-
摘要:
从斜率复原波前是夏克-哈特曼波前传感器这一类斜率采样探测器的核心流程。传统的复原算法中,区域法对局部波前的复原效果好,但易受斜率噪声的影响,同时空间分辨率较低;模式法抗噪能力强,但没有精确复原局部波前的能力。本文提出了基于B样条函数的快速复原算法,将波前展开为B样条曲面的线性组合,并将复原问题从斜率最小二乘问题转化为泊松方程,利用斜率的Taylor展开式估计散度,再通过超松驰迭代法进行快速求解。该方法将B样条函数的理论散度积分和实际散度估计分离,可以方便地扩展到不同阶次和不同节点数量的B样条基复原算法中。另外,通过改变散度估计的计算区域,可以灵活控制并平衡算法的局部复原能力和抗噪能力。对变形镜驱动器响应函数的测量实验表明,该方法具有较好的局部复原能力、抗噪能力和任意精度的空间分辨率。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Traditional schemes for Shack-Hartmann wavefront reconstruction can be classified into zonal and modal methods. The zonal methods are good at reconstructing the local details of the wavefront, but are sensitive to the noise in the slope data. The modal methods are much more robust to the noise, but they have limited capability of recovering the local details of the wavefront. In this paper, a B-spline based fast wavefront reconstruction algorithm in which the wavefront is expanded to the linear combination of bi-variable B-spline curved surfaces is proposed. Then, a method based on successive over relaxation (SOR) algorithm is proposed to fast reconstruct the wavefront. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can recover the local details of the wavefront as good as the zonal methods, while is much more robust to the slope noise.
-
Key words:
- B-spline function /
- wavefront reconstruction /
- Hartmann wavefront sensor
-

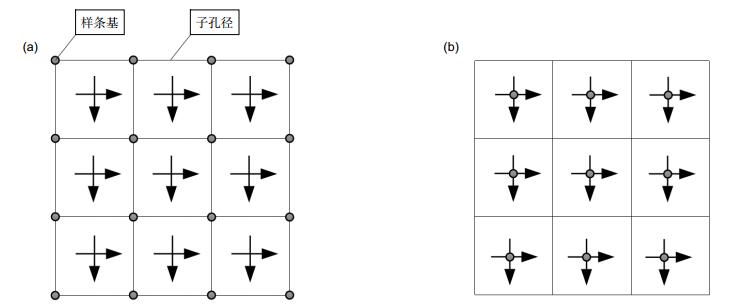
Overview: Reconstructing wavefront from sampled slopes is the key to the slope sampling wavefront sensors, such as the Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensors and the pyramid wavefront sensors. Traditional reconstruction schemes can be classified into zonal and modal methods. The zonal methods reconstruct the wavefront by solving the slope differential-based least squares problem, in which the slopes are related to the wavefront data sampled in a predefined grid. These methods are good at reconstructing the local details of the wavefront, but are sensitive to the noise in the slope data. Besides, as it can only calculate the wavefront data in the grid, interpolation methods are needed to retrieve the wavefront data of higher spatial resolution, which may introduce additional error. The modal methods expand the wavefront to the linear combination of orthogonal polynomials, such as Zernike polynomials for the radical pupil and Legendre polynomials for the rectangle pupil. These methods are much more robust to the noise, but they have limited ability in recovering the local details of the wavefront. Hence, more polynomials are needed to recover the local details, but it will make the reconstruction process more ill-posed at the same time.
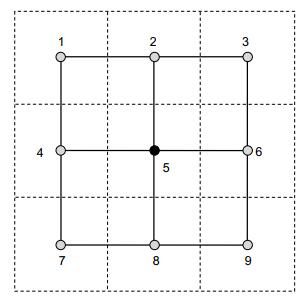
In this paper, a B-spline based fast wavefront reconstruction algorithm is proposed. The wavefront is expanded to the linear combination of bi-variable B-spline curved surfaces first. Then the reconstruction problem is converted from the least-mean squares of slopes to a Poisson problem, in which only the theoretical divergence and the measured divergence are utilized. The theoretical divergence can be calculated efficiently by the integration of divergences of the related B-spline bases, and the measured divergence can be easily estimated by the Taylor expanding of the local slopes. Then, the Poisson problem can be efficiently solved by employing successive over relaxation (SOR) method.
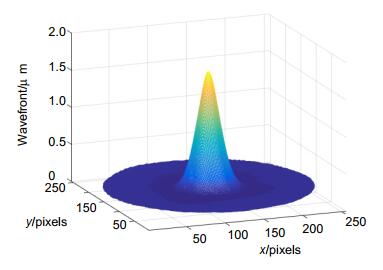
To evaluate the performance of the proposed method, an experiment of measuring the influence functions of the actuators of a piezoelectric deformed mirror is performed. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can recover the local details of the wavefront as good as the zonal methods, while is much more robust to the slope noise. Besides, thanks to the analytic solution of wavefront, it can retrieve the high spatial resolution data directly. As the proposed method separates the theory divergence calculation of the B-spline bases from the slopes, it can be easily extended to other reconstruction problems with different orders and control knots of B-spline surfaces utilized. Last but not least, the ability of recovering the local details and robustness to slope noise can be easily balanced by changing the layout of the knot and the calculation area of divergence estimation.
-

-
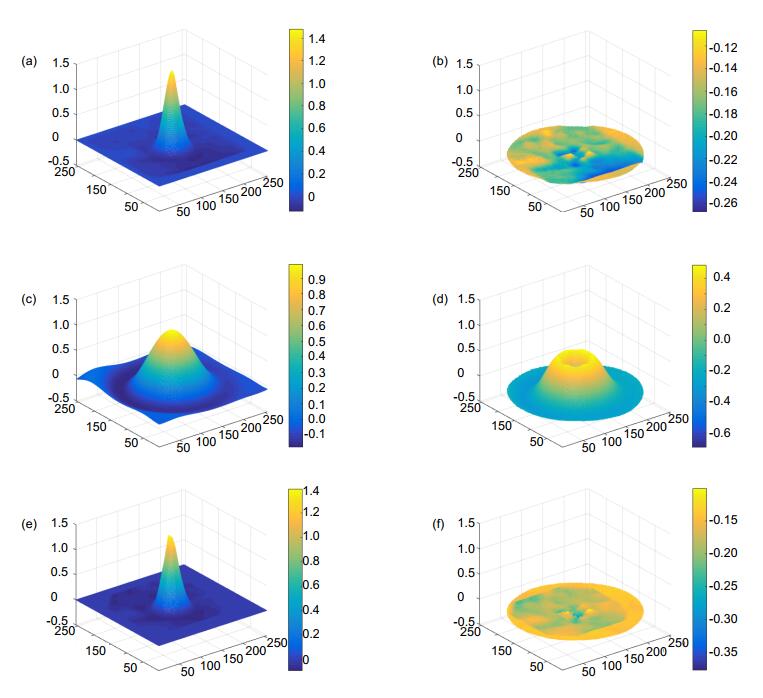
图 6 不同复原方法复原结果。(a) 本文算法重建波前;(b) 本文算法的残余波前;(c) 基于Zernike多项式的模式法重建波前;(d) 模式法的残余波前;(e) Fried区域法重建波前;(f) 区域法的残余波前
Figure 6. Wavefronts restored by different methods. (a) Wavefront restored by our method; (b) Residual wavefront error of (a); (c) Wavefront restored by the modal method; (d) Residual wavefront error of (c); (e) Wavefront restored by the zonal method; (f) Residual wavefront error of (e)
表 1 不同复原方法结果比较(4#驱动器)
Table 1. Comparison results of different wavefront reconstruction methods
数据类型 波前 残差 相关值/% PV/μm RMS/μm PV/μm RMS/μm 原始 1.579 0.159 - - - 区域法 1.493 0.184 0.277 0.026 94.8 Zernike模式法(35项) 1.163 0.259 1.185 0.232 85.1 本文方法 1.612 0.167 0.162 0.028 97.2 表 2 不同驱动器复原残差及相关值
Table 2. Residual reconstruction error and correlation values of different actuators
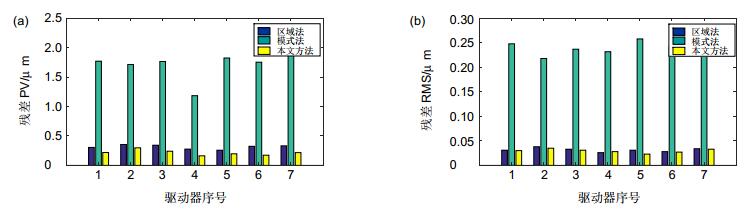
驱动器序号 区域法 Zernike模式法(35项) 本文方法 PV/μm RMS/μm 相关值/% PV/μm RMS/μm 相关值/% PV/μm RMS/μm 相关值/% 1 0.305 0.031 99.4 1.772 0.248 84.3 0.219 0.030 99.8 2 0.355 0.038 99.1 1.715 0.218 82.5 0.299 0.035 99.7 3 0.343 0.033 99.7 1.767 0.237 81.2 0.241 0.031 99.6 4 0.277 0.026 94.8 1.185 0.232 85.1 0.162 0.028 97.2 5 0.258 0.031 98.7 1.825 0.258 85.6 0.196 0.023 99.8 6 0.323 0.028 99.6 1.754 0.243 78.3 0.172 0.027 99.7 7 0.332 0.034 99.5 2.004 0.261 82.9 0.217 0.033 99.6 -
[1] Furukawa Y, Takaie Y, Maeda Y, et al. Development of one-shot aspheric measurement system with a Shack-Hartmann sensor[J]. Appl Opt, 2016, 55(29): 8138–8144. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.008138
[2] Wu Y, He J C, Zhou X T, et al. A limitation of Hartmann-Shack system in measuring wavefront aberrations for patients received laser refractive surgery[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2): e0117256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117256
[3] 杨泽平, 李恩德, 张小军, 等. "神光-Ⅲ"主机装置的自适应光学波前校正系统[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 180049. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180049
Yang Z P, Li E D, Zhang X J, et al. Adaptive optics correction systems on Shen Guang Ⅲ facility[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(3): 180049. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180049
[4] 周睿, 魏凌, 李新阳, 等. 点光源哈特曼最优阈值估计方法研究[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(9): 090701. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB201709006.htm
Zhou R, Wei L, Li X Y, et al. Shack-Hartmann optimum threshold estimation for the point source[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2017, 66(9): 090701. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB201709006.htm
[5] Wei L, Shi G H, Lu J, et al. Centroid offset estimation in the Fourier domain for a highly sensitive Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. J Opt, 2013, 15(5): 055702. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/15/5/055702
[6] Fried D L. Least-square fitting a wave-front distortion estimate to an array of phase-difference measurements[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1977, 67(3): 370–375. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.67.000370
[7] Southwell W H. Wave-front estimation from wave-front slope measurements[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1980, 70(8): 998–1006. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.70.000998
[8] Dai F Z, Tang F, Wang X Z, et al. Modal wavefront reconstruction based on Zernike polynomials for lateral shearing interferometry: comparisons of existing algorithms[J]. Appl Opt, 2012, 51(21): 5028–5037. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.005028
[9] Lee H. Use of Zernike polynomials for efficient estimation of orthonormal aberration coefficients over variable noncircular pupils[J]. Opt Lett, 2010, 35(13): 2173–2175. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.002173
[10] Nam J, Thibos L N, Iskander D R. Zernike radial slope polynomials for wavefront reconstruction and refraction[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2009, 26(4): 1035–1048. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.26.001035
[11] 汤国茂, 何玉梅, 廖周. 大型光学系统径向哈特曼像质检测方法[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(3): 795–799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201003040.htm
Tang G M, He Y M, Liao Z. Radial Hartmann method for measuring large optical system[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2010, 37(3): 795–799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201003040.htm
[12] Darudi A, Bakhshi H, Asgari R. Image restoration using aberration taken by a Hartmann wavefront sensor on extended object, towards real-time deconvolution[J]. Proc SPIE, 2015, 9530: 95300Q. doi: 10.1117/12.2184852
[13] Seifert L, Tiziani H J, Osten W. Wavefront reconstruction with the adaptive Shack–Hartmann sensor[J]. Opt Commun, 2005, 245(1–6): 255–269. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2004.09.074
[14] Ares M, Royo S. Comparison of cubic B-spline and Zernike-fitting techniques in complex wavefront reconstruction[J]. Appl Opt, 2006, 45(27): 6954–6964. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.006954
[15] de Visser C C, Verhaegen M. Wavefront reconstruction in adaptive optics systems using nonlinear multivariate splines[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2013, 30(1): 82–95. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.30.000082
[16] Huang L, Xue J P, Gao B, et al. Spline based least squares integration for two-dimensional shape or wavefront reconstruction[J]. Opt Lasers Eng, 2017, 91: 221–226. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.12.004
[17] Pant K K, Burada D R, Bichra M, et al. Weighted spline based integration for reconstruction of freeform wavefront[J]. Appl Opt, 2018, 57(5): 1100–1109. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.001100
[18] Knott G D. Interpolating Cubic Splines[M]. Boston: Birkhäuser, 2000.
[19] 叶其孝, 沈永欢. 实用数学手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
[20] Yang J S, Wei L, Chen H L, et al. Absolute calibration of Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor by spherical wavefronts[J]. Opt Commun, 2010, 283(6): 910–916. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.11.022
[21] Xie D X. A new block parallel SOR method and its analysis[J]. SIAM J Sci Comput, 2006, 27(5): 1513–1533. doi: 10.1137/040604777
[22] Chamot S R, Dainty C, Esposito S. Adaptive optics for ophthalmic applications using a pyramid wavefront sensor[J]. Opt Express, 2006, 14(2): 518–526. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.14.000518
[23] Chanteloup J C F, Cohen M. Compact high resolution four wave lateral shearing interferometer[J]. Proc SPIE, 2004, 5252: 282–292. doi: 10.1117/12.513739
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: