-
摘要:
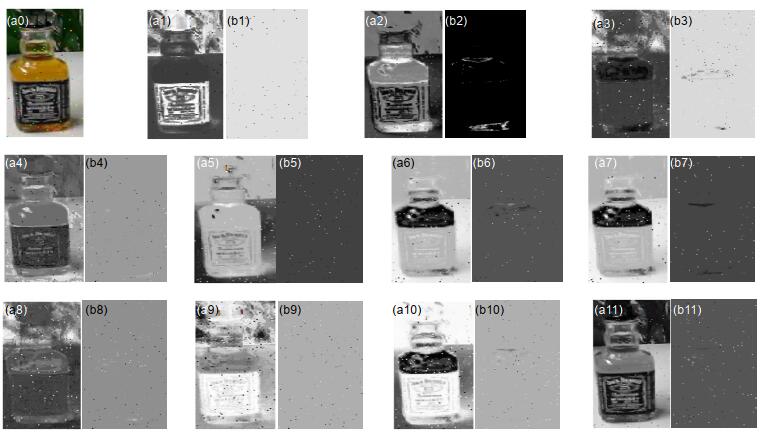
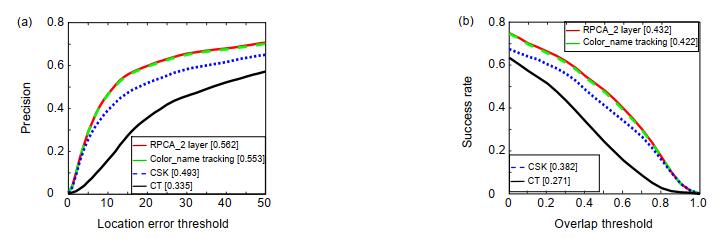
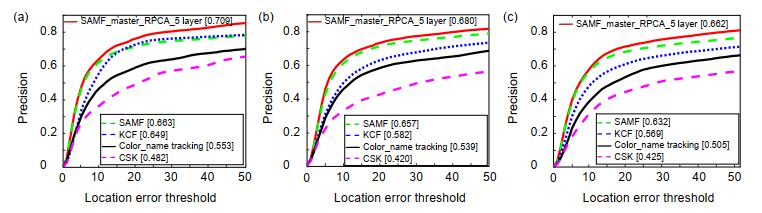
目前使用颜色属性特征表征目标的几种主流算法中,均使用主成分分析法(PCA)处理颜色属性特征,而PCA方法假设输入数据中存在的噪声必须服从高斯分布,该方法存在明显不足。针对这一问题,本文根据鲁棒主成分分析法(Robust PCA)对颜色属性特征进行处理。将输入图像从原始RGB颜色空间映射至颜色属性空间,得到11种不同的颜色属性层;之后,基于Robust PCA处理颜色属性特征,使得映射后的图片信息都集中在少数层上,在保留原始图片大量信息的前提下滤除噪声。本文将使用Robust PCA处理后的颜色属性特征用于原始CN算法框架中并设置不同的降维层数对比其带来的算法性能差异。在OTB100中,与原始CN框架相比,算法成功率提升1.0%,精度提升0.9%。经实验数据证明,通过Robust PCA处理后的颜色属性特征具有更强的鲁棒性,可以更好地发挥出其优势并提升算法性能。
 Abstract:
Abstract:At present, several mainstream algorithms using color name (CN) all adopt principal component analysis (PCA) to process the feature. However, PCA assumes that the noise of input data must obey Gaussian distribution, which is a conspicuous defect. Aim to address this problem, in this paper, we take robust principal component analysis (Robust PCA) to process CN features. The method projects the original RGB color space to a robust color space–CN space, which means that the input image is stratified to 11 layers according to color name. Then, it processes the CN features by the Robust PCA, so that the mapped image information is concentrated on a few layers, retaining a great quantity of image information and filting out noise. The processed feature is used for Color-tracking frame at the standard benchmark OTB100, and we set up different layers to compare the performance differences of the algorithm. The experimental results show that the success rate increases by 1.0% and the accuracy increases by 0.9% at OTB100. The result illustrates that the Robust PCA method can better bring color name feature superiority into full play and improve the performance of the algorithm effectively.
-
Key words:
- visual tracking /
- PCA /
- robust PCA /
- color name
-

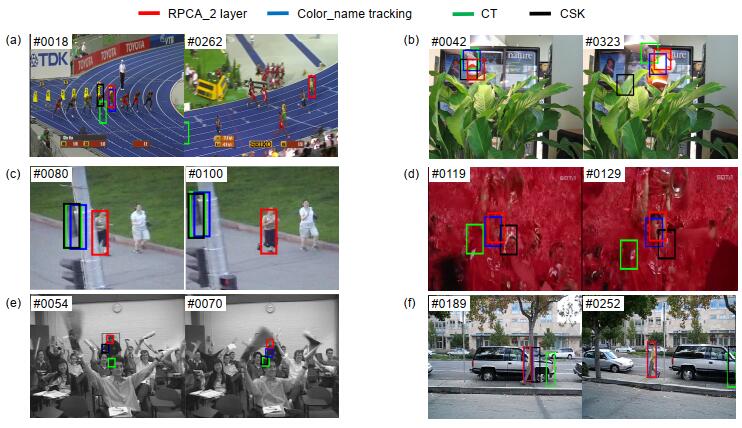
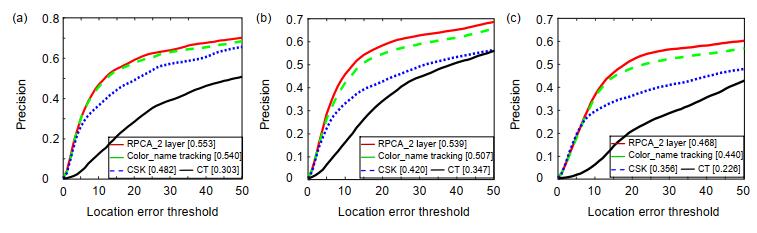
Overview: In the field of image processing, the way of exacting image feature has always been one of the fundamental tasks. Different image descriptions will affect the performance of tracking algorithm directly. There are so many domestic and international researchers proposed classical image features, which can be sorted as two class: 1) based on deep learning, which have gained excellent results, including VGGNet and DenseNet, but it needs a large number of data to train the model and has several restrictions on the experimental platform; 2) based on manual features, which can be took on any platform in exit and also have obtained remarkable performance in image processing, including scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT), histogram of oriented gradient (HOG), and color name (CN). So, making a profound study on manual features is crucial. At present, several mainstream algorithms using CN all adopt principal component analysis (PCA) to process the feature. However, PCA assumes that the noise of input data must obey Gaussian distribution, which is a conspicuous defect. Aim to address this problem, in this paper, we take robust principal component analysis (Robust PCA) to process CN features. The method projects the original RGB color space to a robust color space–CN space, which means that the input image is layered to 11 layers according to CN feature. Then, it processes the CN features by the Robust PCA, so that the mapped image information is concentrated on a few layers, retaining a great quantity of image information and filting out noise. The processed feature is used for Color-name tracking frame at the standard benchmark OTB100, with mainly 11 challenges (e.g., occlusion, deformation). We set up different layers to compare the performance differences of the algorithm. The experimental results show that the success rate increases by 1.0% and the accuracy increases by 0.9% at OTB100. Compared with other classical algorithms, this way shows better robust and distinguishability of feature on visual tracking in most cases. Therefore, using Robust PCA to process CN feature can be significantly applied to other image processing applications. However, this way still has shortages, such as filtering the noise of target not completely in the visual tracking process. In follow-up work, we will further optimize the feature with different ways and try our best to combine the processed feature with deep learning-features to obtain excellent features in visual tracking and to remain applicable to other image processing applications simultaneously.
-

-
表 1 Robust PCA对CN降维至不同层时算法结果比较
Table 1. Performance comparison of algorithm with different feature dimension
算法名称 成功率 精度 Color_name tracking 0.422 0.553 RPCA_2 layer 0.432 0.562 RPCA_3 layer 0.427 0.557 RPCA_4 layer 0.424 0.555 RPCA_5 layer 0.424 0.554 注:每个算法对应的最优值标为黑体,次优算法标为下划 表 2 Robust PCA对CN降维至不同层时算法结果比较
Table 2. Performance comparison of algorithm with different feature dimension
算法名称 成功率 精度 SAMF_Robust_PCA_5 layer 0.563 0.707 SAMF_Robust_PCA_4 layer 0.554 0.695 SAMF_Robust_PCA_3 layer 0.552 0.694 SAMF_Robust_PCA_2 layer 0.545 0.688 SAMF 0.549 0.686 注:每个算法对应的最优值标为黑体,次优算法标为下划 -
[1] 侯志强, 王利平, 郭建新, 等.基于颜色、空间和纹理信息的目标跟踪[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(5): 170643. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170643
Hou Z Q, Wang L P, Guo J X, et al. An object tracking algorithm based on color, space and texture information[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(5): 170643. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170643
[2] Bolme D S, Beveridge J R, Draper B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]//Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010.
[3] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[M]//Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, et al. Computer Vision - ECCV 2012. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2012.
[4] Danelljan M, Khan F S, Felsberg M, et al. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, 2014.
[5] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583-596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390
[6] 刘行, 陈莹.自适应多特征融合目标跟踪[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(3): 58-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.03.010
Liu X, Chen Y. Target tracking based on adaptive fusion of multi-feature[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(3): 58-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.03.010
[7] Li Y, Zhu J K. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration[C]//Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014.
[8] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, et al. Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016.
[9] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, et al. ECO: efficient convolution operators for tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 6931-6939.
[10] Song Y B, Ma C, Gong L J, et al. Crest: convolutional residual learning for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2574-2583.
[11] Nam H, Han B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 4293-4302.
[12] Bhat G, Johnander J, Danelljan M, et al. Unveiling the power of deep tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018.
[13] Lukežic A, Vojir T, Cehovin Zajc L, et al. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 4847-4856.
[14] Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310-4318.
[15] Abdi H, Williams L J. Principal component analysis[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 2010, 2(4): 433-459. doi: 10.1002/wics.101
[16] Zhang J M, Ma S G, Sclaroff S. MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization[C]//Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014.
[17] van de Weijer J, Schmid C, Verbeek J. Learning color names from real-world images[C]//Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2007: 1-8.
[18] van de Weijer J, Schmid C, Verbeek J, et al. Learning color names for real-world applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(7): 1512-1523. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2019809
[19] Shlens J. A tutorial on principal component analysis[Z]. arXiv: 1404.1100[cs: CV], 2014.
[20] 毕笃彦, 库涛, 查宇飞, 等.基于颜色属性直方图的尺度目标跟踪算法研究[J].电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(5): 1099-1106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=pre_c87f6827-2ebd-4204-a91a-37d09c768561
Bi D Y, Ku T, Zha Y F, et al. Scale-adaptive object tracking based on color names histogram[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(5): 1099-1106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=pre_c87f6827-2ebd-4204-a91a-37d09c768561
[21] Shahid N, Perraudin N, Kalofolias V, et al. Fast robust PCA on graphs[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2016, 10(4): 740-756. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2555239
[22] Netrapalli P, Niranjan U N, Sanghavi S, et al. Non-convex robust PCA[C]//Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2014: 1107-1115.
[23] Xu H, Caramanis C, Sanghavi S. Robust PCA via outlier pursuit[C]//Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 2010: 2496-2504.
[24] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834-1848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226
[25] Zhang K H, Zhang L, Yang M H. Real-time compressive tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 864-877.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: