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(12): 180350. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180350 http://www.oejournal.org/J/OEE/Article/Details/A181130000018/CN
Dai W C, Jin L X, Li G N, et al. Real-time airplane detection algorithm in remote-sensing images based on improved YOLOv3[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(12): 180350. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180350 http://www.oejournal.org/J/OEE/Article/Details/A181130000018/CN
[7] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]// Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 580–587.
[8] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1440–1448.
[9] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]// Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 91–99.
[10] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 779–788.
[11] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[Z]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018.
[12] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2014, 37(9): 1904–1916. http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
[13] Howard A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[Z]. arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017.
[14] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 936–944.
[15] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 770–778.
[16] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[Z]. arXiv: 1502.03167, 2015.
[17] LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker J S, et al. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Comput, 1989, 1(4): 541–551.
[18] Maas A L, Hannum A Y, Ng A Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2013.
[19] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M L, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 4510–4520.
[20] Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[Z]. arXiv: 1511.07122, 2015.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: