-
摘要:
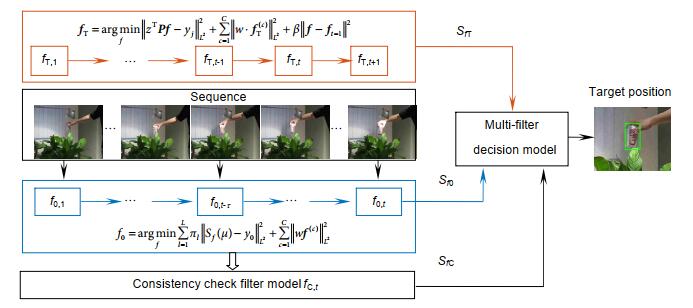
针对单一滤波器难以适应复杂变化的目标跟踪环境的问题,本文在高效卷积算子目标跟踪算法的基础上,提出了自适应多滤波器的目标跟踪算法。该算法使用时空正则化滤波器、一致性检验滤波器和高效卷积算子算法中的相关滤波器分别与目标特征进行卷积,得到三个滤波检测得分。其中,时空正则化滤波器是通过将时间正则化引入相关滤波损失函数而得到;一致性检验滤波器是通过反向定位前几帧目标,比较反向与正向定位坐标的误差,只有误差小于阈值时才更新滤波器;选择峰值旁瓣比最大滤波检测得分,估计目标的位置。使用OTB-2015数据集和UAV123数据集对改进算法进行测试,实验结果表明,本文算法能够更好地适应跟踪过程中的复杂变化的环境,具有较高的精度和鲁棒性。
 Abstract:
Abstract:With the problem of difficulty that a single filter to adapt to various complex changes in the tracking process, an adaptive multi-filter target tracking algorithm based on the efficient convolution operators for tracking is proposed. Spatial-temporal regularized filter, the consistency check filter and the correlation filter in the efficient convolution operator tracker, convolve with target features respectively, which obtains three detection scores. The training method of spatial-temporal regularized filter is to introduce temporal regularization into loss function. The consistency check filter is a filter that uses current filter to track the target of previous several frames and updates only when the error of forward and backward position is less than the threshold. Target position is estimated by the best filter detection score with the peak-to-side ratio is maximum. The improved algorithm is tested with the OTB-2015 dataset and UAV123 dataset. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can better adapt to the complex environment in tracking process, which has high precision and robustness.
-

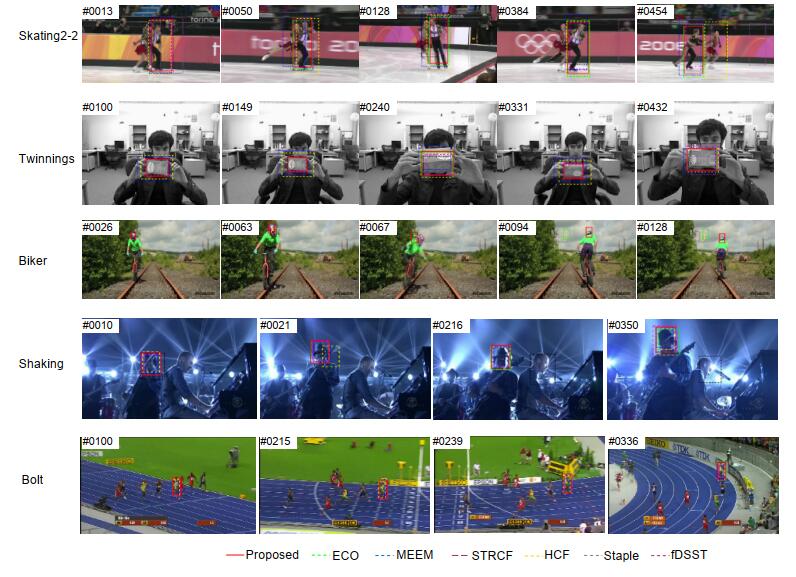
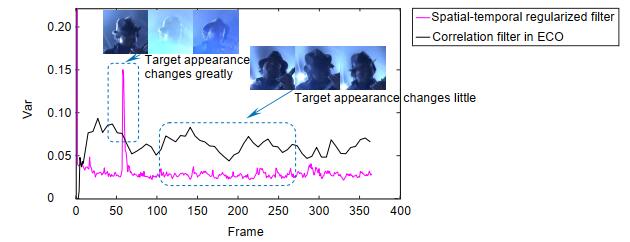
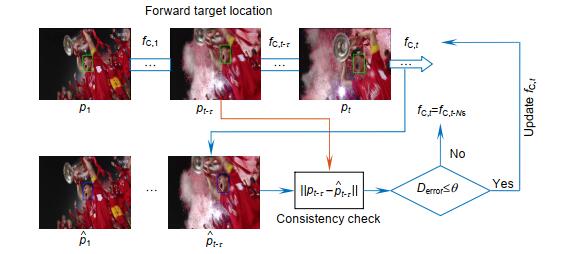
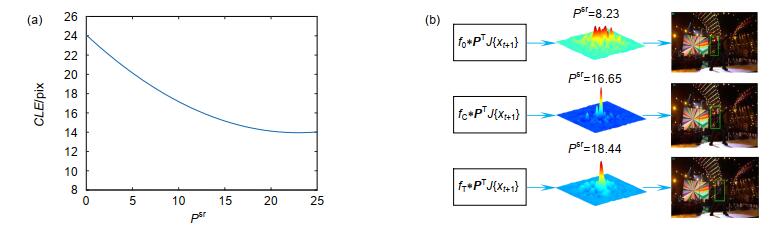
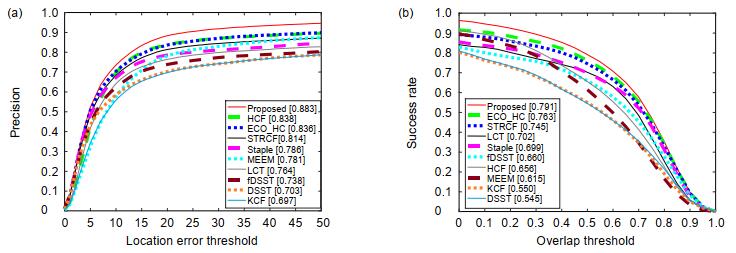
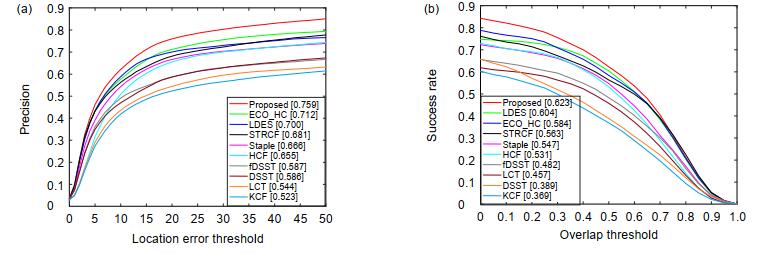
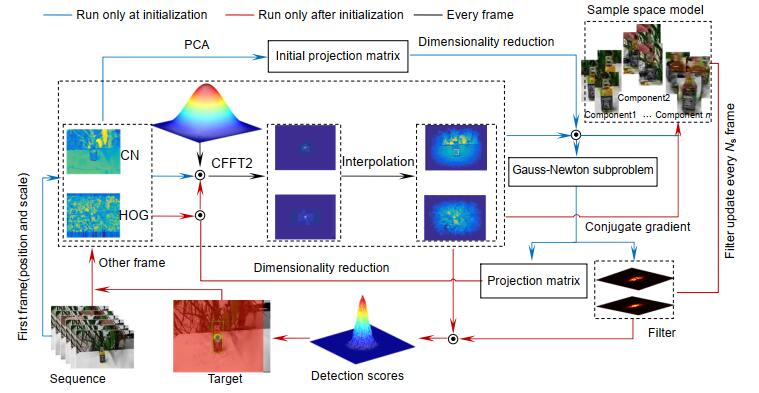
Overview: In the actual target tracking process, the shape and posture of the target are different, and the environment in tracking is complex and changeable. It is difficult for a single filter to cope with the complex changes of the video sequence and tracking environment. To solve this problem, based on the efficient convolution operators for tracking algorithm, a multi-filter target tracking algorithm which can adapt to more complex environments is proposed. The algorithm trains two more filters of spatial-temporal regularization filter and consistency checking filter than the efficient convolution operators for tracking algorithm. The spatial-temporal regularization filter is obtained by introducing the temporal regularization into the loss function of correlation filtering. Spatial-temporal regularization filter can well adapt to the huge changes in the appearance of the target, so it can adapt to the environment that targets variable. The training method of consistency check filter is: firstly, the current filter is used to locate the target that has been tracked forward, and then the errors between the reverse location coordinate and the forward location coordinate are compared. When the error is less than the threshold, the consistency check filter is updated, but not be updated when the distance error is greater than the threshold. The consistency check filter reduces the noise information introduced in the filter update process, so it can be used in the case of more background clutter and noise. The correlation filter in the efficient convolution operators for tracking algorithm retains the most comprehensive target and background feature information, so it is suitable for relatively stable tracking environment with less interference. Spatial-temporal regularization filter, consistency check filter and correlation filter in efficient convolution operators for tracking are convolved with target features respectively, and three filter detection scores are obtained. The filter detection score obeys the Gaussian distribution. The higher the peak to side ratio of detection score, the higher the target tracking accuracy. The position of the target is estimated by the best filter detection score witch the peak to side ratio is more than the other filter detection score. The improved algorithm is evaluated on the OTB-2015 data set and UAV123 data set. Through qualitative and quantitative analysis, the experimental results show that the improved algorithm can better adapt to the complex changing environment in the tracking process, and its accuracy and success are improved, which is superior to most existing tracking algorithms.
-

-
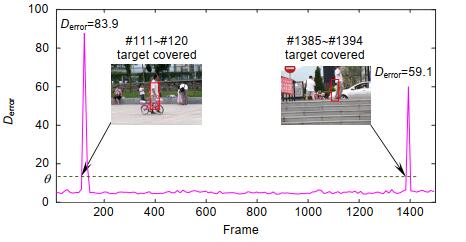
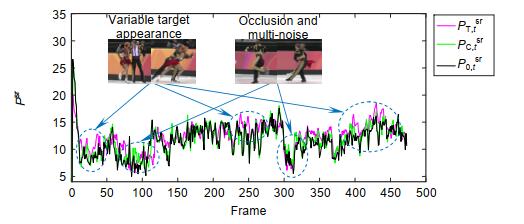
表 1 前向与后向目标轨迹坐标
Table 1. Direction and backward target trajectory coordinates
Frame Backward trace Forward trace Error x y x y 120 371 251 370 251 1.39 121 374 250 378 251 4.41 122 303 227 384 252 83.93 123 310 227 389 252 82.56 124 312 227 310 227 1.89 125 313 226 312 227 1.01 126 294 226 310 226 15.63 127 296 227 311 226 15.55 128 295 227 311 227 15.40 129 295 228 296 226 1.4 130 294 228 295 227 1.77 表 2 不同情况下跟踪算法的精度
Table 2. Accuracy of tracking algorithm in different cases
Tracker STRCF ECO HCF Staple LCT fDSST Proposed IV 0.776 0.787 0.808 0.758 0.714 0.73 0.856 OPR 0.815 0.828 0.804 0.756 0.739 0.751 0.878 SV 0.759 0.769 0.776 0.714 0.642 0.663 0.831 OCC 0.813 0.846 0.819 0.765 0.711 0.695 0.898 DEF 0.821 0.812 0.817 0.76 0.768 0.733 0.871 MB 0.755 0.768 0.805 0.735 0.704 0.701 0.824 FM 0.778 0.754 0.832 0.748 0.717 0.675 0.824 IPR 0.772 0.784 0.792 0.736 0.712 0.674 0.845 OV 0.759 0.736 0.676 0.69 0.59 0.576 0.786 BC 0.783 0.809 0.83 0.731 0.696 0.724 0.870 LR 0.772 0.758 0.797 0.591 0.501 0.599 0.767 表 3 不同情况下跟踪算法的成功率
Table 3. Success of tracking algorithm in different cases
Tracker STRCF ECO HCF Staple LCT fDSST Proposed IV 0.738 0.752 0.604 0.699 0.685 0.658 0.802 OPR 0.728 0.735 0.587 0.645 0.656 0.65 0.762 SV 0.697 0.703 0.544 0.632 0.583 0.574 0.732 OCC 0.729 0.753 0.632 0.673 0.629 0.617 0.778 DEF 0.798 0.783 0.692 0.717 0.757 0.708 0.819 MB 0.72 0.725 0.649 0.653 0.665 0.649 0.743 FM 0.684 0.661 0.659 0.642 0.627 0.603 0.690 IPR 0.686 0.695 0.616 0.645 0.65 0.586 0.727 OV 0.712 0.658 0.543 0.566 0.531 0.559 0.669 BC 0.731 0.761 0.701 0.672 0.665 0.66 0.818 LR 0.688 0.664 0.421 0.46 0.407 0.468 0.637 表 4 8种算法平均重叠率、中心位置误差和速度
Table 4. Overlapping ratio, center location error and speed of 8 tracking algorithms
Tracker ECO fDSST Staple KCF STRCF LCT HCF Proposed OR 0.64 0.55 0.59 0.48 0.65 0.57 0.56 0.67 CLE/(pixel) 24.2 47.4 30.8 44.6 20.5 66.3 22.5 15.2 f/s 50.4 94.3 67.7 249.6 18.2 21.1 3.2 30.5 -
[1] 卢湖川, 李佩霞, 王栋.目标跟踪算法综述[J].模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(1): 61-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mssbyrgzn201801008
Lu H C, Li P X, Wang D. Visual object tracking: a survey[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(1): 61-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mssbyrgzn201801008
[2] 樊香所, 徐智勇, 张建林.改进粒子滤波的弱小目标跟踪[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(8): 170569. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170569
Fan X S, Xu Z Y, Zhang J L. Dim small target tracking based on improved particle filter[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(8): 170569. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170569
[3] 李双双, 赵高鹏, 王建宇.基于特征融合和尺度自适应的干扰感知目标跟踪[J].光学学报, 2017, 37(5): 0515005. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201705025
Li S S, Zhao G P, Wang J Y. Distractor-aware object tracking based on multi-feature fusion and scale-adaption[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(5): 0515005. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201705025
[4] Ross D A, Lim J, Lin R S, et al. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1-3): 125-141. doi: 10.1007/s11263-007-0075-7
[5] Babenko B, Yang M H, Belongie S. Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(8): 1619-1632. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.226
[6] 朱文青, 刘艳, 卞乐, 等.基于生成式模型的目标跟踪方法综述[J].微处理机, 2017, 38(1): 41-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2279.2017.01.011
Zhu W Q, Liu Y, Bian L, et al. Survey on object tracking method base on generative model[J]. Microprocessors, 2017, 38(1): 41-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2279.2017.01.011
[7] 葛宝义, 左宪章, 胡永江.视觉目标跟踪方法研究综述[J].中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(8): 1091-1107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgtxtxxb-a201808001
Ge B Y, Zuo X Z, Hu Y J. Review of visual object tracking technology[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(8): 1091-1107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgtxtxxb-a201808001
[8] Bolme D S, Beveridge J R, Draper B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]//2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010.
[9] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012: 702-715.
[10] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583-596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390
[11] Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310-4318.
[12] Danelljan M, Robinson A, Khan F S, et al. Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016, Cham, 2016: 472-488.
[13] Lukežic A, Vojír T, Zajc L C, et al. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 4847-4856.
[14] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, et al. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 6638-6646.
[15] Li F, Tian C, Zuo W M, et al. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 4904-4913.
[16] 胡硕, 赵银妹, 孙翔.基于卷积神经网络的目标跟踪算法综述[J].高技术通讯, 2018, 28(3): 207-213. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2018.03.003
Hu S, Shao Y M, Sun X. Review of object tracking based on convolutional neural networks[J]. High Technology Letters, 2018, 28(3): 207-213. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2018.03.003
[17] 孙航, 李晶, 杜博, 等.基于多阶段学习的相关滤波目标跟踪[J].电子学报, 2017, 45(10): 2337-2342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.10.004
Sun H, Li J, Du B, et al. Correlation filtering target tracking based on online multi-lifespan learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(10): 2337-2342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.10.004
[18] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834-1848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226
[19] Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016, Cham, 2016: 445-461.
[20] Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F S, et al. Discriminative scale space tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1561-1575. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609928
[21] Ma C, Huang J B, Yang X K, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking[C]//2015 IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3074-3082.
[22] Zhang J M, Ma S G, Sclaroff S. MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization[C]//2014 European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, 2014: 188-203.
[23] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, et al. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 1401-1409.
[24] Ma C, Yang X K, Zhang C Y, et al. Long-term correlation tracking[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 5388-5396.
[25] Li Y, Zhu J K, Hoi S C H, et al. Robust estimation of similarity transformation for visual object tracking[Z]. arXiv: 1712.05231[cs.CV], 2017.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: