-
摘要:
金属材料的激光加工目前正向着低表面粗糙度、小热影响区及大深径比结构的趋势发展。新近发展了一种基于激光-水射流耦合原理的水导激光加工技术,本文阐述了水导激光加工技术的基本原理及其相对于传统激光加工方法的优势,基于激光-水射流耦合原理构建了一套水导激光加工设备,对多种金属材料进行了水导激光加工实验。利用超景深显微镜对加工工件表面进行了观测与分析,发现两种金属材料加工得到的盲孔边缘规则圆滑,切槽的边缘平直无毛刺,没有热影响区。实验结果说明对金属材料的水导激光精密加工具有可行性且有重要的应用价值。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The development direction of metal material laser processing is to achieve small roughness, less heat-affected zone and high depth-diameter ratio. Recently, a kind of water-conducting laser processing technology based on laser water-jet coupling technology has been developed. The basic principle of water-conducting laser processing technology and its advantages over traditional laser processing methods are expounded. Based on the principle of laser water-jet coupling technology, a set of water-conducting laser processing equipment is constructed. The experiments of water-conducting laser processing for various metal materials are carried out. The surfaces of work piece are observed and analyzed by Leica DVM6 digital microscope. The edges of blind holes in two kinds of metal materials are regular and smooth, the edges of grooves are straight and without burrs, and there is no heat-affected zone in both materials. The results of experiments show that water-conducting laser processing technology on metal precision machining is practical and has important application value.
-
Key words:
- laser water-jet /
- coupling technology /
- laser processing /
- surface quality
-

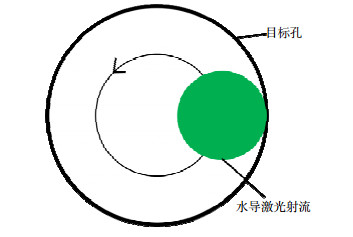
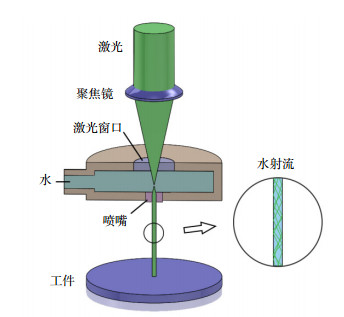
Overview: The laser processing technology of metal material is developing with a trend of low surface roughness, small heat-affected zone and high depth-diameter ratio. Recently, a kind of water-conducting laser processing technology has been developed based on water-jet coupling technology. In this technology, the laser is completely reflected at the interface between water jet and air. The flushing and cooling effect of water jet improve the surface roughness and decrease the size of heat-affected zone. The water jet in steady state which can be used to conduct laser and remove material has high depth-diameter ratio. And this technology also makes laser processing of structures with high depth-diameter ratio become possible.
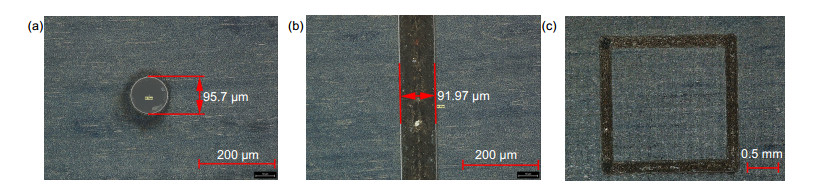
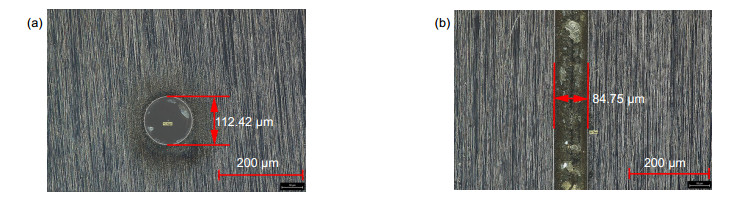
To reveal the material removing feature of water-conducting laser processing technology, a set of water-conducing laser processing equipment is developed. This equipment consists of coupling and observation system, motion control system and water supply system. The experiments of water-conducting laser processing for C276 alloy and SAE 1070 alloy are carried out. The laser used in experiments has a wavelength of 532 nm. The diameter of water jet nozzle hole is 100 μm and the diameter of water jet is about 83 μm. Holes and groves are machined on both materials and the morphology of machining zone is measured by Leica DVM6 digital microscope.
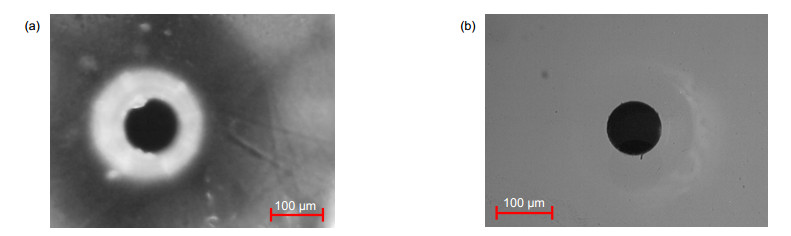
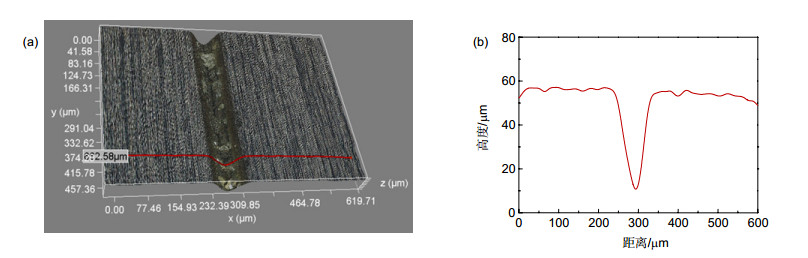
In the blind hole machining experiment, the edge of hole is regular and smooth. And the diameter of blind hole is larger than the diameter of water jet. The reason is that the side walls of blind hole also absorb the energy of laser in machining process. And the diameter of blind holes machined for longer time is also bigger. But there is molten sediment around the blind hole for the reason that the drainage condition in blind hole machining is not good. The water connot flush the molten materials away efficiently. To improve the drainage condition of water and eliminate the molten sediment, the rotary cutting method can be used.
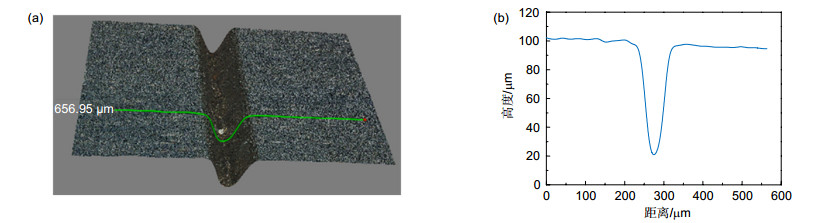
In the grove machining experiment, the edges of grooves are straight and without burrs, and there is no heat-affected zone in both materials. The section shape of grove is nearly a fillet triangle, and the reason is that the central part of water jet has higher energy density. In the machining of grove, no molten sediment is observed because the flow of water is unimpeded and the water brings molten sediment away efficiently.
The material removing feature of water-conducting laser processing technology is revealed and the results of machining experiments show that water-conducting laser processing technology on metal precision machining is practical and has important application value.
-

-
表 1 实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters
激光器电流/A 重频/kHz 脉宽/ns 喷嘴直径/μm 水压/MPa 切槽移动速度/(μm/s) 5.5 32.7 20 100 18 20 -
[1] 孙博宇, 乔红超, 赵吉宾, 等.水导激光切割技术研究现状[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(11): 1039-1044. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.11.001
Sun B Y, Qiao H C, Zhao J B, et al. Current status of water-jet guided laser cutting technology[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(11): 1039-1044. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.11.001
[2] 杨立军, 孔宪俊, 王扬, 等.激光微孔加工技术及应用[J].航空制造技术, 2016(19): 32-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hkgyjs201619004
Yang L J, Kong X J, Wang Y, et al. Laser micro-holes machining technology and its application[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2016(19): 32-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hkgyjs201619004
[3] Perrottet D, Housh R, Richerzhagen B, et al. Heat damage-free laser-microjet cutting achieves highest die fracture strength[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5713: 285-293. doi: 10.1117/12.586710
[4] 王宏智.微水导激光划片工艺原理及应用[J].电子工业专用设备, 2008, 37(3): 27-31, 49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4507.2008.03.008
Wang H Z. The technology principle and application of water-jet-guided laser scribing[J]. Equipment For Electronic Products Manufacturing, 2008, 37(3): 27-31, 49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4507.2008.03.008
[5] 周永恒, 廖健宏, 蒙红云, 等.血管内支架的激光精细切割技术[J].应用激光, 2005, 25(3): 161-164, 154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-372X.2005.03.006
Zhou Y H, Liao J H, Meng H Y, et al. Laser micro-fabrication of endovascular stent[J]. Applied Laser, 2005, 25(3): 161-164, 154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-372X.2005.03.006
[6] Richerzhagen B. Entwicklung und konstruktion eines systems zur uebertragung von laserenergie für die laserzahnbehandlung[D]. Lausanne: EPFL, 1994.
[7] Nilsson T, Wagner F, Housh R, et al. Scribing of GaN wafer for white LED by water-jet-guided laser[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5366: 200-206. doi: 10.1117/12.529012
[8] 李灵.水导激光微细加工技术研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008: 1-107.
Li L. Study on water-jet guided laser micromachining technology[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008: 1-107.
[9] 叶瑞芳, 沈阳, 王磊, 等.新型水导引激光耦合系统研究[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 48(3): 369-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.2009.03.015
Ye R F, Shen Y, Wang L, et al. Novel coupling system of water-jet guided laser[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2009, 48(3): 369-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.2009.03.015
[10] 孙冬, 王军华, 韩福柱.基于离轴光学系统的水导激光耦合技术研究[J].红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(12): 1206001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201812002
Sun D, Wang J H, Han F Z. Research on coupling technology for water-jet guided laser machining based on off-axis optical system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(12): 1206001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201812002
[11] Adelmann B, Ngo C, Hellmann R. High aspect ratio cutting of metals using water jet guided laser[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 80(9-12): 2053-2060. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7161-8
[12] Porter J A, Louhisalmi Y A, Karjalainen J A, et al. Cutting thin sheet metal with a water jet guided laser using various cutting distances, feed speeds and angles of incidence[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 33(9-10): 961-967. doi: 10.1007/s00170-006-0521-7
[13] Couty P, Wagner F R, Hoffmann P W. Laser coupling with a multimode water-jet waveguide[J]. Optical Engineering, 2005, 44(6): 068001. doi: 10.1117/1.1928280
[14] 孙冬, 王军华, 韩福柱.单晶硅水导/水辅助激光切割加工对比研究[J].应用激光, 2016, 36(6): 723-727. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yyjg201606014
Sun D, Wang J H, Han F Z. Contrastive study of water jet guided laser and water jet assisted laser cutting of Monocrystalline silicon[J]. Applied Laser, 2016, 36(6): 723-727. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yyjg201606014
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: