| Citation: |
|
-
Abstract
From metamaterials to metasurfaces, optical nano-structure has been widely investigated for novel and high efficiency functionalities. Apart from the intrisinsic properties of composite material, rich capabilities can be derived from the judicious design of metasurfaces, which enable more excellent and highly integrated optical devices than traditional bulk optical elements. In the meantime, the abundant manipulation abilites of light in the classical domain can be carried over into quantum domain. In this review, we highlight recent development of quantum optics based on metasurfaces, ranging from quantum plasmonics, generation, manipulation and appplication of quantum light to quantum vaccum engineering etc. Finally, some promising avenues for quantum optics with the help of optical metasurface are presented.-
Keywords:
- metasurfaces /
- quantum optics /
- quantum information
-

-
References
[1] Shalaev VM. Optical negative-index metamaterials. Nat Photonics 1, 41–48 (2007). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2006.49 [2] Valentine J, Zhang S, Zentgraf T, Ulin-Avila E, Genov DA et al. Three-dimensional optical metamaterial with a negative refractive index. Nature 455, 376–379 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nature07247 [3] Moitra P, Yang YM, Anderson Z, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP et al. Realization of an all-dielectric zero-index optical metamaterial. Nat Photonics 7, 791–795 (2013). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.214 [4] Fang N, Zhang X. Imaging properties of a metamaterial superlens. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology 225–228 (IEEE, 2002); http://doi.org/10.1109/NANO.2002.1032233 [5] Jacob Z, Alekseyev LV, Narimanov E. Optical hyperlens: far-field imaging beyond the diffraction limit. Opt Express 14, 8247–8256 (2006). doi: 10.1364/OE.14.008247 [6] Liu ZW, Lee H, Xiong Y, Sun C, Zhang X. Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects. Science 315, 1686 (2007). doi: 10.1126/science.1137368 [7] Cai WS, Chettiar UK, Kildishev AV, Shalaev VM. Optical cloaking with metamaterials. Nat Photonics 1, 224–227 (2007). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.28 [8] Smolyaninov II, Smolyaninova VN, Kildishev AV, Shalaev VM. Anisotropic metamaterials emulated by tapered waveguides: application to optical cloaking. Phys Rev Lett 102, 213901 (2009). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.213901 [9] Yu NF, Genevet P, Kats MA, Aieta F, Tetienne JP et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 334, 333–337 (2011). doi: 10.1126/science.1210713 [10] Klein MW, Enkrich C, Wegener M, Linden S. Second-harmonic generation from magnetic metamaterials. Science 313, 502–504 (2006). doi: 10.1126/science.1129198 [11] Kim S, Jin J, Kim YJ, Park IY, Kim Y et al. High-harmonic generation by resonant plasmon field enhancement. Nature 453, 757–760 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nature07012 [12] Lee J, Tymchenko M, Argyropoulos C, Chen PY, Lu F et al. Giant nonlinear response from plasmonic metasurfaces coupled to intersubband transitions. Nature 511, 65–69 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nature13455 [13] Luu TT, Garg M, Kruchinin SY, Moulet A, Hassan MT et al. Extreme ultraviolet high-harmonic spectroscopy of solids. Nature 521, 498–502 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nature14456 [14] Kuznetsov AI, Miroshnichenko AE, Brongersma ML, Kivshar YS, Luk'yanchuk B. Optically resonant dielectric nanostructures. Science 354, aag2472 (2016). doi: 10.1126/science.aag2472 [15] Sivis M, Taucer M, Vampa G, Johnston K, Staudte A et al. Tailored semiconductors for high-harmonic optoelectronics. Science 357, 303–306 (2017). doi: 10.1126/science.aan2395 [16] Koshelev K, Kruk S, Melik-Gaykazyan E, Choi JH, Bogdanov A et al. Subwavelength dielectric resonators for nonlinear nanophotonics. Science 367, 288–292 (2020). doi: 10.1126/science.aaz3985 [17] Bomzon ZE, Biener G, Kleiner V, Hasman E. Space-variant Pancharatnam–Berry phase optical elements with computer-generated subwavelength gratings. Opt Lett 27, 1141–1143 (2002). doi: 10.1364/OL.27.001141 [18] Zayats AV, Smolyaninov II, Maradudin AA. Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys Rep 408, 131–314 (2005). doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2004.11.001 [19] Bouhelier A, Beversluis M, Hartschuh A, Novotny L. Near-field second-harmonic generation induced by local field enhancement. Phys Rev Lett 90, 013903 (2003). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.013903 [20] Kim EM, Elovikov SS, Murzina TV, Nikulin AA, Aktsipetrov OA et al. Surface-enhanced optical third-harmonic generation in Ag island films. Phys Rev Lett 95, 227402 (2005). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.227402 [21] Kinkhabwala A, Yu ZF, Fan SH, Avlasevich Y, Müllen K et al. Large single-molecule fluorescence enhancements produced by a bowtie nanoantenna. Nat Photonics 3, 654–657 (2009). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.187 [22] Renger J, Quidant R, van Hulst N, Novotny L. Surface-enhanced nonlinear four-wave mixing. Phys Rev Lett 104, 046803 (2010). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.046803 [23] Park IY, Kim S, Choi J, Lee DH, Kim YJ et al. Plasmonic generation of ultrashort extreme-ultraviolet light pulses. Nat Photonics 5, 677–681 (2011). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.258 [24] Sivis M, Duwe M, Abel B, Ropers C. Extreme-ultraviolet light generation in plasmonic nanostructures. Nat Phys 9, 304–309 (2013). doi: 10.1038/nphys2590 [25] Aouani H, Rahmani M, Navarro-Cia M, Maier SA. Third-harmonic-upconversion enhancement from a single semiconductor nanoparticle coupled to a plasmonic antenna. Nat Nanotechnol 9, 290–294 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.27 [26] Zhu WQ, Crozier KB. Quantum mechanical limit to plasmonic enhancement as observed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nat Commun 5, 5228 (2014). doi: 10.1038/ncomms6228 [27] Han S, Kim H, Kim YW, Kim YJ, Kim S et al. High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure. Nat Commun 7, 13105 (2016). doi: 10.1038/ncomms13105 [28] Zhong JH, Vogelsang J, Yi JM, Wang D, Wittenbecher L et al. Nonlinear plasmon-exciton coupling enhances sum-frequency generation from a hybrid metal/semiconductor nanostructure. Nat Commun 11, 1464 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15232-w [29] Zhang XY, Cao QT, Wang Z, Liu YX, Qiu CW et al. Symmetry-breaking-induced nonlinear optics at a microcavity surface. Nat Photonics 13, 21–24 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0297-y [30] Miroshnichenko AE, Evlyukhin AB, Yu YF, Bakker RM, Chipouline A et al. Nonradiating anapole modes in dielectric nanoparticles. Nat Commun 6, 8069 (2015). doi: 10.1038/ncomms9069 [31] Grinblat G, Li Y, Nielsen MP, Oulton RF, Maier SA. Enhanced third harmonic generation in single germanium nanodisks excited at the anapole mode. Nano Lett 16, 4635–4640 (2016). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01958 [32] Carletti L, Koshelev K, De Angelis C, Kivshar Y. Giant nonlinear response at the nanoscale driven by bound states in the continuum. Phys Rev Lett 121, 033903 (2018). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.033903 [33] Liu ZJ, Xu Y, Lin Y, Xiang J, Feng TH et al. High-Q quasibound states in the continuum for nonlinear metasurfaces. Phys Rev Lett 123, 253901 (2019). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.253901 [34] Yang YM, Wang WY, Boulesbaa A, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP et al. Nonlinear fano-resonant dielectric metasurfaces. Nano Lett 15, 7388–7393 (2015). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02802 [35] Carletti L, Locatelli A, Stepanenko O, Leo G, De Angelis C. Enhanced second-harmonic generation from magnetic resonance in AlGaAs nanoantennas. Opt Express 23, 26544–26550 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OE.23.026544 [36] Shcherbakov MR, Neshev DN, Hopkins B, Shorokhov AS, Staude I et al. Enhanced third-harmonic generation in silicon nanoparticles driven by magnetic response. Nano Lett 14, 6488–6492 (2014). doi: 10.1021/nl503029j [37] Kruk S, Poddubny A, Smirnova D, Wang L, Slobozhanyuk A et al. Nonlinear light generation in topological nanostructures. Nat Nanotechnol 14, 126–130 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0324-7 [38] Smirnova D, Kruk S, Leykam D, Melik-Gaykazyan E, Choi DY et al. Third-harmonic generation in photonic topological metasurfaces. Phys Rev Lett 123, 103901 (2019). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.103901 [39] Wang SM, Wu PC, Su VC, Lai YC, Chu CH et al. Broadband achromatic optical metasurface devices. Nat Commun 8, 187 (2017). doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00166-7 [40] Wang SM, Wu PC, Su VC, Lai YC, Chen MK et al. A broadband achromatic metalens in the visible. Nat Nanotechnol 13, 227–232 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0052-4 [41] Ye WM, Zeuner F, Li X, Reineke B, He S et al. Spin and wavelength multiplexed nonlinear metasurface holography. Nat Commun 7, 11930 (2016). doi: 10.1038/ncomms11930 [42] Ni XJ, Kildishev AV, Shalaev VM. Metasurface holograms for visible light. Nat Commun 4, 2807 (2013). doi: 10.1038/ncomms3807 [43] Zheng GX, Mühlenbernd H, Kenney M, Li GX, Zentgraf T et al. Metasurface holograms reaching 80% efficiency. Nat Nanotechnol 10, 308–312 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.2 [44] Huang LL, Chen XZ, Mühlenbernd H, Zhang H, Chen SM et al. Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface. Nat Commun 4, 2808 (2013). doi: 10.1038/ncomms3808 [45] Yin XB, Ye ZL, Rho J, Wang Y, Zhang X. Photonic spin Hall effect at metasurfaces. Science 339, 1405–1407 (2013). doi: 10.1126/science.1231758 [46] Yang YM, Wang WY, Moitra P, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP et al. Dielectric meta-reflectarray for broadband linear polarization conversion and optical vortex generation. Nano Lett 14, 1394–1399 (2014). doi: 10.1021/nl4044482 [47] Karimi E, Schulz SA, De Leon I, Qassim H, Upham J et al. Generating optical orbital angular momentum at visible wavelengths using a plasmonic metasurface. Light Sci Appl 3, e167 (2014). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.48 [48] Cerf NJ, Bourennane M, Karlsson A, Gisin N. Security of quantum key distribution using d-level systems. Phys Rev Lett 88, 127902 (2002). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.127902 [49] Gisin N, Ribordy GG, Tittel W, Zbinden H. Quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys 74, 145–195 (2002). doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.145 [50] Gisin N, Thew R. Quantum communication. Nat Photonics 1, 165–171 (2007). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.22 [51] Scarani V, Bechmann-Pasquinucci H, Cerf NJ, Dušek M, Lütkenhaus N et al. The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev Mod Phys 81, 1301–1350 (2009). doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1301 [52] Lo HK, Curty M, Tamaki K. Secure quantum key distribution. Nat Photonics 8, 595–604 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.149 [53] Wang XL, Cai XD, Su ZE, Chen MC, Wu D et al. Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Nature 518, 516–519 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nature14246 [54] Knill E, Laflamme R, Milburn GJ. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001). doi: 10.1038/35051009 [55] O'Brien JL. Optical quantum computing. Science 318, 1567–1570 (2007). doi: 10.1126/science.1142892 [56] Lanyon BP, Barbieri M, Almeida MP, Jennewein T, Ralph TC et al. Simplifying quantum logic using higher-dimensional Hilbert spaces. Nat Phys 5, 134–140 (2009). doi: 10.1038/nphys1150 [57] Neeley M, Ansmann M, Bialczak RC, Hofheinz M, Lucero E et al. Emulation of a quantum spin with a superconducting phase qudit. Science 325, 722–725 (2009). doi: 10.1126/science.1173440 [58] Kaltenbaek R, Lavoie J, Zeng B, Bartlett SD, Resch KJ. Optical one-way quantum computing with a simulated valence-bond solid. Nat Phys 6, 850–854 (2010). doi: 10.1038/nphys1777 [59] Aspuru-Guzik A, Walther P. Photonic quantum simulators. Nat Phys 8, 285–291 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nphys2253 [60] Georgescu IM, Ashhab S, Nori F. Quantum simulation. Rev Mod Phys 86, 153–185 (2014). doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.86.153 [61] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L. Advances in quantum metrology. Nat Photonics 5, 222–229 (2011). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.35 [62] Pirandola S, Bardhan BR, Gehring T, Weedbrook C, Lloyd S. Advances in photonic quantum sensing. Nat Photonics 12, 724–733 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0301-6 [63] You JQ, Nori F. Atomic physics and quantum optics using superconducting circuits. Nature 474, 589–597 (2011). doi: 10.1038/nature10122 [64] Diehl S, Micheli A, Kantian A, Kraus B, Büchler H et al. Quantum states and phases in driven open quantum systems with cold atoms. Nat Phys 4, 878–883 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nphys1073 [65] Leibfried D, Blatt R, Monroe C, Wineland D. Quantum dynamics of single trapped ions. Rev Mod Phys 75, 281–324 (2003). doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.75.281 [66] Li CL, Yu P, Huang YJ, Zhou Q, Wu J et al. Dielectric metasurfaces: from wavefront shaping to quantum platforms. Prog Surf Sci 95, 100584 (2020). doi: 10.1016/j.progsurf.2020.100584 [67] Uriri S, Ismail Y, Petruccione F. Quantum metamaterials: applications in quantum information science. arXiv: 2006.03757 (2020). [68] Rivera N, Kaminer I. Light-matter interactions with photonic quasiparticles. Nat Rev Phys 2, 538–561 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s42254-020-0224-2 [69] Solntsev AS, Agarwal GS, Kivshar YS. Metasurfaces for quantum photonics. arXiv: 2007.14722 (2020). [70] Heeres RW, Kouwenhoven LP, Zwiller V. Quantum interference in plasmonic circuits. Nat Nanotechnol 8, 719–722 (2013). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.150 [71] Fakonas JS, Lee H, Kelaita YA, Atwater HA. Two-plasmon quantum interference. Nat Photonics 8, 317–320 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.40 [72] Altewischer E, van Exter MP, Woerdman JP. Plasmon-assisted transmission of entangled photons. Nature 418, 304–306 (2002). doi: 10.1038/nature00869 [73] Moreno E, García-Vidal FJ, Erni D, Cirac JI, Martín-Moreno L. Theory of plasmon-assisted transmission of entangled photons. Phys Rev Lett 92, 236801 (2004). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.236801 [74] Fasel S, Robin F, Moreno E, Erni D, Gisin N et al. Energy-time entanglement preservation in plasmon-assisted light transmission. Phys Rev Lett 94, 110501 (2005). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.110501 [75] Huck A, Smolka S, Lodahl P, Sørensen AS, Boltasseva A et al. Demonstration of quadrature-squeezed surface plasmons in a gold waveguide. Phys Rev Lett 102, 246802 (2009). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.246802 [76] Tan SF, Wu L, Yang JKW, Bai P, Bosman M et al. Quantum plasmon resonances controlled by molecular tunnel junctions. Science 343, 1496–1499 (2014). doi: 10.1126/science.1248797 [77] Kolesov R, Grotz B, Balasubramanian G, Stöhr RJ, Nicolet AAL et al. Wave–particle duality of single surface plasmon polaritons. Nat Phys 5, 470–474 (2009). doi: 10.1038/nphys1278 [78] Dheur MC, Devaux E, Ebbesen TW, Baron A, Rodier JC et al. Single-plasmon interferences. Sci Adv 2, e1501574 (2016). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501574 [79] Erhard M, Krenn M, Zeilinger A. Advances in high-dimensional quantum entanglement. Nat Rev Phys 2, 365–381 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s42254-020-0193-5 [80] Reck M, Zeilinger A, Bernstein HJ, Bertani P. Experimental realization of any discrete unitary operator. Phys Rev Lett 73, 58–61 (1994). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.58 [81] Krenn M, Hochrainer A, Lahiri M, Zeilinger A. Entanglement by path identity. Phys Rev Lett 118, 080401 (2017). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.080401 [82] Wang JW, Paesani S, Ding YH, Santagati R, Skrzypczyk P et al. Multidimensional quantum entanglement with large-scale integrated optics. Science 360, 285–291 (2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aar7053 [83] Siomau M, Kamli AA, Moiseev SA, Sanders BC. Entanglement creation with negative index metamaterials. Phys Rev A 85, 050303 (2012). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.85.050303 [84] Poddubny AN, Iorsh IV, Sukhorukov AA. Generation of photon-plasmon quantum states in nonlinear hyperbolic metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 117, 123901 (2016). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.123901 [85] Marino G, Solntsev AS, Xu L, Gili VF, Carletti L et al. Spontaneous photon-pair generation from a dielectric nanoantenna. Optica 6, 1416–1422 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001416 [86] Santiago-Cruz T, Sultanov V, Zhang HZ, Krivitsky LA, Chekhova MV. Spontaneous parametric down-conversion from subwavelength nonlinear films. arXiv: 2009.00324 (2020). [87] Ming Y, Zhang W, Tang J, Liu Y, Xia ZL et al. Photonic entanglement based on nonlinear metamaterials. Laser Photonics Rev 14, 1900146 (2020). doi: 10.1002/lpor.201900146 [88] Li L, Liu ZX, Ren XF, Wang SM, Su VC et al. Metalens-array-based high-dimensional and multiphoton quantum source. Science 368, 1487–1490 (2020). doi: 10.1126/science.aba9779 [89] Stav T, Faerman A, Maguid E, Oren D, Kleiner V et al. Quantum entanglement of the spin and orbital angular momentum of photons using metamaterials. Science 361, 1101–1104 (2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aat9042 [90] Wang K, Titchener JG, Kruk SS, Xu L, Chung HP et al. Quantum metasurface for multiphoton interference and state reconstruction. Science 361, 1104–1108 (2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aat8196 [91] Asano M, Bechu M, Tame M, Özdemir Ş K, Ikuta R et al. Distillation of photon entanglement using a plasmonic metamaterial. Sci Rep 5, 18313 (2015). [92] Uriri SA, Tashima T, Zhang X, Asano M, Bechu M et al. Active control of a plasmonic metamaterial for quantum state engineering. Phys Rev A 97, 053810 (2018). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.97.053810 [93] Roger T, Vezzoli S, Bolduc E, Valente J, Heitz JJF et al. Coherent perfect absorption in deeply subwavelength films in the single-photon regime. Nat Commun 6, 7031 (2015). doi: 10.1038/ncomms8031 [94] Altuzarra C, Vezzoli S, Valente J, Gao WB, Soci C et al. Coherent perfect absorption in metamaterials with entangled photons. ACS Photonics 4, 2124–2128 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00514 [95] Lyons A, Oren D, Roger T, Savinov V, Valente J et al. Coherent metamaterial absorption of two-photon states with 40% efficiency. Phys Rev A 99, 011801 (2019). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.99.011801 [96] Altuzarra C, Lyons A, Yuan GH, Simpson C, Roger T et al. Imaging of polarization-sensitive metasurfaces with quantum entanglement. Phys Rev A 99, 020101 (2019). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.99.020101 [97] Zhou JX, Liu SK, Qian HL, Li YH, Luo HL et al. Metasurface enabled quantum edge detection. Sci Adv 6, eabc4385 (2020). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc4385 [98] Georgi P, Massaro M, Luo KH, Sain B, Montaut N et al. Metasurface interferometry toward quantum sensors. Light Sci Appl 8, 70 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0182-6 [99] Chen SZ, Zhou XX, Mi CQ, Liu ZX, Luo HL et al. Dielectric metasurfaces for quantum weak measurements. Appl Phys Lett 110, 161115 (2017). doi: 10.1063/1.4982164 [100] Lundeen JS, Sutherland B, Patel A, Stewart C, Bamber C. Direct measurement of the quantum wavefunction. Nature 474, 188–191 (2011). doi: 10.1038/nature10120 [101] Hosten O, Kwiat P. Observation of the spin hall effect of light via weak measurements. Science 319, 787–790 (2008). doi: 10.1126/science.1152697 [102] Jha PK, Ni XJ, Wu C, Wang Y, Zhang X. Metasurface-enabled remote quantum interference. Phys Rev Lett 115, 025501 (2015). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.025501 [103] Jha PK, Shitrit N, Kim J, Ren XX, Wang Y et al. Metasurface-mediated quantum entanglement. ACS Photonics 5, 971–976 (2018). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01241 [104] Jha PK, Shitrit N, Ren XX, Wang Y, Zhang X. Spontaneous exciton valley coherence in transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers interfaced with an anisotropic metasurface. Phys Rev Lett 121, 116102 (2018). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.116102 [105] Kornovan D, Petrov M, Iorsh I. Noninverse dynamics of a quantum emitter coupled to a fully anisotropic environment. Phys Rev A 100, 033840 (2019). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.100.033840 [106] Lassalle E, Lalanne P, Aljunid S, Genevet P, Stout B et al. Long-lifetime coherence in a quantum emitter induced by a metasurface. Phys Rev A 101, 013837 (2020). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.013837 -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
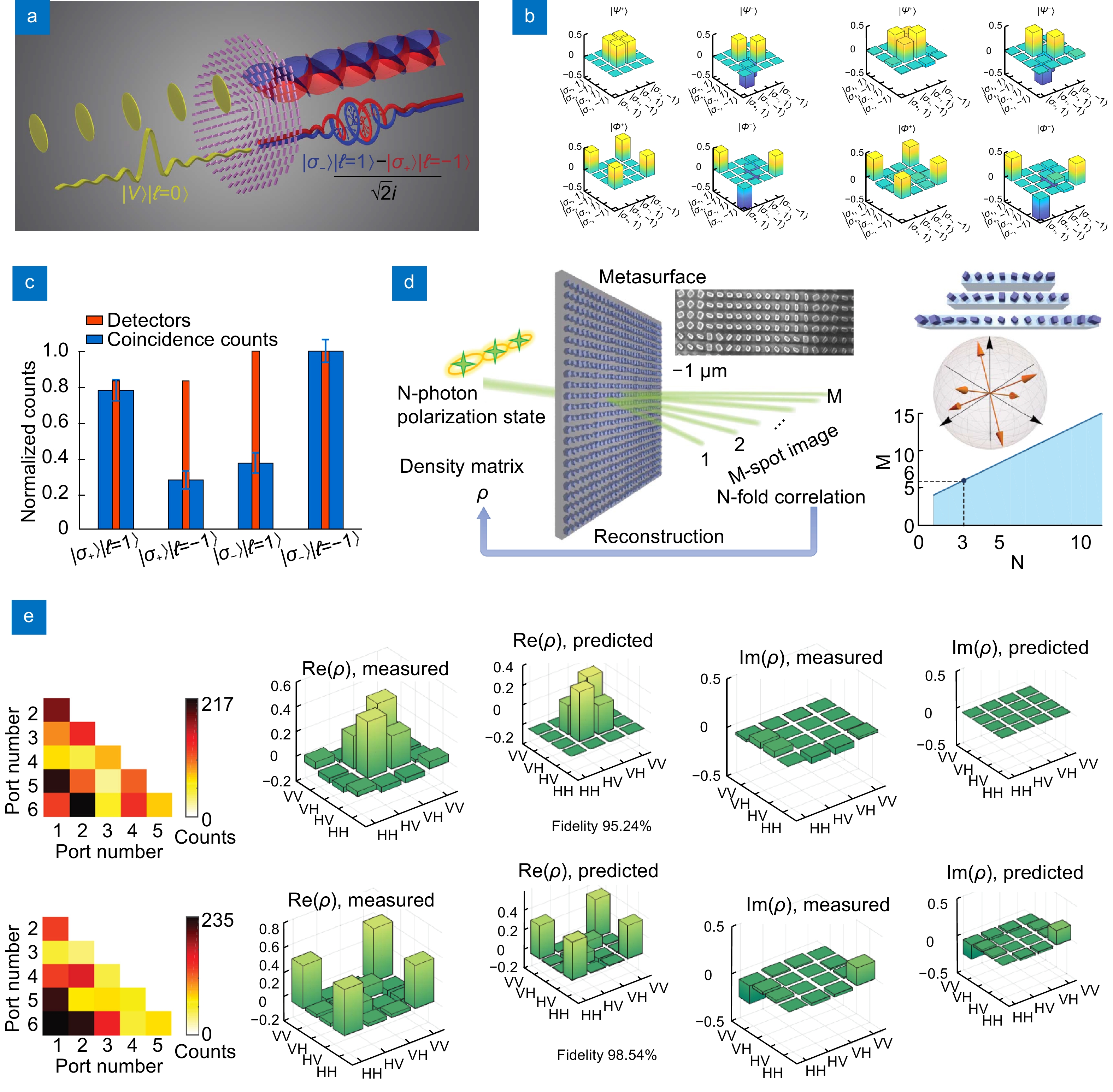
Figure 1.
Quantum source based on metasurfaces. (a) Schematic of quantum source based on metasurfaces. (b) Characterization of three-dimensional, four-dimensional two-photon quantum states. (c) Manipulating the phase gradient of metasurface to prepare four kinds of bell states. (d) Characterization of multiphoton quantum source based on metasurface. Figure reproduced from: (a-d) ref.88, The American Association for the Advancement of Science.
-
Figure 2.
Manipulation of quantum states based on metasurface. (a) Employing geometric phase associated with metasurface to make photons with different spin polarization state acquire different orbital angular momentum. (b) Four bell states of single photon with entanglement of spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. (c) The mutual entanglement between a photon pair. (d) Left is the schematic of quantum state tomography based on metasurface, top right is three different inter-leaved metasurface, middle-right is the graphical representation of 6 different polarization states, bottom right is relationship between the minimum number of channels required and the number of photons. (e) The reconstruction of density matrix of two different photon pair state with fidelities 95.24%, 98.54% respectively. Figure reproduced from: (a-c) ref.89,The American Association for the Advancement of Science; (d-e) ref.90, The American Association for the Advancement of Science.
-
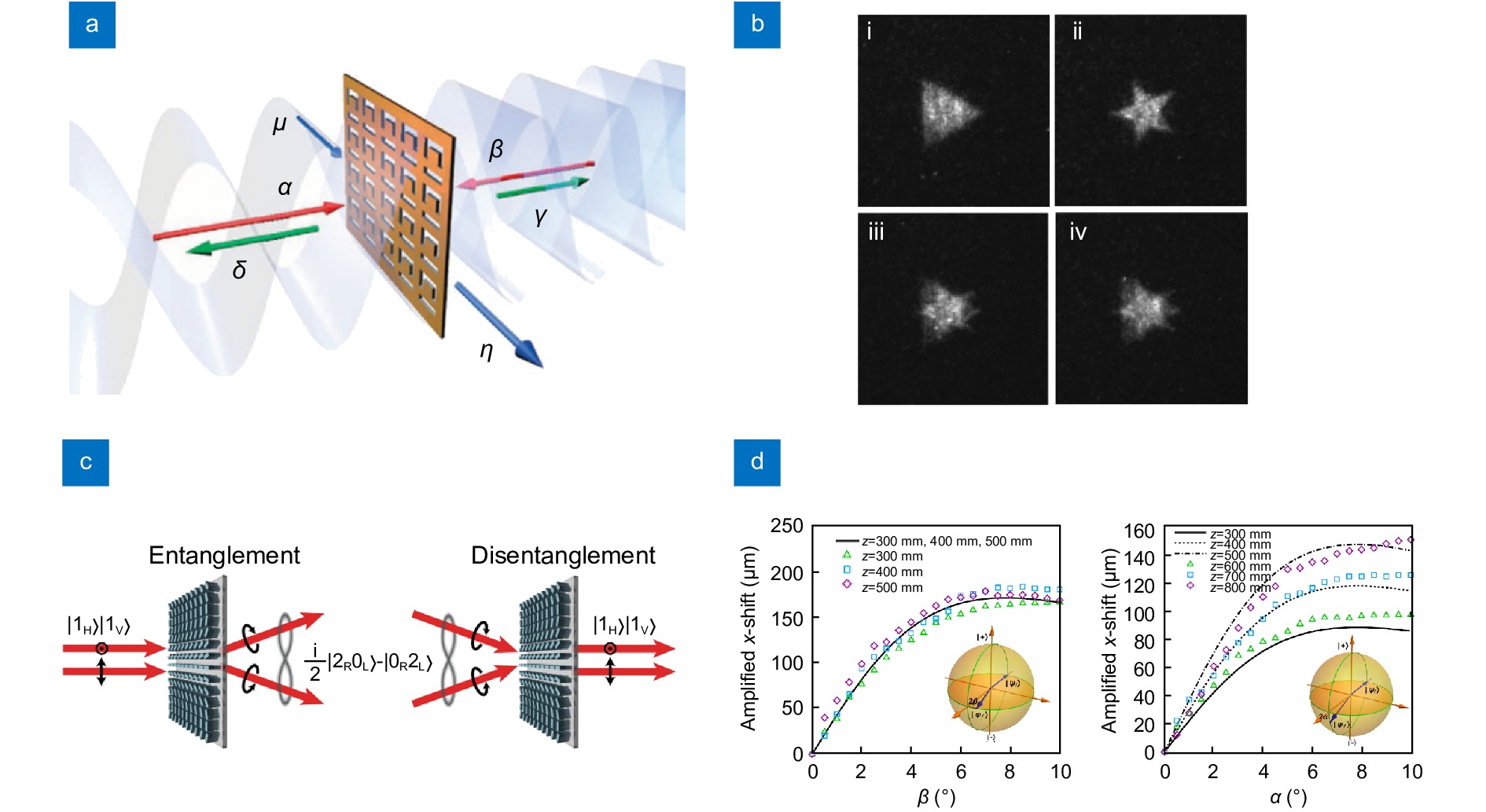
Figure 3.
Quantum photonic applications based on metasurfaces. (a) Absorption of single photon based on metallic metasurfaces, α and β represent two photon input channels, δ and γ represent two photon output channels, μ and η represent plasmonic input and output channel respectively. (b) Figure i and ii use signal photon of photon pair to image the metasurface, projective measurements on idle photon is carried out to clearly distinguish triangle and star pattern. Figure iii and iv use photons of mixed state to image metasurface which cannot distinguish the two patterns. (c) Metasurface is used to entangle and disentangle two photon NOON state. (d) The position shift and momentum shift of photon wavefunction induced by quantum weak measurement based on metasurfaces. Figure reproduced from: (a) ref.93, Springer Nature; (b) ref.96, American Physical Society; (c) ref.98, Springer Nature; (d) ref.99, AIP Publishing.
-
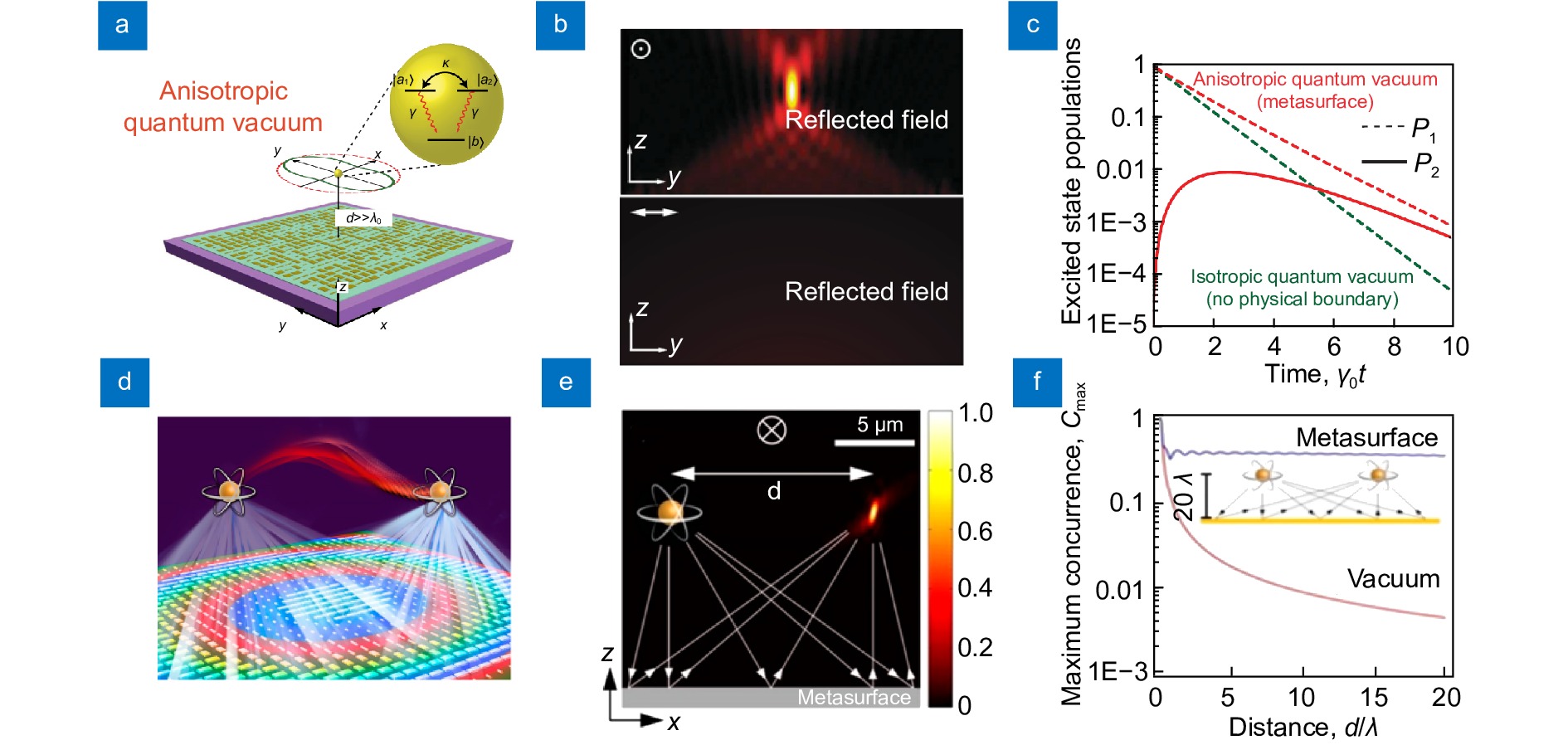
Figure 4.
Quantum vacuum engineering based on metasurfaces. (a) Based on metasurfaces, the quantum vacuum symmetry of quantum emitter is broken, so that quantum interference between different energy levels of multi-level quantum emitter occurs. (b) The electromagnetic field radiated by an electric dipole in the x direction above metasurface can be focused back to the source point along the original path with the maximum efficiency being 81% and the electromagnetic field radiated by an electric dipole in the y direction has no such effect. (c) When there is no metasurface, the energy level |a1
$\left. \right\rangle $ $\left. \right\rangle $ $\left. \right\rangle $ $\left. \right\rangle $

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: