| Citation: | Zhang Z, Li GY, Liu YL et al. Robust measurement of orbital angular momentum of a partially coherent vortex beam under amplitude and phase perturbations. Opto-Electron Sci 3, 240001 (2024). doi: 10.29026/oes.2024.240001 |
Robust measurement of orbital angular momentum of a partially coherent vortex beam under amplitude and phase perturbations
-
Abstract
The ability to overcome the negative effects, induced by obstacles and turbulent atmosphere, is a core challenge of long-distance information transmission, and it is of great significance in free-space optical communication. The spatial-coherence structure, that characterizes partially coherent fields, provides a new degree of freedom for carrying information. However, due to the influence of the complex transmission environment, the spatial-coherence structure is severely damaged during the propagation path, which undoubtedly limits its ability to transmit information. Here, we realize the robust far-field orbital angular momentum (OAM) transmission and detection by modulating the spatial-coherence structure of a partially coherent vortex beam with the help of the cross-phase. The cross-phase enables the OAM information, quantified by the topological charge, hidden in the spatial-coherence structure can be stably transmitted to the far field and can resist the influence of obstructions and turbulence within the communication link. This is due to the self-reconstruction property of the spatial-coherence structure embedded with the cross-phase. We demonstrate experimentally that the topological charge information can be recognized well by measuring the spatial-coherence structure in the far field, exhibiting a set of distinct and separated dark rings even under amplitude and phase perturbations. Our findings open a door for robust optical signal transmission through the complex environment and may find application in optical communication through a turbulent atmosphere. -

-
References
[1] Gbur GJ. Singular Optics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2017). [2] Willner AE, Huang H, Yan Y et al. Optical communications using orbital angular momentum beams. Adv Opt Photonics 7, 66 (2015). doi: 10.1364/AOP.7.000066 [3] He H, Friese MEJ, Heckenberg NR et al. Direct observation of transfer of angular momentum to absorptive particles from a laser beam with a phase singularity. Phys Rev Lett 75, 826–829 (1995). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.826 [4] Paterson L, MacDonald MP, Arlt J et al. Controlled rotation of optically trapped microscopic particles. Science 292, 912–914 (2001). doi: 10.1126/science.1058591 [5] Yang YJ, Ren YX, Chen MZ et al. Optical trapping with structured light: a review. Adv Photonics 3, 034001 (2021). doi: 10.1117/1.AP.3.3.034001 [6] Tamburini F, Anzolin G, Umbriaco G et al. Overcoming the rayleigh criterion limit with optical vortices. Phys Rev Lett 97, 163903 (2006). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.163903 [7] Qiu XD, Li FS, Zhang WH et al. Spiral phase contrast imaging in nonlinear optics: seeing phase objects using invisible illumination. Optica 5, 208–212 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.000208 [8] Lavery MPJ, Speirits FC, Barnett SM et al. Detection of a spinning object using light's orbital angular momentum. Science 341, 537–540 (2013). doi: 10.1126/science.1239936 [9] Kong LJ, Zhang WX, Li P et al. High capacity topological coding based on nested vortex knots and links. Nat Commun 13, 2705 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30381-w [10] Wen YH, Chremmos I, Chen YJ et al. Arbitrary multiplication and division of the orbital angular momentum of light. Phys Rev Lett 124, 213901 (2020). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.213901 [11] Fang XY, Ren HR, Gu M. Orbital angular momentum holography for high-security encryption. Nat Photonics 14, 102–108 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0560-x [12] Andrews LC, Phillips RL. Laser Beam Propagation through Random Media 2nd ed (SPIE Press, Bellingham, 2005). [13] Popoff S, Lerosey G, Fink M et al. Image transmission through an opaque material. Nat Commun 1, 81 (2010). doi: 10.1038/ncomms1078 [14] Zeng J, Liu XL, Zhao CL et al. Spiral spectrum of a Laguerre-Gaussian beam propagating in anisotropic non-Kolmogorov turbulent atmosphere along horizontal path. Opt Express 27, 25342–25356 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.025342 [15] Ricklin JC, Davidson FM. Atmospheric turbulence effects on a partially coherent Gaussian beam: implications for free-space laser communication. J Opt Soc Am A 19, 1794–1802 (2002). [16] Wang F, Chen YH, Liu XL et al. Self-reconstruction of partially coherent light beams scattered by opaque obstacles. Opt Express 24, 23735–23746 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OE.24.023735 [17] Korotkova O, Gbur G. Applications of optical coherence theory. Prog Opt 65, 43–104 (2020). [18] Chen YH, Ponomarenko SA, Cai YJ. Experimental generation of optical coherence lattices. Appl Phys Lett 109, 061107 (2016). doi: 10.1063/1.4960966 [19] Liu XL, Shen Y, Liu L et al. Experimental demonstration of vortex phase-induced reduction in scintillation of a partially coherent beam. Opt Lett 38, 5323–5326 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OL.38.005323 [20] Wang HT, Wang H, Ruan QF et al. Coloured vortex beams with incoherent white light illumination. Nat Nanotechnol 18, 264–272 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41565-023-01319-0 [21] Yang GL, Su JH, Li Y et al. A study of resolution improvement in Noncoherent optical coherence imaging. Adv Math Phys 2022, 3232323 (2022). [22] Zhao CL, Cai YJ. Trapping two types of particles using a focused partially coherent elegant Laguerre-Gaussian beam. Opt Lett 36, 2251–2253 (2011). doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002251 [23] Chen YH, Wang F, Cai YJ. Partially coherent light beam shaping via complex spatial coherence structure engineering. Adv Phys X 7, 2009742 (2022). [24] Bai YH, Lv HR, Fu X et al. Vortex beam: generation and detection of orbital angular momentum [Invited]. Chin Opt Lett 20, 012601 (2022). doi: 10.3788/COL202220.012601 [25] Liu XL, Zeng J, Cai YJ. Review on vortex beams with low spatial coherence. Adv Phys X 4, 1626766 (2019). doi: 10.1080/23746149.2019.1626766 [26] Zhao CL, Wang F, Dong Y et al. Effect of spatial coherence on determining the topological charge of a vortex beam. Appl Phys Lett 101, 261104 (2012). doi: 10.1063/1.4773236 [27] Yang YJ, Mazilu M, Dholakia K. Measuring the orbital angular momentum of partially coherent optical vortices through singularities in their cross-spectral density functions. Opt Lett 37, 4949–4951 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004949 [28] Liu RF, Wang FR, Chen DX et al. Measuring mode indices of a partially coherent vortex beam with Hanbury brown and Twiss type experiment. Appl Phys Lett 108, 051107 (2016). doi: 10.1063/1.4941422 [29] Liu XL, Wu TF, Liu L et al. Experimental determination of the azimuthal and radial mode orders of a partially coherent LGpl beam. Chin Opt Lett 3, 030002 (2017). doi: 10.3788/COL201715.030002 [30] Liu YL, Chen YH, Wang F et al. Robust far-field imaging by spatial coherence engineering. Opto-Electron Adv 4, 210027 (2021). doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.210027 [31] Liu YL, Zhang X, Dong Z et al. Robust far-field optical image transmission with structured random light beams. Phys Rev Appl 17, 024043 (2022). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.17.024043 [32] Liu XL, Peng XF, Liu L et al. Self-reconstruction of the degree of coherence of a partially coherent vortex beam obstructed by an opaque obstacle. Appl Phys Lett 110, 181104 (2017). doi: 10.1063/1.4982786 [33] Peng XF, Liu L, Wang F et al. Twisted Laguerre-Gaussian Schell-model beam and its orbital angular moment. Opt Express 26, 33956–33969 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OE.26.033956 [34] Gbur G, Tyson RK. Vortex beam propagation through atmospheric turbulence and topological charge conservation. J Opt Soc Am A 25, 225–230 (2008). doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.25.000225 [35] Li JH, Zeng J, Duan ML. Classification of coherent vortices creation and distance of topological charge conservation in non-Kolmogorov atmospheric turbulence. Opt Express 23, 11556–11565 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OE.23.011556 [36] Yu JY, Huang Y, Wang F et al. Scintillation properties of a partially coherent vector beam with vortex phase in turbulent atmosphere. Opt Express 27, 26676–26688 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.026676 [37] Liang G, Wang Q. Controllable conversion between Hermite Gaussian and Laguerre Gaussian modes due to cross phase. Opt Express 27, 10684–10691 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OE.27.010684 [38] Wan LP, Zhao DM. Controllable rotating Gaussian Schell-model beams. Opt Lett 44, 735–738 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OL.44.000735 [39] Ren Y, Wang C, Liu T et al. Polygonal shaping and multi-singularity manipulation of optical vortices via high-order cross-phase. Opt Express 28, 26257–26266 (2020). doi: 10.1364/OE.397345 [40] Xin L, Li ZQ, Monfared YE et al. Flexible autofocusing properties of ring Pearcey beams by means of a cross phase. Opt Lett 46, 70–73 (2021). doi: 10.1364/OL.413380 [41] Simon R, Mukunda N. Twist phase in Gaussian-beam optics. J Opt Soc Am A 15, 2373–2382 (1998). doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.15.002373 [42] Xu ZH, Liu XL, Chen YH et al. Self-healing properties of Hermite-Gaussian correlated Schell-model beams. Opt Express 28, 2828–2837 (2020). doi: 10.1364/OE.383805 [43] Mandel L, Wolf E. Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1995). [44] Ma PJ, Kacerovská B, Khosravi R et al. Numerical approach for studying the evolution of the degrees of coherence of partially coherent beams propagation through an ABCD optical system. Appl Sci 9, 2084 (2019). doi: 10.3390/app9102084 [45] Peng DM, Huang ZF, Liu YL et al. Optical coherence encryption with structured random light. PhotoniX 2, 6 (2021). doi: 10.1186/s43074-021-00027-z [46] Zhang Z, Liu ZZ, Liu X et al. Measuring the orbital angular momentum of a vortex beam under extremely low coherence. Appl Phys Lett 122, 011101 (2023). doi: 10.1063/5.0127582 [47] Liu X, Chen Q, Zeng J et al. Measurement of optical coherence structures of random optical fields using generalized Arago spot experiment. Opto-Electron Sci 2, 220024 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oes.2023.220024 [48] Wang F, Cai YJ. Experimental observation of fractional Fourier transform for a partially coherent optical beam with Gaussian statistics. J Opt Soc Am A 24, 1937–1944 (2007). doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.24.001937 [49] Vallone G, D’Ambrosio V, Sponselli A et al. Free-space quantum key distribution by rotation-invariant twisted photons. Phys Rev Lett 113, 060503 (2014). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.060503 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Robust measurement of orbital angular momentum of a partially coherent vortex beam under amplitude and phase perturbations 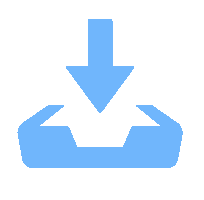
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram probing the OAM of a partially coherent optical vortex via a cross-phase.
-
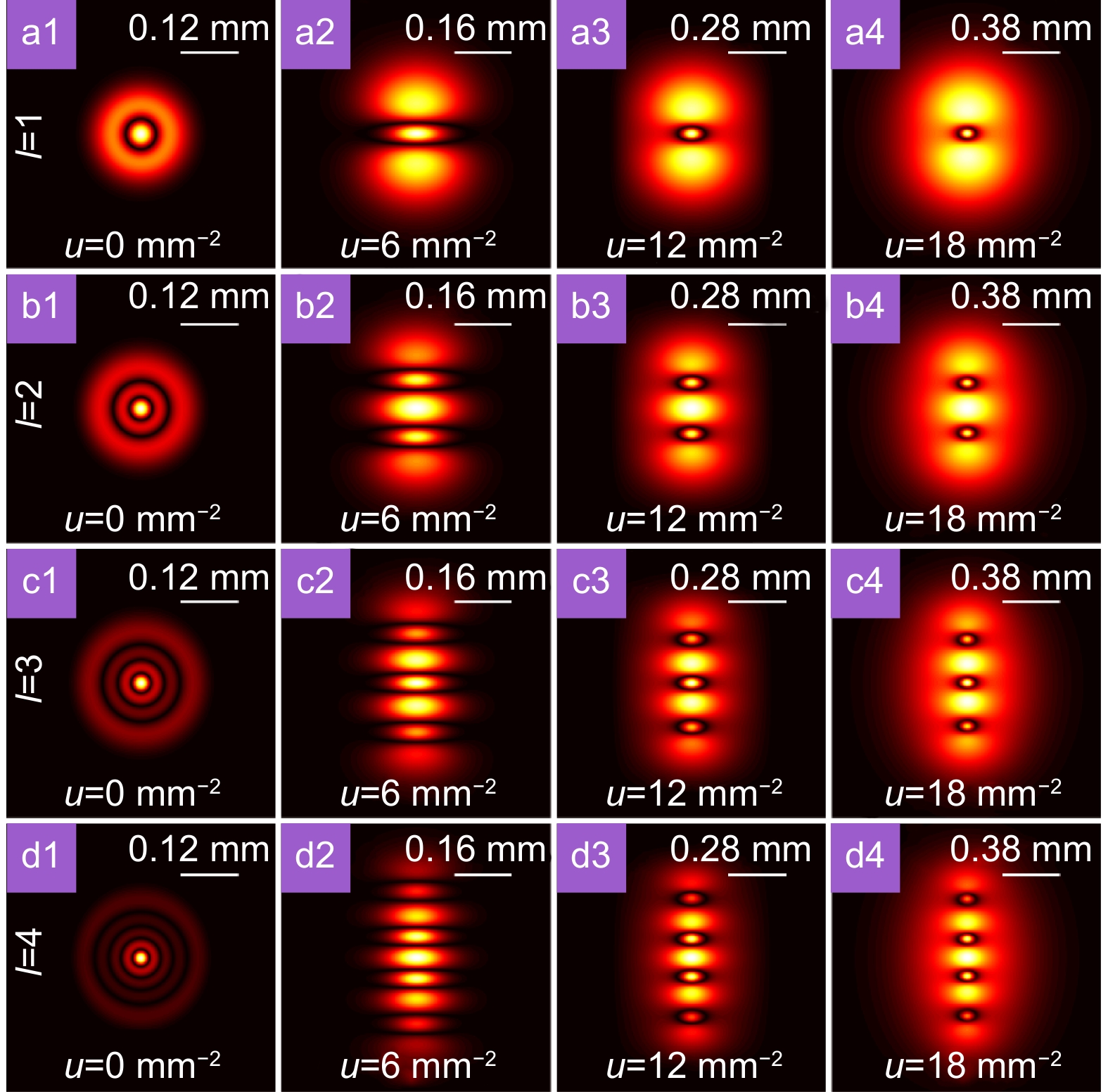
Figure 2.
The evolution for the modulus of the degree of coherence of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam carrying different topological charges in the focal plane versus the values of u.
-
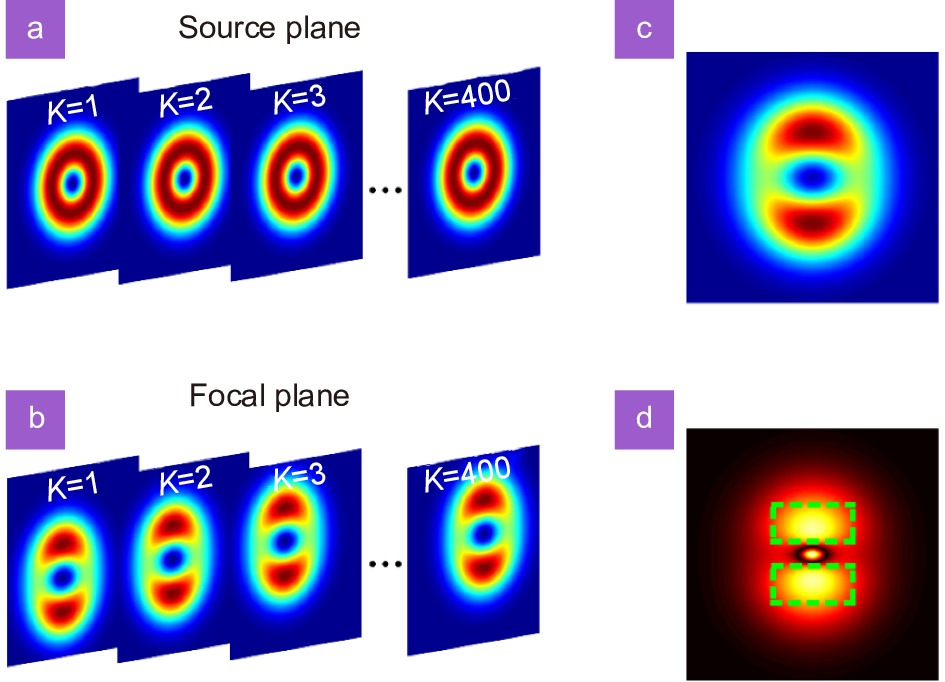
Figure 3.
The schematic diagram of the pseudo-mode superposition principle and cross-phase induced spatial-coherence structure splitting. (a) The intensity distribution of each individual Laguerre Gaussian sub-mode embedded with cross-phase for u=12 mm−2 and l=1 in the source plane. (b) The intensity distribution of each individual Laguerre Gaussian sub-mode embedded with cross-phase for u=12 mm−2 and l=1 in the focal plane. (c) The average intensity of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam embedded with cross-phase for u=12 mm−2 and l=1 in the focal plane. (d) The distribution of modulus of the degree of coherence of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam embedded with cross-phase for u=12 mm−2 and l=1 in the focal plane. The green line is used to mark the main lobe structure.
-
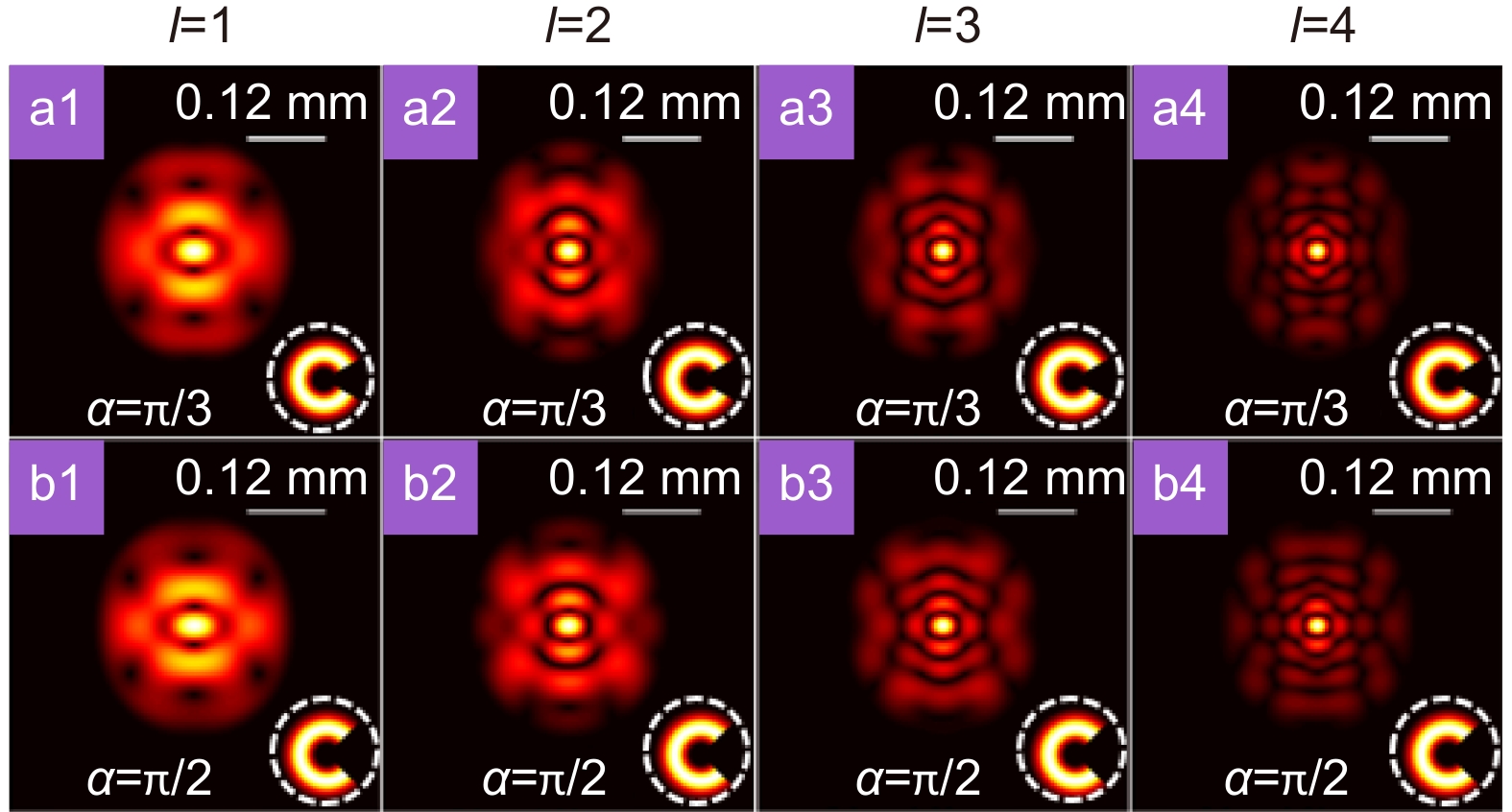
Figure 4.
The distributions of modulus of the degree of coherence of partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beams without cross-phase in the focal plane when obstacles with different occlusion angles α are placed in the source plane. The illustrations in the lower right corner represents the corresponding intensity distribution in the source plane when obstacles with different occlusion angles α are placed in the source plane.
-
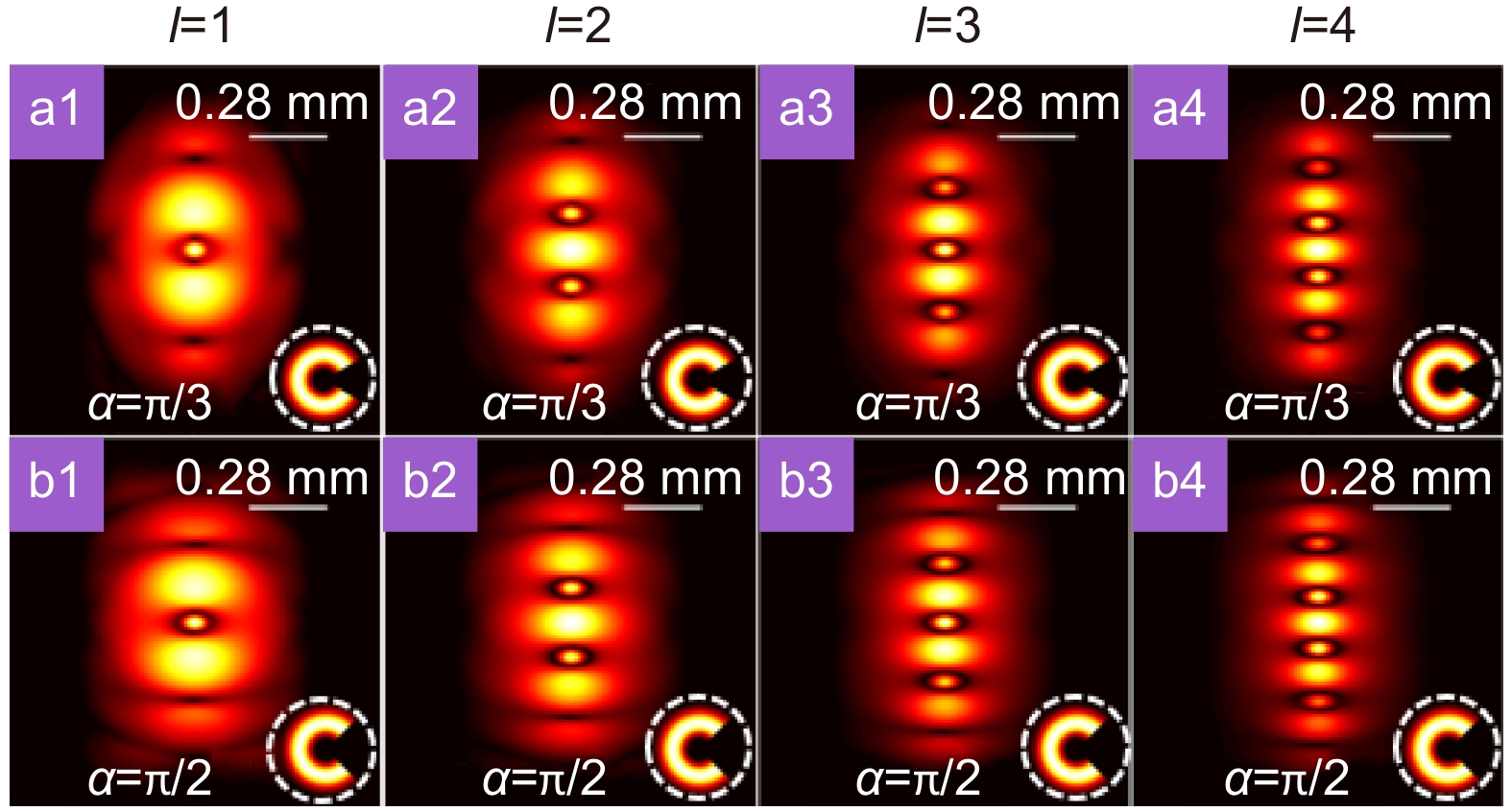
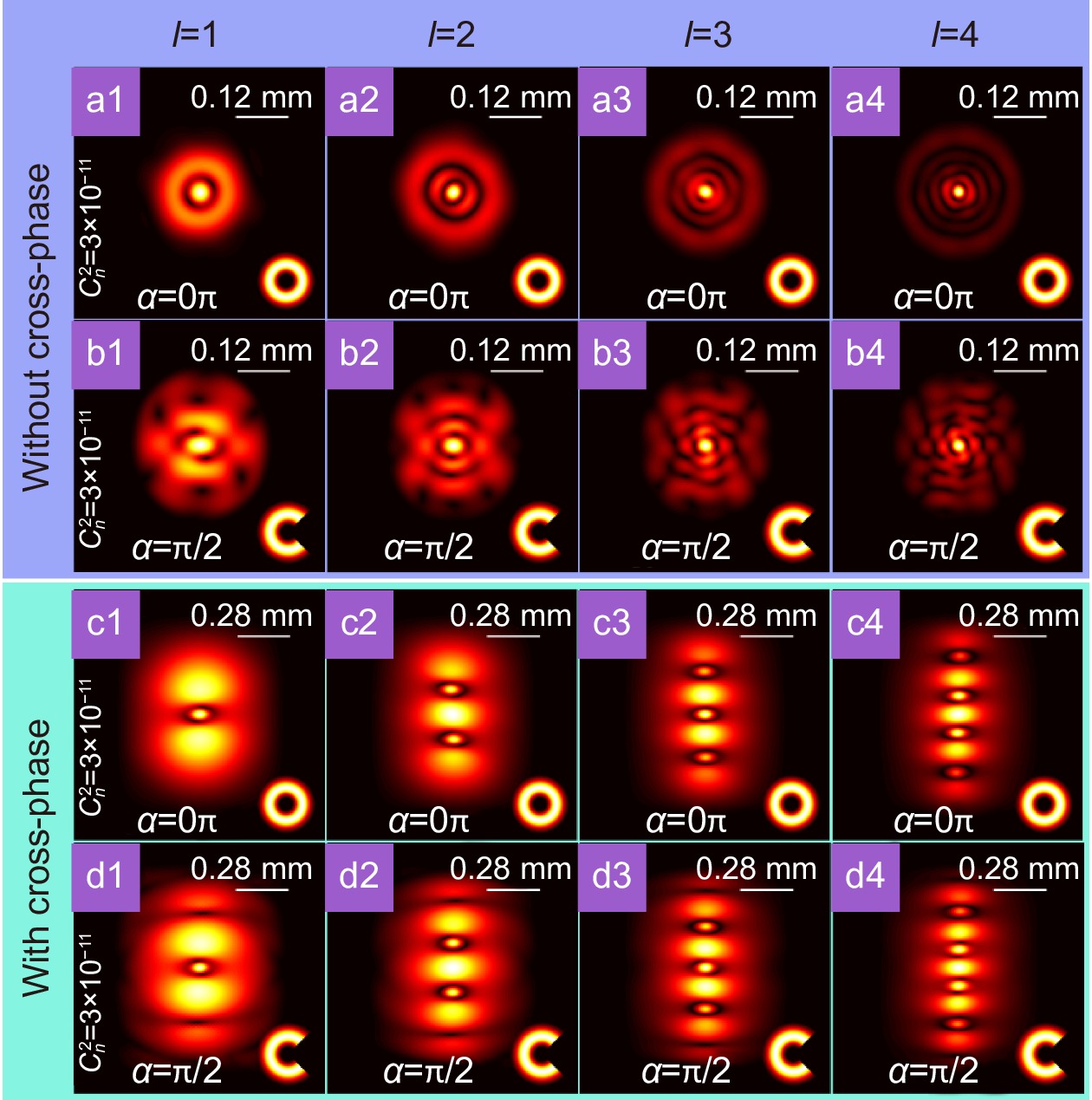
Figure 5.
The distributions of modulus of the degree of coherence of partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beams with cross-phase (u=12 mm−2) in the focal plane when obstacles with different occlusion angles α are placed in the source plane. The illustrations in the lower right corner represents the corresponding intensity distributions in the source plane when obstacles with different occlusion angles α are placed in the source plane.
-
Figure 6.
(a1–a4) The distributions of modulus of the degree of coherence of partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beams without cross-phase in the focal plane in the presence of turbulence. (b1–b4) The distributions of modulus of the degree of coherence partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beams without cross-phase in the focal plane in the presence of an obstacle with occlusion angle α=π/2 and turbulence. (c1–c4) The distributions of modulus of the degree of coherence of partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beams with cross-phase in the focal plane in the presence of turbulence. (d1–d4) The distributions of modulus of the degree of coherence of partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beams with cross-phase in the focal plane in the presence of an obstacle with occlusion angle α=π/2 and turbulence. The illustrations in the lower right corner represents the corresponding intensity distributions in the source plane obstructed by obstacles with different occlusion angles α.
-
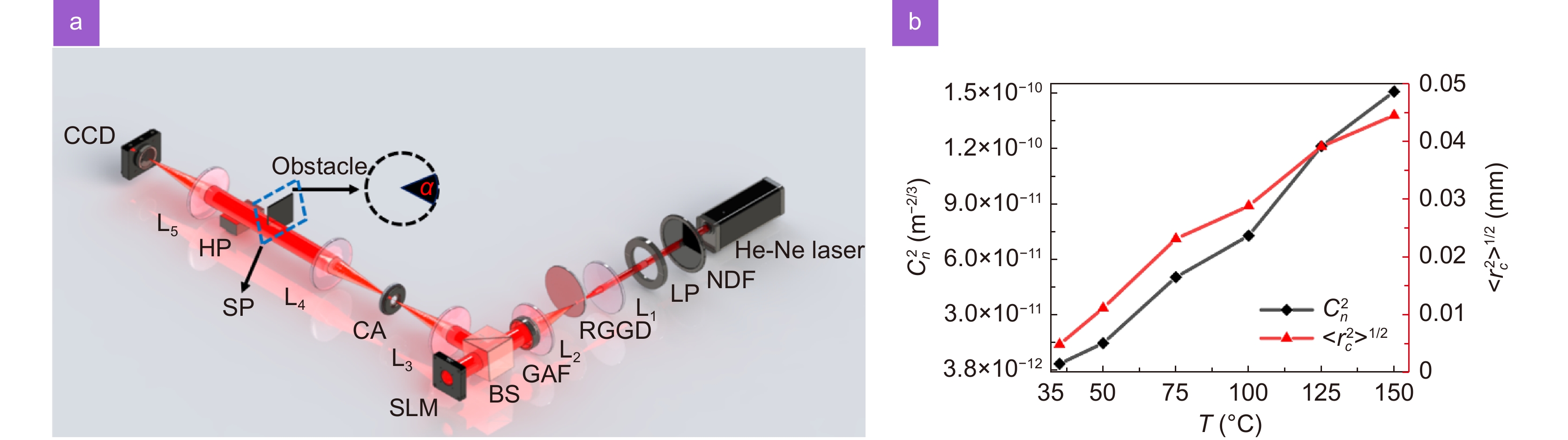
Figure 7.
(a) Experiment setup for the generation of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam with a controllable cross-phase and the measurement of the distribution of modulus of the degree of coherence of this beam, when obstructed by an obstacle in the far field propagation in free space (without hot plate) as well as in a turbulent atmosphere (with hot plate). Laser, a He-Ne laser with wavelength 632.8 nm; NDF, neutral density filter; LP, linear polarizer; RGGD, rotating ground glass disk; L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, thin lenses; GAF, Gaussian amplitude filter; BS, beam splitter; SLM, spatial light modulator; CA, circular aperture; SP, source plane; HP, hot plate; CCD, charge-coupled device. (b) Measured atmospheric refractive index structure constant
$ {\text{C}}_{\text{n}}^{\text{2}} $ $ {\left\langle {{\text{r}}_{\text{c}}^{\text{2}}} \right\rangle ^{\text{1/2}}} $ -
Figure 8.
The experimental results for the modulus of the degree of coherence of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam carrying a cross-phase for u=12 mm−2 in the focal plane. (a1–a4) The experimental results for the cases with different topological charges l when the obstacle is removed. (b1–b4) The experimental results for the cases with different topological charges l when the obstacle with occlusion angle α=π/3 is placed in the source plane. (c1–c4) The experimental results for the cases with different topological charges l when the obstacle with occlusion angle α=π/2 is placed in the source plane.
-
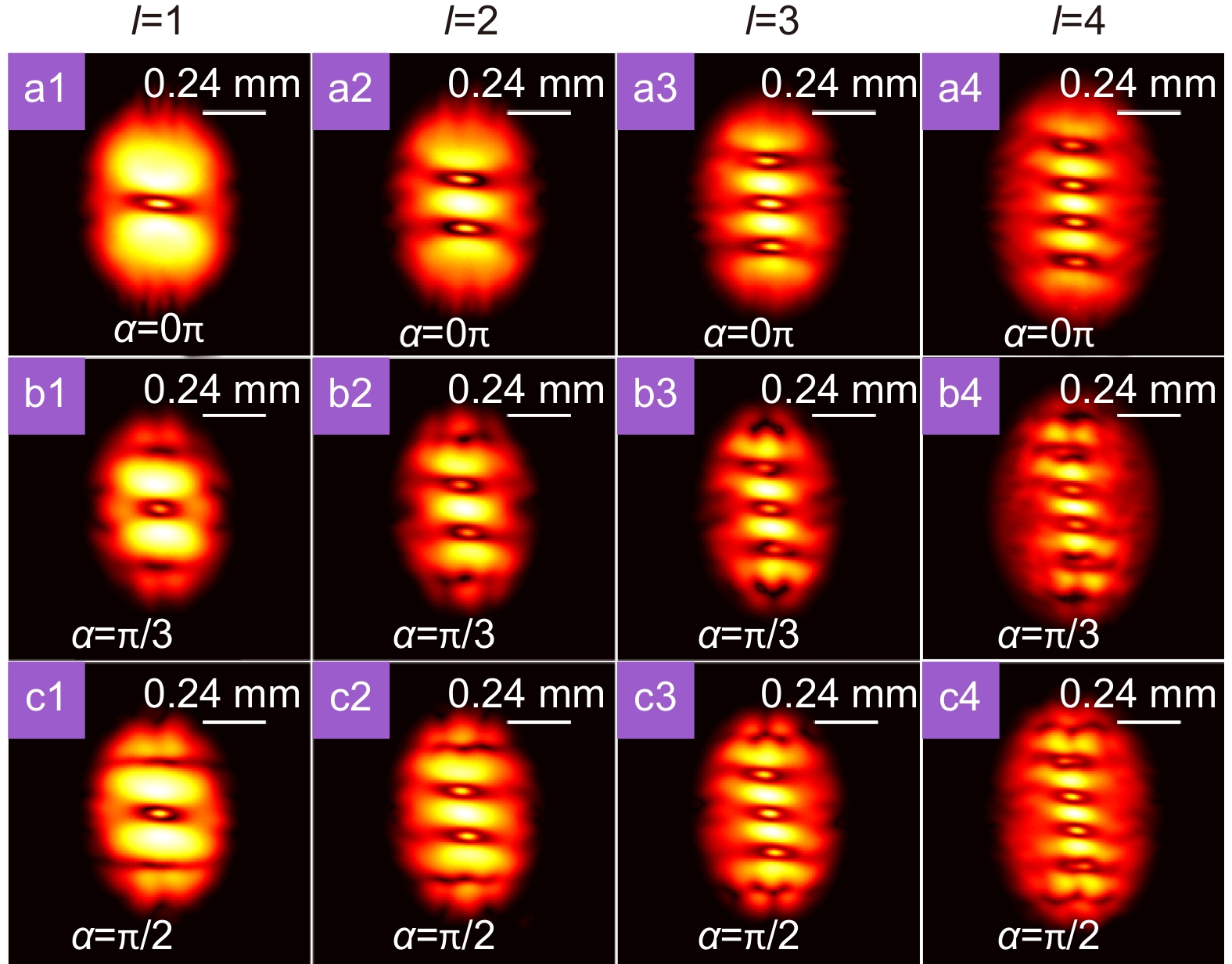
Figure 9.
Experimental results for the effect of the obstacle and turbulence on the modulus of the degree of coherence of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam carrying a cross-phase in the focal plane for u=12 mm−2. (a1–a4) The experimental results for the cases in the presence of turbulence with temperature T=50 °C when the obstacle is removed. (b1–b4) The experimental results for the cases in the presence of turbulence with temperature T=50 °C when the obstacle with occlusion angle α=π/3 is placed in the source plane. (c1–c4) The experimental results for the cases in the presence of turbulence with temperature T=50 °C when the obstacle with occlusion angle α=π/2 is placed in the source plane.
-
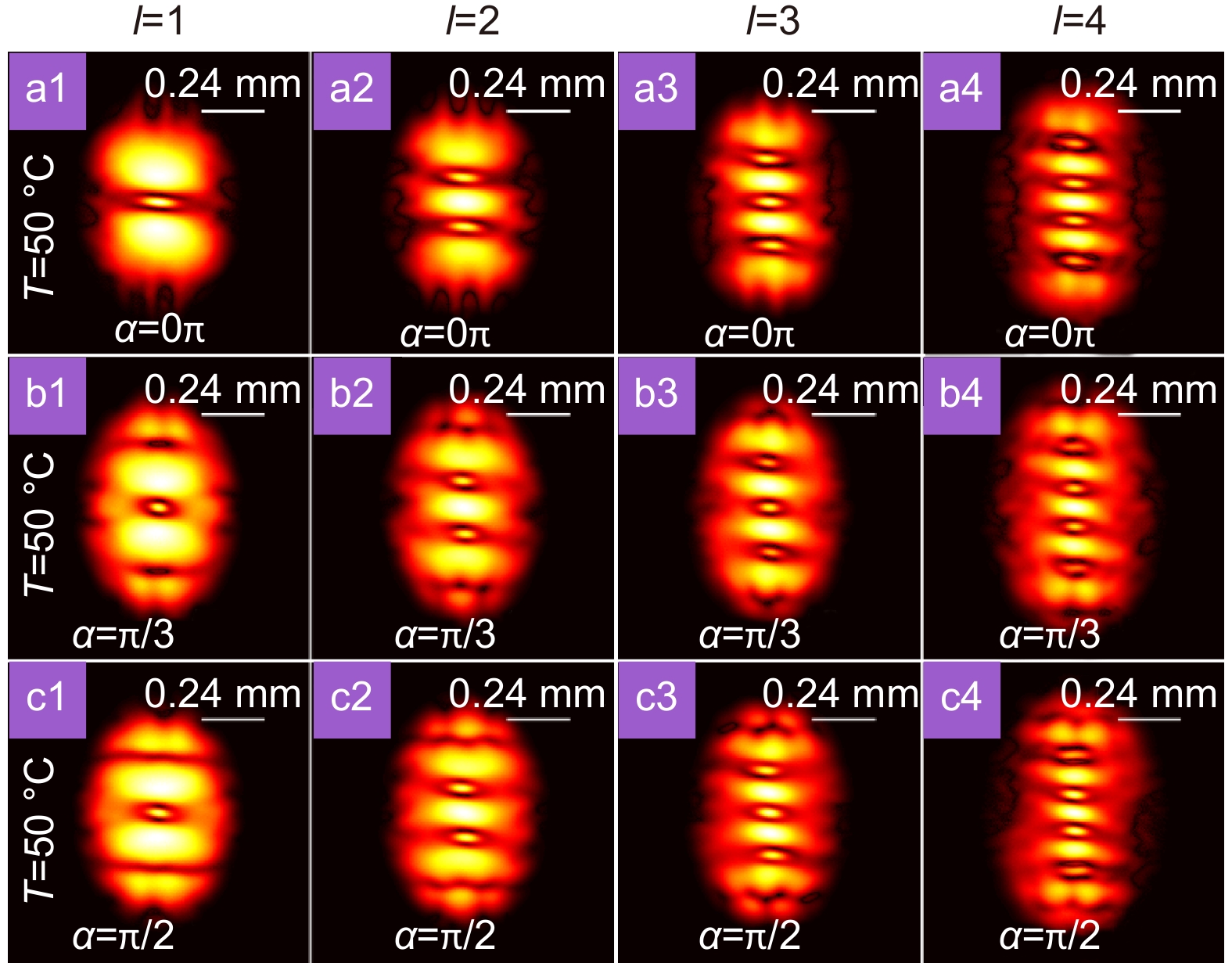
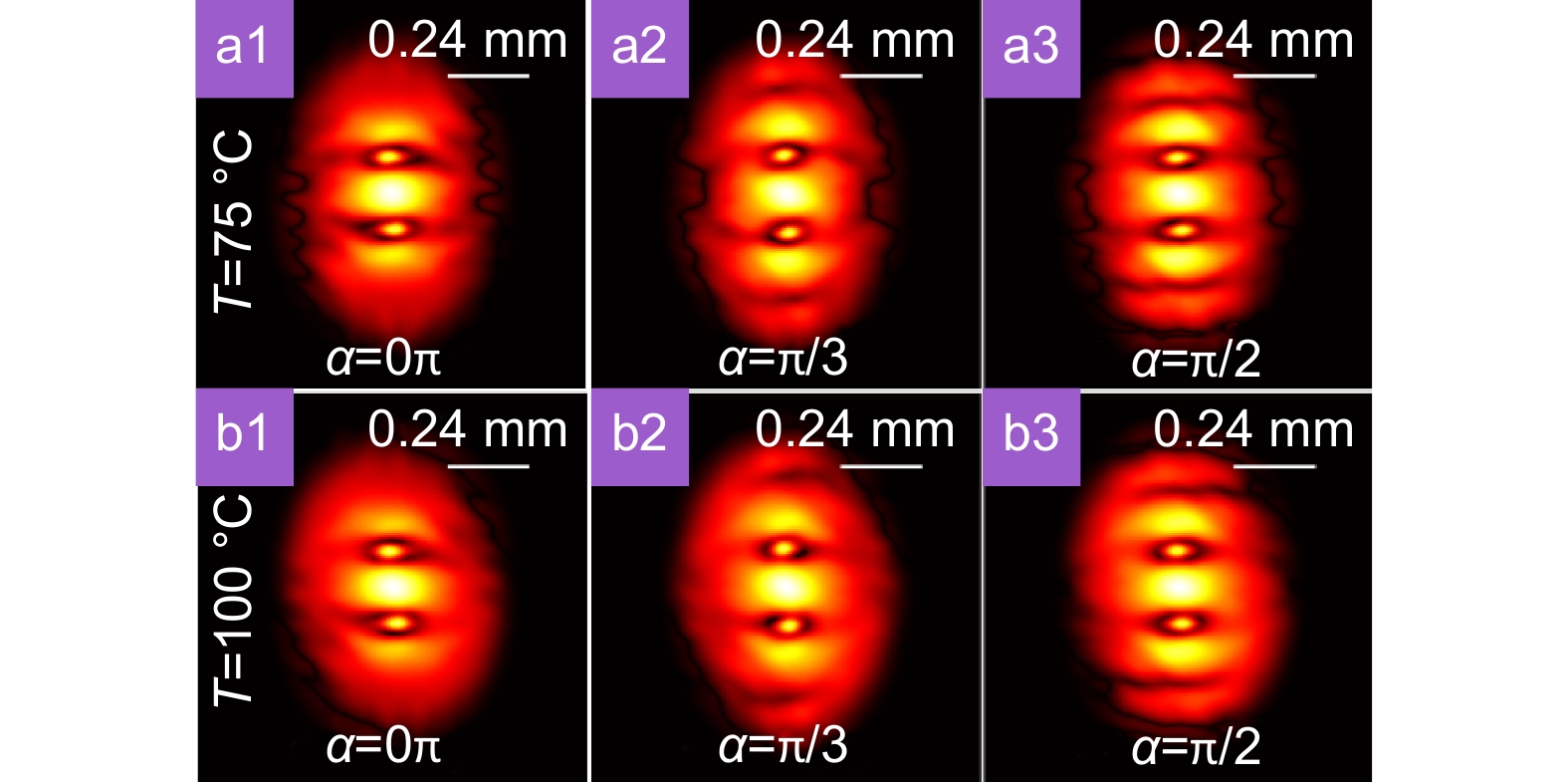
Figure 10.
Experimental results for the effect of the temperature on the modulus of the degree of coherence of a partially coherent Laguerre Gaussian beam carrying a cross-phase for l=2 and u=12 mm−2 in the focal plane. (a1–a3) The experimental results for the cases in the presence of turbulence with temperature T=75 °C when obstacles with different occlusion angles α are placed in the source plane. (b1–b3) The experimental results for the cases in the presence of turbulence with temperature T=100 °C when obstacles with different occlusion angles α are placed in the source plane.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: