| Citation: | Wang XY, Qiu XK, Liu ML et al. Flat soliton microcomb source. Opto-Electron Sci 2, 230024 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oes.2023.230024 |
-
Abstract
Mode-locked microcombs with flat spectral profiles provide the high signal-to-noise ratio and are in high demand for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)-based applications, particularly in future high-capacity communication and parallel optical computing. Here, we present two solutions to generate local relatively flat spectral profiles. One microcavity with ultra-flat integrated dispersion is pumped to generate one relatively flat single soliton source spanning over 150 nm. Besides, one extraordinary soliton crystal with single vacancy demonstrates the local relatively flat microcomb lines when the inner soliton spacings are slightly irregular. Our work paves a new way for soliton-based applications owing to the relatively flat spectral characteristics. -

-
References
[1] Akhmediev N, Ankiewicz A. Dissipative Solitons (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005). [2] Chang L, Liu ST, Bowers JE. Integrated optical frequency comb technologies. Nat Photonics 16, 95–108 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41566-021-00945-1 [3] Gaeta AL, Lipson M, Kippenberg TJ. Photonic-chip-based frequency combs. Nat Photonics 13, 158–169 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0358-x [4] Kippenberg TJ, Gaeta AL, Lipson M, Gorodetsky ML. Dissipative Kerr solitons in optical microresonators. Science 361, eaan8083 (2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aan8083 [5] Runge AFJ, Hudson DD, Tam KKK, de Sterke CM, Blanco-Redondo A. The pure-quartic soliton laser. Nat Photonics 14, 492–497 (2020). [6] Grelu P, Akhmediev N. Dissipative solitons for mode-locked lasers. Nat Photonics 6, 84–92 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.345 [7] Marpaung D, Yao JP, Capmany J. Integrated microwave photonics. Nat Photonics 13, 80–90 (2019). [8] Riemensberger J, Lukashchuk A, Karpov M, Weng WL, Lucas E et al Massively parallel coherent laser ranging using a soliton microcomb. Nature 581, 164–170 (2020). [9] Suh MG, Vahala KJ. Soliton microcomb range measurement. Science 359, 884–887 (2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aao1968 [10] Trocha P, Karpov M, Ganin D, Pfeiffer MHP, Kordts A et al. Ultrafast optical ranging using microresonator soliton frequency combs. Science 359, 887–891 (2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aao3924 [11] Suh MG, Yang QF, Yang KY, Yi X, Vahala KJ. Microresonator soliton dual-comb spectroscopy. Science 354, 600–603 (2016). doi: 10.1126/science.aah6516 [12] Dutt A, Joshi C, Ji XC, Cardenas J, Okawachi Y et al. On-chip dual comb source for spectroscopy. Sci Adv 4, e1701858 (2018). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701858 [13] Xu BX, Fan XY, Wang S, He ZY. Sub-femtometer-resolution absolute spectroscopy with sweeping electro-optic combs. Opto-Electron Adv 5, 210023 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.210023 [14] Raja AS, Lange S, Karpov M, Shi K, Fu X et al. Ultrafast optical circuit switching for data centers using integrated soliton microcombs. Nat Commun 12, 5867 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25841-8 [15] Feldmann J, Youngblood N, Karpov M, Gehring H, Li X et al. Parallel convolutional processing using an integrated photonic tensor core. Nature 589, 52–58 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03070-1 [16] Xu XY, Tan MX, Corcoran B, Wu JY, Boes A et al. 11 TOPS photonic convolutional accelerator for optical neural networks. Nature 589, 44–51 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03063-0 [17] Wang XY, Xie P, Chen BH, Zhang XC. Chip-based high-dimensional optical neural network. Nano-Micro Lett 14, 221 (2022). doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00957-8 [18] Rizzo A, Novick A, Gopal V, Kim BY, Ji XC et al. Massively scalable Kerr comb-driven silicon photonic link. Nat Photonics 17, 781–790 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41566-023-01244-7 [19] Herr T, Brasch V, Jost JD, Wang CY, Kondratiev NM et al. Temporal solitons in optical microresonators. Nat Photonics 8, 145–152 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.343 [20] Yi X, Yang QF, Yang KY, Suh MG, Vahala K. Soliton frequency comb at microwave rates in a high-Q silica microresonator. Optica 2, 1078–1085 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.2.001078 [21] Shen BQ, Chang L, Liu JQ, Wang HM, Yang QF et al. Integrated turnkey soliton microcombs. Nature 582, 365–369 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2358-x [22] Li Q, Briles TC, Westly DA, Drake TE, Stone JR et al. Stably accessing octave-spanning microresonator frequency combs in the soliton regime. Optica 4, 193–203 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000193 [23] Wang XY, Xie P, Wang WQ, Wang Y, Lu ZZ et al. Program-controlled single soliton microcomb source. Photonics Res 9, 66–72 (2021). doi: 10.1364/PRJ.408612 [24] He Y, Yang QF, Ling JW, Luo R, Liang HX et al. Self-starting bi-chromatic LiNbO3 soliton microcomb. Optica 6, 1138–1144 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001138 [25] Xue XX, Xuan Y, Liu Y, Wang PH, Chen S et al. Mode-locked dark pulse Kerr combs in normal-dispersion microresonators. Nat Photonics 9, 594–600 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.137 [26] Bruch AW, Liu XW, Gong Z, Surya JB, Li M et al. Pockels soliton microcomb. Nat Photonics 15, 21–27 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00704-8 [27] Cole DC, Lamb ES, Del’Haye P, Diddams SA, Papp SB. Soliton crystals in Kerr resonators. Nat Photonics 11, 671–676 (2017). doi: 10.1038/s41566-017-0009-z [28] Boggio JMC, Bodenmüller D, Ahmed S, Wabnitz S, Modotto D et al. Efficient Kerr soliton comb generation in micro-resonator with interferometric back-coupling. Nat Commun 13, 1292 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28927-z [29] Xue XX, Zheng XP, Zhou BK. Super-efficient temporal solitons in mutually coupled optical cavities. Nat Photonics 13, 616–622 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0436-0 [30] Helgason ÓB, Girardi M, Ye ZC, Lei FC, Schröder J et al. Surpassing the nonlinear conversion efficiency of soliton microcombs. Nat Photonics 17, 992–999 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41566-023-01280-3 [31] Parriaux A, Hammani K, Millot G. Electro-optic frequency combs. Adv Opt Photonics 12, 223–287 (2020). doi: 10.1364/AOP.382052 [32] Xue XX, Grelu P, Yang BF, Wang M, Li SY et al. Dispersion-less Kerr solitons in spectrally confined optical cavities. Light Sci Appl 12, 19 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-01052-8 [33] Kim BY, Okawachi Y, Jang JK, Ji XC, Lipson M et al. Coherent combining for high-power Kerr combs. Laser Photonics Rev 17, 2200607 (2023). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202200607 [34] Meng Y, Chen YZ, Lu LH, Ding YM, Cusano A et al. Optical meta-waveguides for integrated photonics and beyond. Light Sci Appl 10, 235 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00655-x [35] Lucas E, Yu SP, Briles TC, Carlson DR, Papp SB. Tailoring microcombs with inverse-designed, meta-dispersion microresonators. Nat Photonics 17, 943–950 (2023). [36] Xiao ZY, Li TY, Cai ML, Zhang HY, Huang Y et al. Near-zero-dispersion soliton and broadband modulational instability Kerr microcombs in anomalous dispersion. Light Sci Appl 12, 33 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41377-023-01076-8 [37] Anderson MH, Weng WL, Lihachev G, Tikan A, Liu JQ et al. Zero dispersion Kerr solitons in optical microresonators. Nat Commun 13, 4764 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31916-x [38] Godey C, Balakireva IV, Coillet A, Chembo YK. Stability analysis of the spatiotemporal Lugiato–Lefever model for Kerr optical frequency combs in the anomalous and normal dispersion regimes. Phys Rev A 89, 063814 (2014). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.89.063814 [39] Herr T, Brasch V, Jost JD, Mirgorodskiy I, Lihachev G et al. Mode spectrum and temporal soliton formation in optical microresonators. Phys Rev Lett 113, 123901 (2014). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.123901 [40] Lu ZZ, Wang WQ, Zhang WF, Liu ML, Wang LR et al. Raman self-frequency-shift of soliton crystal in a high index doped silica micro-ring resonator [Invited]. Opt Mater Express 8, 2662–2669 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OME.8.002662 [41] Wang WQ, Lu ZZ, Zhang WF, Chu ST, Little BE et al. Robust soliton crystals in a thermally controlled microresonator. Opt Lett 43, 2002–2005 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OL.43.002002 -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
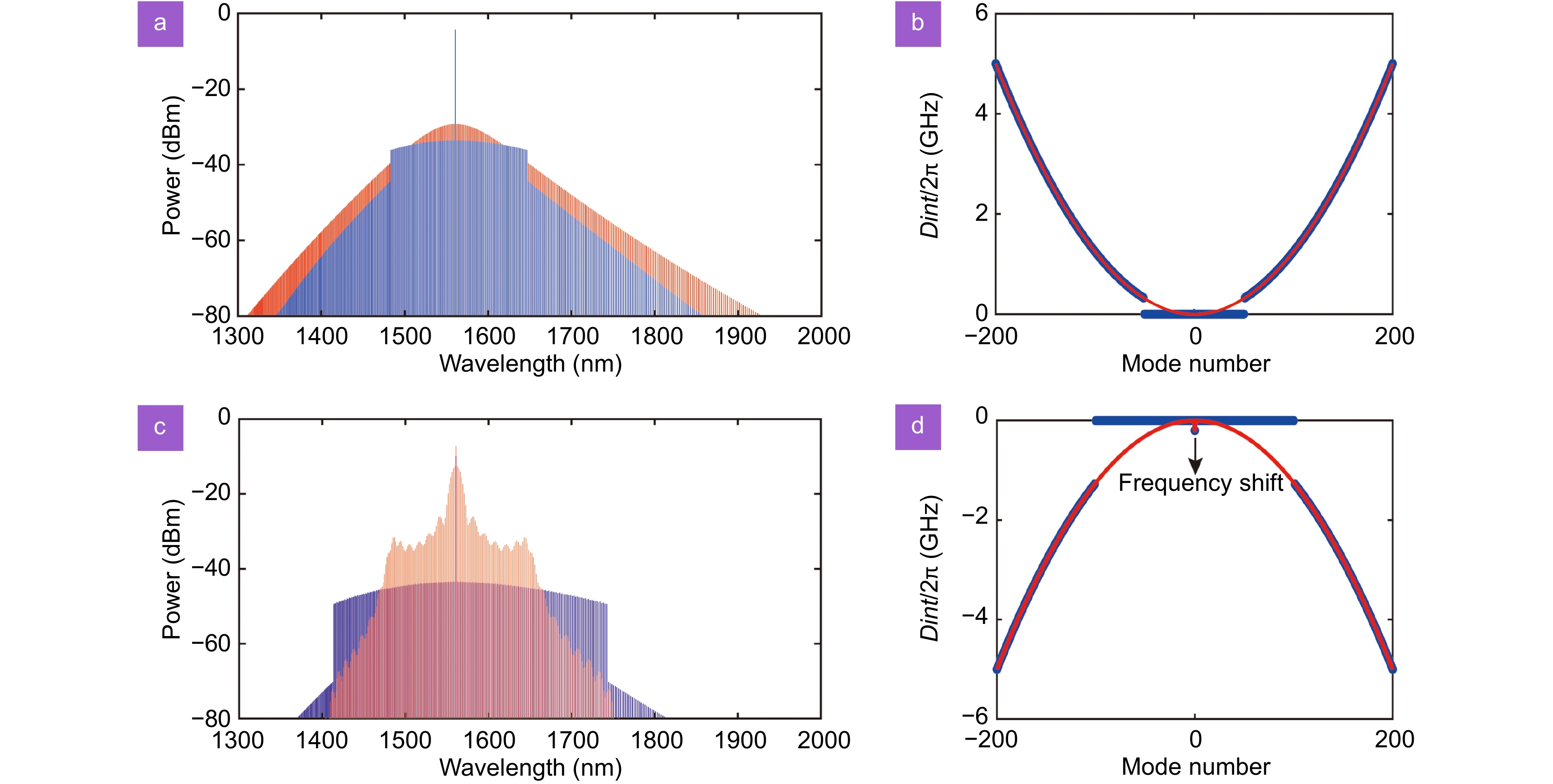
Optical spectrums of single SMC source and dispersion curves. (a, c) and (b, d) are the simulated optical spectrums of single soliton and dispersion curves, respectively. Blue line and red line in dispersion curves correspond to the conditions of local flat integrated dispersion and initial dispersion. Large-scale flat dispersion reduces the microcomb power variations at the ultra-weak dispersion regime.
-
Figure 2.
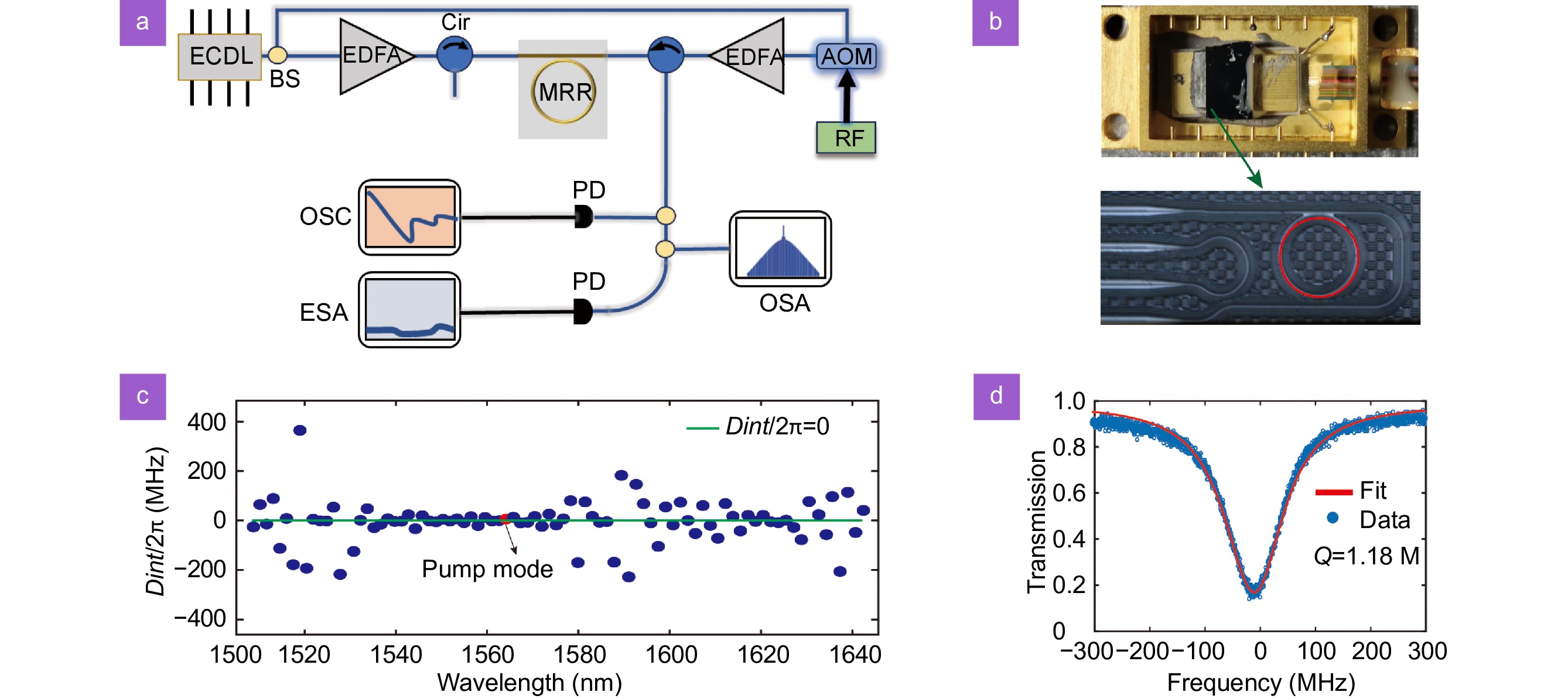
Experimental setup. (a) Experimental setup for the robust single SMC formation. An auxiliary laser is introduced for the stable soliton formation. ECDL, External cavity diode laser; EDFA, Erbium-doped fiber amplifier; OSA, Optical spectrum analyzer; OSC, Oscilloscope; ESA, Electrical spectrum analyzer; MRR, Micro-ring resonator; PD, Photodetector; Cir, Circulator. (b) Microscope image of the high-index doped silica glass micro-ring resonator with a radius of 148.1 μm (lower panel). Butterfly-packaged device (upper panel). (c) Dispersion characteristic of the MRR. The green line (Dint=0) is one referenced integrated dispersion curve. The micro-cavity demonstrates the ultra-flat dispersion characteristic. The red-dot is the soliton mode. (d) The transmission spectra of the soliton mode.
-
Figure 3.
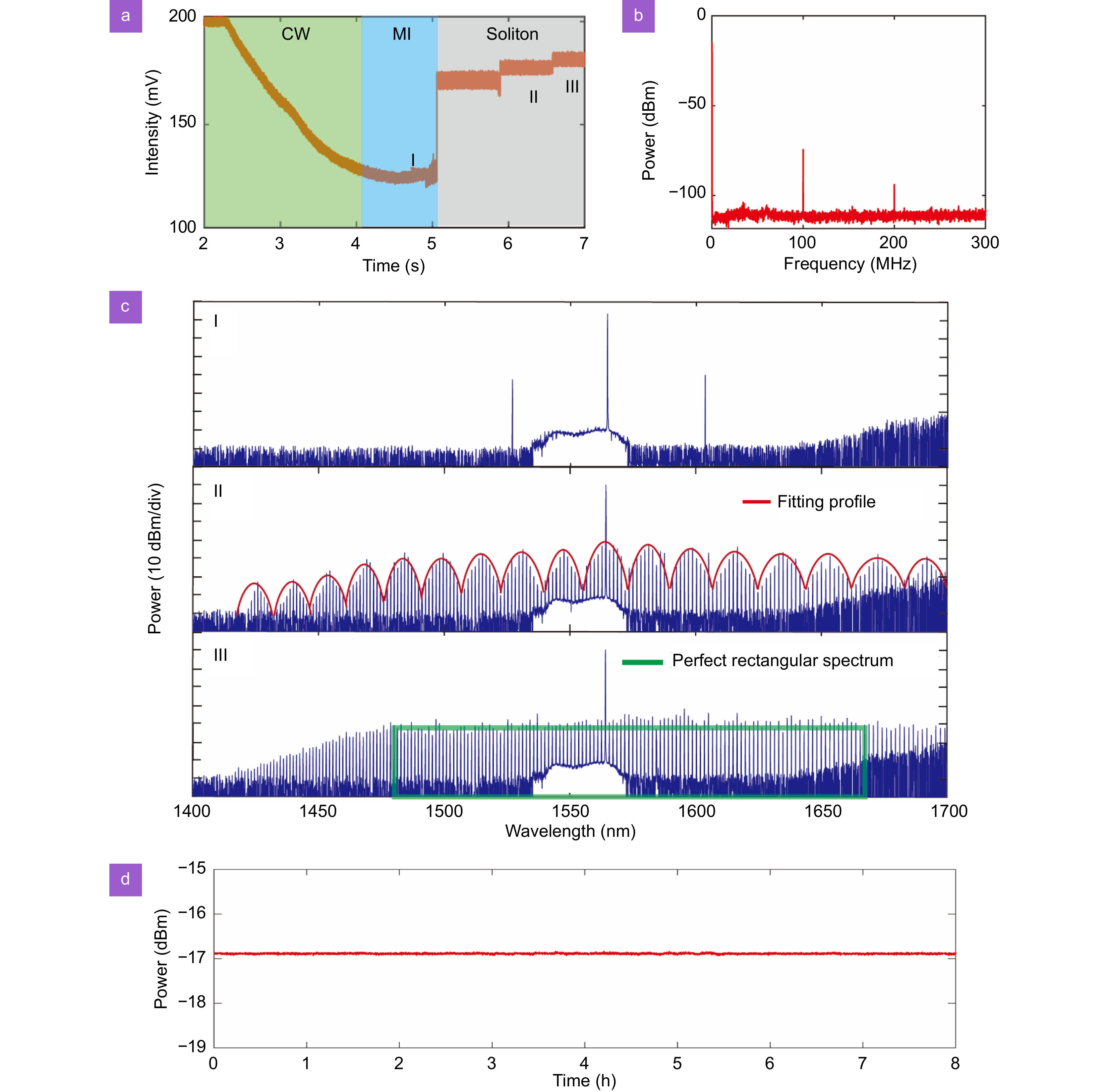
Experimental results at the flat dispersion regime. (a) Power trace of microcomb evolution from the continuous wave (CW) state to single soliton state. MI: Modulation instability. I: Turning pattern. II: Dual-soliton microcomb. III: Single soliton microcomb. (b) Radio frequency spectrum of single soliton state. (c) Optical spectrums of Turning pattern (I), dual-soliton microcomb (II) and single SMC source (III). Via introducing the perfect rectangular spectrum as one standard reference, the single SMC demonstrates the trapezoidal spectrum with weak power-varied spectral profile. (d) Long-term power trace of single SMC.
-
Figure 4.
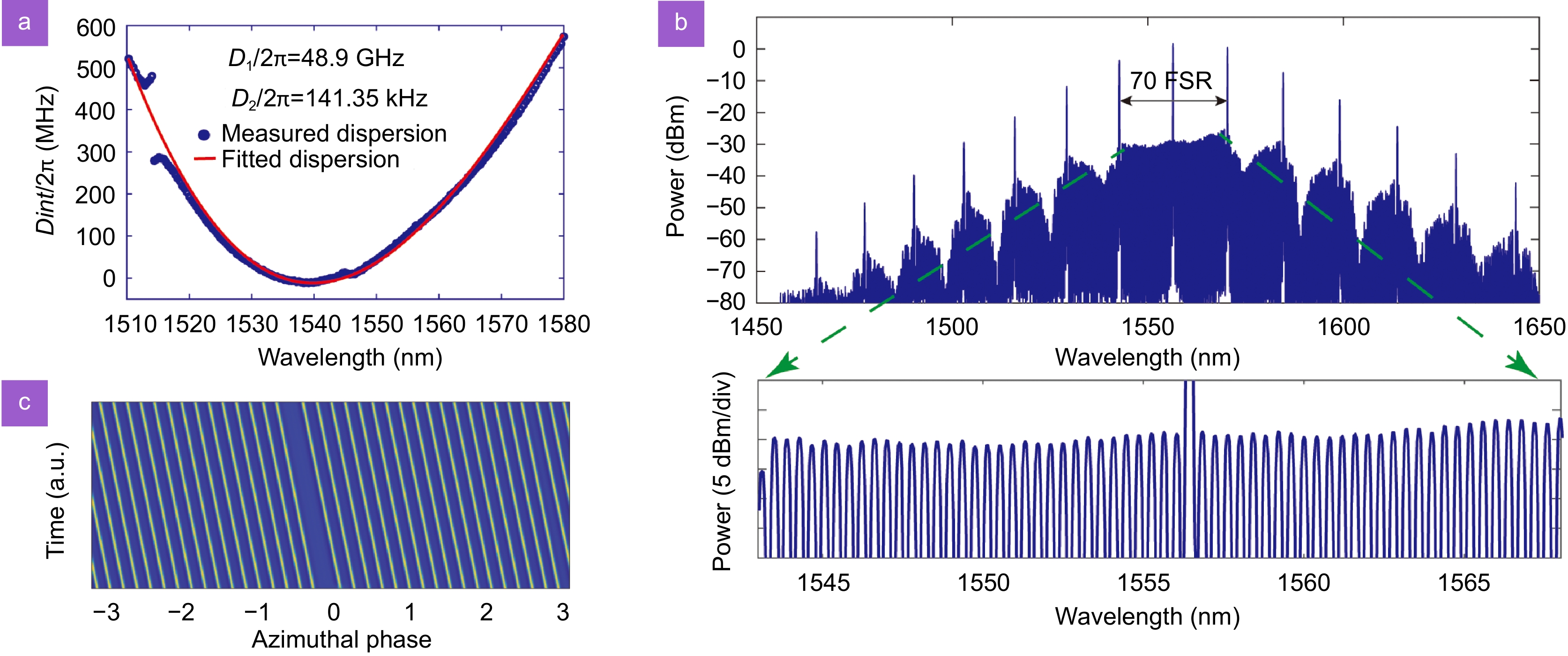
Experimental results for SC formation with local relatively flat spectrum. (a) Dispersion characteristic of microcavity. (b) Soliton crystal with irregular inter-soliton spacings. Zoom-in local spectrum. At this frequency region, the microcomb demonstrates the relatively flat spectral profile. (c) Temporal evolution of SC with local relatively flat spectral lines.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: