| Citation: | Lu F F, Zhang W D, Huang L G, Liang S H, Mao D et al. Mode evolution and nanofocusing of grating-coupled surface plasmon polaritons on metallic tip. Opto-Electron Adv 1, 180010 (2018). doi: 10.29026/oea.2018.180010 |
Mode evolution and nanofocusing of grating-coupled surface plasmon polaritons on metallic tip
-
Abstract
We present a detailed analysis on mode evolution of grating-coupled surface plasmonic polaritons (SPPs) on a conical metal tip based on the guided-wave theory. The eigenvalue equations for SPPs modes are discussed, revealing that cylindrical metal waveguides only support TM01 and HEm1 surface modes. During propagation on the metal tip, the grating-coupled SPPs are converted to HE31, HE21, HE11 and TM01 successively, and these modes are sequentially cut off except TM01. The TM01 mode further propagates with drastically increasing effective mode index and is converted to localized surface plasmons (LSPs) at the tip apex, which is responsible for plasmonic nanofocusing. The gap-mode plasmons can be excited with the focusing TM01 mode by approaching a metal substrate to the tip apex, resulting in further enhanced electric field and reduced size of the plasmonic focus. -

-
References
[1] Gramotnev D K, Bozhevolnyi S I. Nanofocusing of electromagnetic radiation. Nat Photonics 8, 13-22 (2013). [2] Stöckle R M, Suh Y D, Deckert V, Zenobi R. Nanoscale chemical analysis by tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lett 318, 131-136 (2000). doi: 10.1016/S0009-2614(99)01451-7 [3] Jiang S, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Hu C R, Liao M H et al. Distinguishing adjacent molecules on a surface using plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering. Nat Nanotechnol 10, 865-869 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.170 [4] Zhong J H, Jin X, Meng L Y, Wang X, Su H S et al. Probing the electronic and catalytic properties of a bimetallic surface with 3 nm resolution. Nat Nanotechnol 12, 132-136 (2017). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2016.241 [5] Li J F, Huang Y F, Ding Y, Yang Z L, Li S B et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464, 392-395 (2010). doi: 10.1038/nature08907 [6] Zhang W D, Li C, Gao K, Lu F F, Liu M et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with Au-nanoparticle substrate fabricated by using femtosecond pulse. Nanotechnology 29, 205301 (2018). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aab294 [7] Wei H, Hao F, Huang Y Z, Wang W Z, Nordlander P et al. Polarization dependence of surface-enhanced Raman scattering in gold nanoparticle-nanowire systems. Nano Lett 8, 2497-2502 (2008). doi: 10.1021/nl8015297 [8] Xu K C, Wang Z Y, Tan C F, Kang N, Chen L W et al. Uniaxially stretched flexible surface Plasmon resonance film for versatile surface enhanced Raman scattering diagnostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9, 26341-26349 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b06669 [9] Neacsu C C, Reider G A, Raschke M B. Second-harmonic generation from nanoscopic metal tips: symmetry selection rules for single asymmetric nanostructures. Phys Rev B 71, 201402 (2005). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.71.201402 [10] Kauranen M, Zayats A V. Nonlinear plasmonics. Nat Photonics 6, 737-748 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.244 [11] Jin Y J, Chen L W, Wu M X, Lu X Z, Zhou R et al. Enhanced saturable absorption of the graphene oxide film via photonic nanojets. Opt Mater Express 6, 1114-1121 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OME.6.001114 [12] Chen L W, Zheng X R, Du Z R, Jia B H, Gu M et al. A frozen matrix hybrid optical nonlinear system enhanced by a particle lens. Nanoscale 7, 14982-14988 (2015). doi: 10.1039/C5NR03304G [13] Du Z R, Chen L W, Kao T S, Wu M X, Hong M H. Improved optical limiting performance of laser-ablation-generated metal nanoparticles due to silica-microsphere-induced local field enhancement. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 6, 1199-1204 (2015). doi: 10.3762/bjnano.6.122 [14] Chen C, Hayazawa N, Kawata S. A 1.7 nm resolution chemical analysis of carbon nanotubes by tip-enhanced Raman imaging in the ambient. Nat Commun 5, 3312 (2014). doi: 10.1038/ncomms4312 [15] Zhang R, Zhang Y, Dong Z C, Jiang S, Zhang C et al. Chemical mapping of a single molecule by plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering. Nature 498, 82-86 (2013). doi: 10.1038/nature12151 [16] Nerkararyan K V. Superfocusing of a surface polariton in a wedge-like structure. Phys Lett A 237, 103-105 (1997). doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(97)00722-6 [17] Lindquist N C, Nagpal P, Lesuffleur A, Norris D J, Oh S H. Three-dimensional plasmonic nanofocusing. Nano Lett 10, 1369-1373 (2010). doi: 10.1021/nl904294u [18] Volkov V S, Bozhevolnyi S I, Rodrigo S G, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J et al. Nanofocusing with channel plasmon polaritons. Nano Lett 9, 1278-1282 (2009). doi: 10.1021/nl900268v [19] Fernández-Domínguez A I, Maier S A, Pendry J B. Collection and concentration of light by touching spheres: a transformation optics approach. Phys Rev Lett 105, 266807 (2010). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.266807 [20] Verhagen E, Polman A, Kuipers L K. Nanofocusing in laterally tapered plasmonic waveguides. Opt Express 16, 45-57 (2008). doi: 10.1364/OE.16.000045 [21] Tugchin B N, Janunts N, Klein A E, Steinert M, Fasold S et al. Plasmonic tip based on excitation of radially polarized conical surface plasmon polariton for detecting longitudinal and transversal fields. ACS Photonics 2, 1468-1475 (2015). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00339 [22] Stadler J, Schmid T, Zenobi R. Developments in and practical guidelines for tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale 4, 1856-1870 (2012). doi: 10.1039/C1NR11143D [23] Huang T X, Huang S C, Li M H, Zeng Z C, Wang X et al. Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: tip-related issues. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 8177-8195 (2015). doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8968-8 [24] Verma P. Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: technique and recent advances. Chem Rev 117, 6447-6466 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00821 [25] Ropers C, Neacsu C C, Elsaesser T, Albrecht M, Raschke M B et al. Grating-coupling of surface plasmons onto metallic tips: a nanoconfined light source. Nano Lett 7, 2784-2788 (2007). doi: 10.1021/nl071340m [26] Neacsu C C, Berweger S, Olmon R L, Saraf L V, Ropers C et al. Near-field localization in plasmonic superfocusing: a nanoemitter on a tip. Nano Lett 10, 592-596 (2010). doi: 10.1021/nl903574a [27] Berweger S, Atkin J M, Olmon R L, Raschke M B. Light on the tip of a needle: plasmonic nanofocusing for spectroscopy on the nanoscale. J Phys Chem Lett 3, 945-952 (2012). doi: 10.1021/jz2016268 [28] Xu T, Wang C T, Du C L, Luo X G. Plasmonic beam deflector. Opt Express 16, 4753-4759 (2008). doi: 10.1364/OE.16.004753 [29] Xu T, Du C L, Wang C T, Luo X G. Subwavelength imaging by metallic slab lens with nanoslits. Appl Phys Lett 91, 201501 (2007). doi: 10.1063/1.2811711 [30] Luo X G, Ishihara T. Surface plasmon resonant interference nanolithography technique. Appl Phys Lett 84, 4780 (2004). doi: 10.1063/1.1760221 [31] Sadiq D, Shirdel J, Lee J S, Selishcheva E, Park N et al. Adiabatic nanofocusing scattering-type optical nanoscopy of individual gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 11, 1609-1613 (2011). doi: 10.1021/nl1045457 [32] Müller M, Kravtsov V, Paarmann A, Raschke M B, Ernstorfer R. Nanofocused Plasmon-driven sub-10 fs electron point source. ACS Photonics 3, 611-619 (2016). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00710 [33] Schmidt S, Piglosiewicz B, Sadiq D, Shirdel J, Lee J S et al. Adiabatic nanofocusing on ultrasmooth single-crystalline gold tapers creates a 10-nm-sized light source with few-cycle time resolution. ACS Nano 6, 6040-6048 (2012). doi: 10.1021/nn301121h [34] Berweger S, Atkin J M, Olmon R L, Raschke M B. Adiabatic Tip-Plasmon focusing for Nano-Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem Lett 1, 3427-3432 (2010). doi: 10.1021/jz101289z [35] Kravtsov V, Atkin J M, Raschke M B. Group delay and dispersion in adiabatic plasmonic nanofocusing. Opt Lett 38, 1322-1324 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OL.38.001322 [36] Esmann M, Becker S F, da Cunha B B, Brauer J H, Vogelgesang R et al. k-space imaging of the eigenmodes of sharp gold tapers for scanning near-field optical microscopy. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 4, 603-610 (2013). doi: 10.3762/bjnano.4.67 [37] Mihaljevic J, Hafner C, Meixner A J. Grating enhanced apertureless near-field optical microscopy. Opt Express 23, 18401-18414 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OE.23.018401 [38] Lee J S, Han S, Shirdel J, Koo S, Sadiq D et al. Superfocusing of electric or magnetic fields using conical metal tips: effect of mode symmetry on the plasmon excitation method. Opt Express 19, 12342-12347 (2011). doi: 10.1364/OE.19.012342 [39] Andrey P. Nanofocusing of surface Plasmons at the apex of metallic probe tips. J Nanoelectron Optoe 5, 310-314 (2010). doi: 10.1166/jno.2010.1116 [40] Johnson P B, Christy R W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6, 4370-4379 (1972). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370 [41] Palik E D. Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (Academic, San Diego, America, 1998). [42] Stockman M I. Nanofocusing of optical energy in tapered plasmonic waveguides. Phys Rev Lett 93, 137404 (2004). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.137404 [43] Fang Z Y, Lin C F, Ma R M, Huang S, Zhu X. Planar plasmonic focusing and optical transport using CdS nanoribbon. ACS Nano 4, 75-82 (2010). doi: 10.1021/nn900729n [44] Fang Z Y, Fan L R, Lin C F, Zhang D, Meixner A J et al. Plasmonic coupling of bow tie antennas with Ag nanowire. Nano Lett 11, 1676-1680 (2011). doi: 10.1021/nl200179y [45] Gurevich V S, Libenson M N. Surface polaritons propagation along micropipettes. Ultramicroscopy 57, 277-281 (1995). doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(94)00152-D [46] Babadjanyan A J, Margaryan N L, Nerkararyan K V. Superfocusing of surface polaritons in the conical structure. J Appl Phys 87, 3785 (2000). doi: 10.1063/1.372414 [47] Zhang W D, Huang L G, Wei K Y, Li P, Jiang B Q et al. Cylindrical vector beam generation in fiber with mode selectivity and wavelength tunability over broadband by acoustic flexural wave. Opt Express 24, 10376-10384 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OE.24.010376 [48] Novotny L, Hafner C. Light propagation in a cylindrical waveguide with a complex, metallic, dielectric function. Phys Rev E 50, 4094-4106 (1994). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.50.4094 [49] Gramotnev D K, Vogel M W, Stockman M I. Optimized nonadiabatic nanofocusing of plasmons by tapered metal rods. J Appl Phys 104, 034311 (2008). doi: 10.1063/1.2963699 [50] Issa N A, Guckenberger R. Optical nanofocusing on tapered metallic waveguides. Plasmonics 2, 31-37 (2007). doi: 10.1007/s11468-006-9022-7 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Mode evolution and nanofocusing of grating-coupled surface plasmon polaritons on metallic tip 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
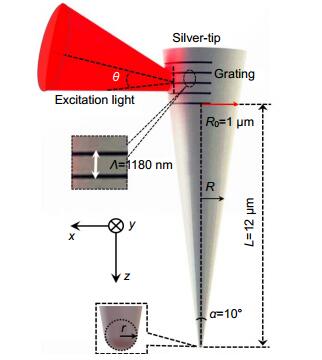
Figure 1.
Geometry of a conical silver tip with grating-assisted light coupling.
-
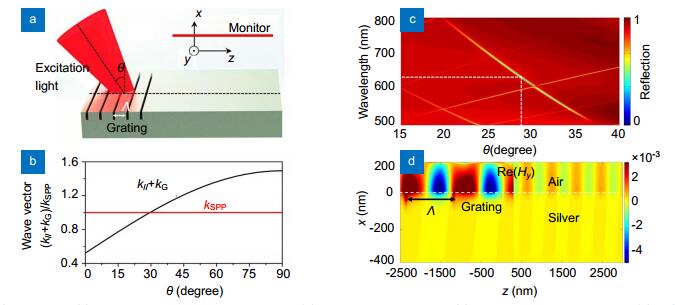
Figure 2.
(a) Sketch map of SPPs excitation using a planar grating; (b) Dispersion relationship of SPPs and the grating coupling; (c) Reflection obtained from the field monitor located above the surface without grating; (d) Re(Hy) distribution of the grating-coupled SPPs generation and propagation along the silver-air interface with excitation wavelength at λ=632.8 nm and θ=28.5°.
-
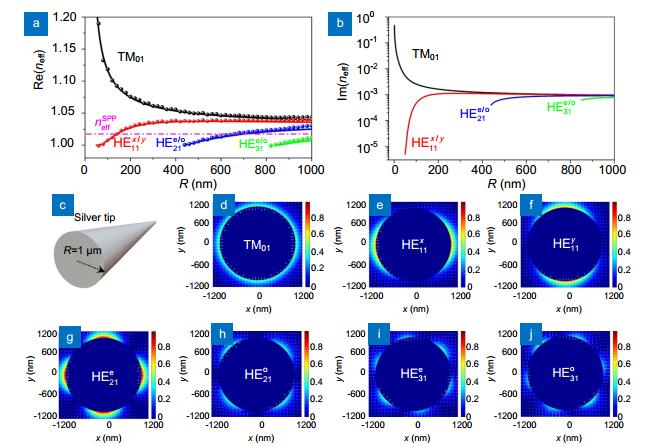
Figure 3.
Effective indices neff in real part (a) and imaginary part (b) of guided SPP modes versus the radius of cylindrical silver guide R. (c) Sketch map of a silver tip removing the diffracting grating. (d–j) Transverse modes intensity distributions of guided modes for R=1 μm.
-
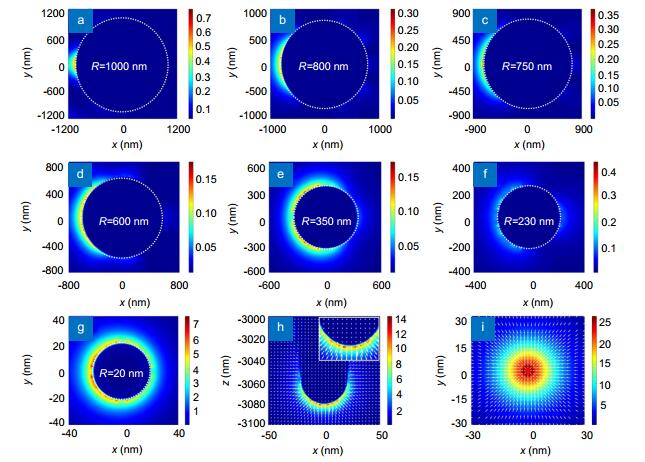
Figure 4.
(a) Transverse mode intensity distributions of the grating-coupled SPPs at R=1 μm; (b–g) Transverse mode intensity distributions of the hybrid mode at R=800, 750, 600, 350, 230, and 20 nm, respectively. (h) Electric field intensity distribution at the tip apex. (i) Transverse electric field intensity distribution at 1 nm below the tip apex.
-
Figure 5.
Adiabatic parameter δ of TM01 mode versus R.
-
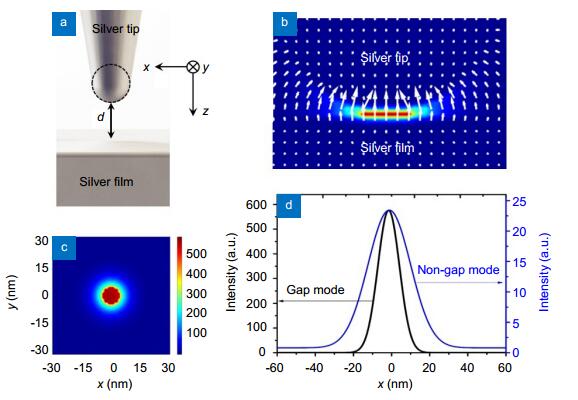
Figure 6.
(a) Gap-mode configuration with the gap distance d=2 nm. (b) Electric field intensity and polarization distributions in the x-z plane. (c) Electric field intensity distribution in the x-y plane at 1 nm below the tip apex. (d) Comparison of electric field enhancement factor between the non-gap mode (Fig. 4(i)) and gap mode located at 1 nm below the apex of the silver tip.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: