Despeckling for side-scan sonar images based on adaptive block-matching and 3D filtering
-
摘要:
侧扫声纳(SSS)是一种利用声波的水下传播特性完成水下探测的电子设备。因为侧扫声纳利用回波强度成像,所以不可避免地引入散斑噪声。本文针对散斑噪声,提出了基于自适应三维块匹配滤波(BM3D)的侧扫声纳图像散斑降噪方法。该算法首先对SSS图像进行幂变换和对数变换,采用小波变换估计整体图像噪声,同时用局部噪声估计结果更新BM3D算法的参数。然后本文算法比较全局估计和局部估计的结果,选择最合适的参数解决噪声分布不均匀的问题。实验结果表明,本文改进的BM3D算法能有效地降低SSS图像中的散斑噪声,获得良好的视觉效果。本文算法的等效视数至少提高了6.83%,散斑抑制指数低于传统方法,散斑抑制和平均保存指数至少减少了3.30%。该方法主要用于声纳图像降噪,对于超声、雷达或OCT图像等受散斑噪声污染的信号也有一定的实用价值。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Side-scan sonar (SSS) is an electronic device that utilizes the propagation characteristics of sound waves under water to complete underwater detection. Because the SSS produces images and maps according to the intensity of acoustic echo, speckle noise will be inevitably involved. A speckle denoising method based on block-matching and 3D filtering (BM3D) is proposed to filter the multiplicative speckle noise in SSS images. First, the SSS image is transformed by power and logarithm. The wavelet transform is used to estimate the general noisy level of the polluted image. Second, the parameters of the BM3D algorithm are updated according to the noise estimation results of each local patch. At last, after comparing the general noise estimation and the local noise estimation, the proposed algorithm chooses the best estimation to filter every patch separately to solve the problem that the noise is not evenly distributed. The experimental results show that the improved BM3D algorithm can effectively reduce the speckle noise in SSS images and obtain good visual effects. The Equivalent Number of Looks of the proposed algorithm is at least 6.83% higher, the Speckle Suppression Index is lower than traditional algorithm, and the Speckle Suppression and Mean Preservation Index is reduced by at least 3.30%. This method is mainly used for sonar image noise reduction, and has certain practical values for ultrasonic, radar or OCT images polluted by speckle noise.
-
Key words:
- side scan sonar /
- speckle noise /
- image denoising /
- BM3D
-

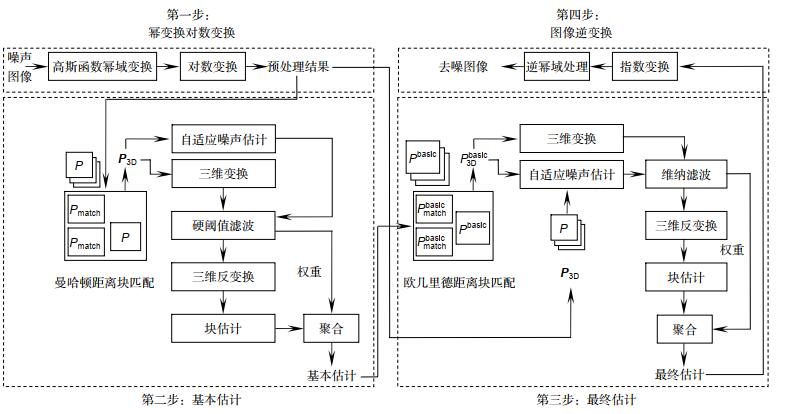
Overview: An understanding of the ocean and its changing environment is increasingly important. Scientific, economic, and political decision-making depends to some extent on this knowledge. However, even lasers can penetrate through only a few tens of meters in very clear water. Acoustic waves, by contrast, can travel over long distances without much attenuation. Therefore, all kinds of sonars play an important role in ocean research. Side-scan sonar (SSS) is an electronic device that utilizes the propagation characteristics of sound waves under water to complete underwater detection and communication tasks through electro-acoustic conversion and information processing. Because the SSS produces images and maps according to the intensity of acoustic echo, speckle noise will inevitably be involved due to the complex underwater environments. Block-matching and 3D filtering (BM3D) is an advanced denoising method based on the fact that an image has a locally sparse representation in transform domain. This sparsity is enhanced by grouping similar 2D image patches into 3D groups. This algorithm performs well in dealing images polluted by Gaussian additive noise. The BM3D algorithm was originally designed for Gaussian additive noise, therefore, it is not reasonable to denoise the side-scan sonar images polluted by speckle noise. In this paper, a speckle denoising method based on BM3D is proposed to filter the multiplicative speckle noise in side-scan sonar images. First, the SSS image is transformed by power and logarithm. The multi-scale two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform is used to estimate the general noisy level of the polluted image. Second, the parameters of the BM3D algorithm are updated according to the noise estimation results of each local patch. Third, after comparing the general noise estimation and the local noise estimation, the proposed algorithm chooses the best estimation to filter every patch separately to solve the problem that the noise is not evenly distributed. Finally, the image properties are recovered by exponential transformation and inverse power transformation. The experimental results show that the improved BM3D algorithm can effectively reduce the speckle noise in SSS images and obtain good visual effects. In this paper, three non-reference image quality evaluation parameters, namely the equivalent noise of looks (ENL), speckle reduction index (SSI), speckle suppression and average preservation index (SMPI), are used to evaluate the noise reduction effect. Compared with two kinds of improved BM3D algorithms and a traditional algorithm, the ENL of the proposed algorithm is at least 6.83% higher than that of others, its SSI is very similar to that of Manhattan distance-based adaptive block-matching and 3D filtering(MD-ABM3D), and its SMPI is reduced by at least 3.30%. This method is mainly used for sonar image noise reduction, and has certain practical values for ultrasonic, radar or OCT images polluted by speckle noise.
-

-
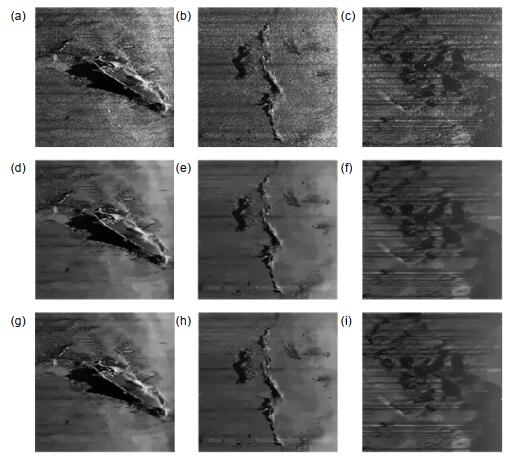
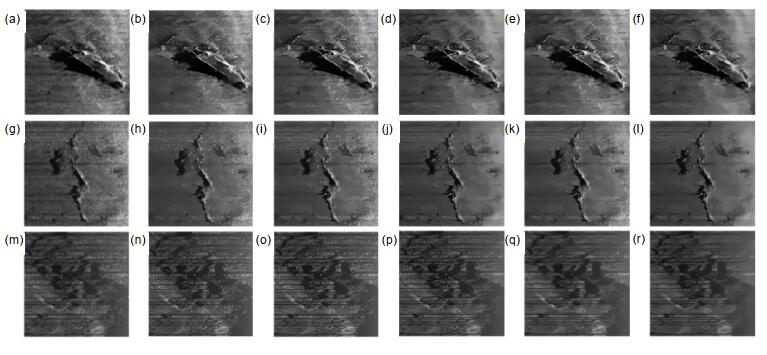
图 4 实际侧扫声纳图像算法处理效果图。(a), (g), (m)中值滤波;(b), (h), (n) NLM;(c), (i), (o)原始BM3D算法;(d), (j), (p) Fan等人[18];(e), (k), (q) MD-ABM3D算法;(f), (l), (r)本文算法
Figure 4. Real side scan sonar image algorithm processing result. (a), (g), (m) Median filtering; (b), (h), (n) NLM; (c), (i), (o) Original BM3D algorithm; (d), (j), (p) Fan et al.[18]; (e), (k), (q) MD-ABM3D; (f), (l), (r) Proposed algorithm
表 1 图像质量评价表
Table 1. Table of image quality assessments
Distance Boat image Undersea bulge image Undulating seabed topography ENL SSI SMPI ENL SSI SMPI ENL SSI SMPI Euclid 182.5115 0.8055 0.7647 567.4178 0.6824 0.6411 1561 0.6537 0.6330 Manhattan 186.2087 0.8019 0.7607 567.8609 0.6823 0.6410 1573.2 0.6526 0.6129 表 2 各算法图像质量评价表
Table 2. Table of image quality assessments for every method
Method Boat image Undersea bulge image Undulating seabed topography ENL SSI SMPI ENL SSI SMPI ENL SSI SMPI NLM 128.6324 0.8526 0.8438 324.71 0.7562 0.7473 505.1883 0.8351 0.8274 Original BM3D 139.4080 0.8328 0.8279 355.2878 0.7368 0.7315 582.1099 0.8050 0.7991 Fan[18] 178.0088 0.8100 0.7967 524.0642 0.6952 0.6543 773.3008 0.7703 0.7348 MD-ABM3D 157.3744 0.8084 0.8031 489.912 0.6819 0.6762 1471.5 0.6401 0.6330 Proposed method 186.2087 0.8019 0.7607 567.8609 0.6823 0.6410 1573.2 0.6526 0.6116 -
[1] Blondel P. The Handbook of Sidescan Sonar[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 1-6.
[2] Ye X F, Li P, Deng Y Y. A side scan sonar image denoising algorithm based on compound of fuzzy weighted average and Kalman filter[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Chengdu, China, 2012: 720-724.
[3] Devapal D, Kumar S S, Sethunadh R. Discontinuity adaptive SAR image despeckling using curvelet-based BM3D technique[J]. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing, 2019, 17(3): 1950016. doi: 10.1142/S0219691319500164
[4] Lee J S, Grunes M R, De Grandi G. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2363-2373. doi: 10.1109/36.789635
[5] Kuan D T, Sawchuk A A, Strand T C, et al. Adaptive noise smoothing filter for images with signal-dependent noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1985, PAMI-7(2): 165-177. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1985.4767641
[6] Frost V S, Stiles J A, Shanmugan K S, et al. A model for radar images and its application to adaptive digital filtering of multiplicative noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, PAMI-4(2): 157-166. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21869022
[7] Buades A, Coll B, Morel J M. Non-local means denoising[J]. Image Processing On Line, 2011, 1: 208-212. doi: 10.5201/ipol.2011.bcm_nlm
[8] Wang J, Guo Y W, Ying Y T, et al. Fast non-local algorithm for image denoising[C]//Proceedings of 2006 International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2006: 1429-1432.
[9] 李世文, 张彬, 刘泽民, 等.基于波原子阈值算法的OCT图像降噪技术[J].光电工程, 2014, 41(7): 75-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.07.013
Li S W, Zhang B, Liu Z M, et al. Noise reduction for OCT images based on wave-atom thresholding algorithm[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2014, 41(7): 75-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.07.013
[10] 王帆, 陈明惠, 高乃珺, 等.基于字典算法的OCT图像散斑稀疏降噪[J].光电工程, 2019, 46(6): 180572. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180572
Wang F, Chen M H, Gao N J, et al. OCT image speckle sparse noise reduction based on dictionary algorithm[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2019, 46(6): 180572. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180572
[11] Lebrun M. An analysis and implementation of the BM3D image denoising method[J]. Image Processing On Line, 2012, 2: 175-213. doi: 10.5201/ipol.2012.l-bm3d
[12] Gao J B, Chen Q, Blasch E. Image denoising in the presence of non-Gaussian, power-law noise[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 2012: 103-108.
[13] Yang J Y, Zhang X, Yue H J, et al. IBM3D: integer BM3D for efficient image denoising[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2019, 38(2): 750-763. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00034-018-0882-9
[14] Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, et al. BM3D image denoising with shape-adaptive principal component analysis[C]//Signal Processing with Adaptive Sparse Structured Representations (SPARS), Saint-Malo, France, 2009: 1-6.
[15] Zhong H, Ma K, Zhou Y. Modified BM3D algorithm for image denoising using nonlocal centralization prior[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 106: 342-347. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.08.014
[16] Zhao T T, Hoffman J, McNitt‐Gray M, et al. Ultra‐low‐dose CT image denoising using modified BM3D scheme tailored to data statistics[J]. Medical Physics, 2019, 46(1): 190-198. doi: 10.1002/mp.13252
[17] Cheng W M, Zhu X, Chen X, et al. Manhattan distance-based adaptive 3D transform-domain collaborative filtering for laser speckle imaging of blood flow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(7): 1726-1735. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2896007
[18] 范习健, 李庆武, 黄河, 等.侧扫声呐图像的3维块匹配降斑方法[J].中国图象图形学报, 2012, 17(1): 68-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgtxtxxb-a201201010
Fan X J, Li Q W, Huang H, et al. Side-scan sonar image despeckling based on block-matching and 3D filtering[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2012, 17(1): 68-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgtxtxxb-a201201010
[19] Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238
[20] James R, Supriya M H. Blind estimation of single look side scan sonar image from the observation model[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 93: 336-343. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.07.218
[21] 张洪科. 数字全息再现像中的噪声抑制[D]. 哈尔滨工程大学,2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10217-1017240756.htm.
Zhang H K. Suppression of Noise in Digital Holography[D]. Harbin Engineering University, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10217-1017240756.htm.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: