Study of low-noise phase-shifting digital holographic microscopy using a long working distance objective
-
摘要:
在数字全息显微技术中,为了提高测量精度,提出了一种利用长工作距离物镜的相移数字全息显微的测量装置和方法。该装置采用LED作为照明光源,可以有效地抑制相位噪声,提高了重建精度。通过在长工作距离物镜和样品之间加入分光棱镜的方法,构建了一种准物参共路的迈克尔逊干涉仪。该装置结构简单,调整方便,在部分相干光照明时,容易实现干涉。重建时,采用盲相移干涉技术,结合两步盲相移算法,重建出物体的表面相位分布。实验中,分别采用LED照明和He-Ne激光照明,测量了一个反射式USAF1951分辨率板的高度分布。结果表明,两者的测量结果相互吻合,但是LED照明时的噪声与激光照明时相比降低了70%。此外,为了进一步验证装置的有效性,使用该装置对刻于硅基底的微纳矩形台阶进行测量,测量结果与标称值具有良好的一致性,表明该装置在微结构的形貌测量方面有广阔的应用前景。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to improve the measurement accuracy, a kind of phase shifting digital holographic microscopy based on a long working distance microscopic objective is proposed. In the setup, an LED is adopted as the illumination light source, which can suppress coherent noise effectively and hence improve the measurement accuracy. A michelson quasi-common-path interferometer is constructed by adding a beam-splitter between the long working distance objective and the sample. The layout of the setup is simple and it can be easily adjusted, and thus the interference can be come into being conveniently especially when the sample is illuminated with a partial light source. The blind phase-shifting interferometry is adopted in the reconstruction procedure, and the two-step blind phase-shifting algorithm is used to reconstruct the phase map of the measured sample. In the experiments, the height maps of a reflective USAF 1951 resolution target are measured under LED illumination and He-Ne laser illumination, respectively. The measurement results show that both coincide with each other; the phase noise under LED illumination is, however, reduced by 70% when compared with that under laser illumination. In addition, in order to further verify the effectiveness of the device, the device is used to measure a micro-nano rectangular step engraved on the silicon substrate. The measurement results are in good agreement with the nominal values. This technique can be potentially used in the topographic measurement of micro-structures.
-

Overview: Digital holographic microscopy (DHM) has been widely applied in biological sample imaging, three-dimensional morphology detection, flow field measurement, and other fields, because it has the advantages of non-contact, non-destructive, high resolution, and so on.
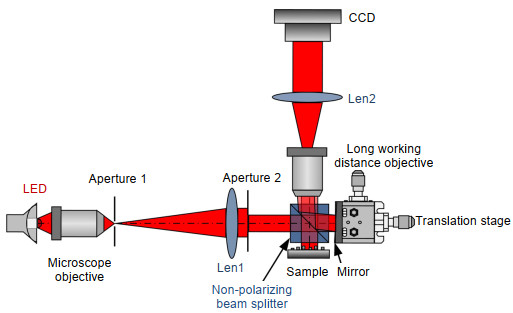
In DHM, the laser is usually used as the illumination source. However, the speckle noise induced by laser is large, and hence it degrades the quality of reconstructed phase image of objects. In order to reduce speckle noise, we use partially coherent light source light emitting diode (LED) as the illumination source. With the adoption of an LED, we proposed a phase-shifting digital holographic microscopic device based on a long working distance objective. By taking advantage of characteristic of long working distance of the objective, a micro-Michelson interferometer is constructed by inserting a non-polarizing beam splitter (NPBS) between the objective and the sample. In the system, as both object wave and reference wave pass through almost the same path, thus the interferometer is a quasi-common-path one. In addition, the system has a compact structure and it is convenient to adjustment. When it is illuminated by an LED, the interference between object wave and reference wave can be easily realized. To reconstruct the phase maps from the holograms, two-step blind phase-shifting algorithm is adopted. To achieve this, a low-cost mechanical micro-displacement platform is used to introduce phase shift between the holograms in the system to replace the usually expensive piezoelectric ceramic transducer (PZT).
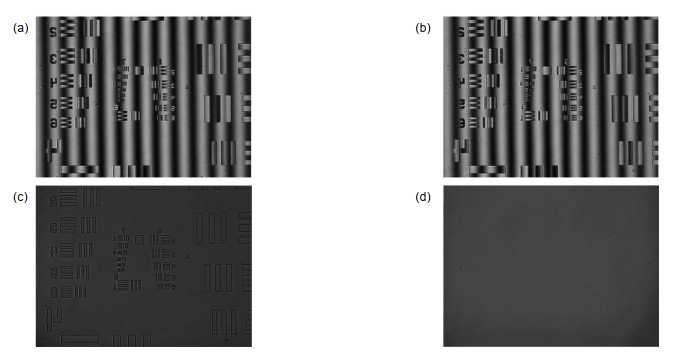
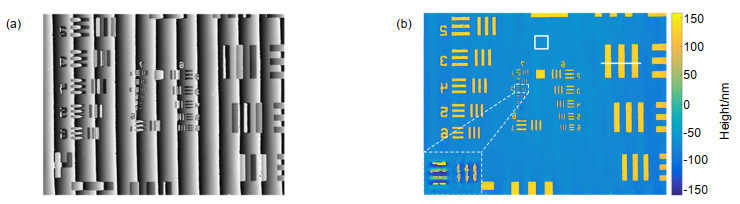
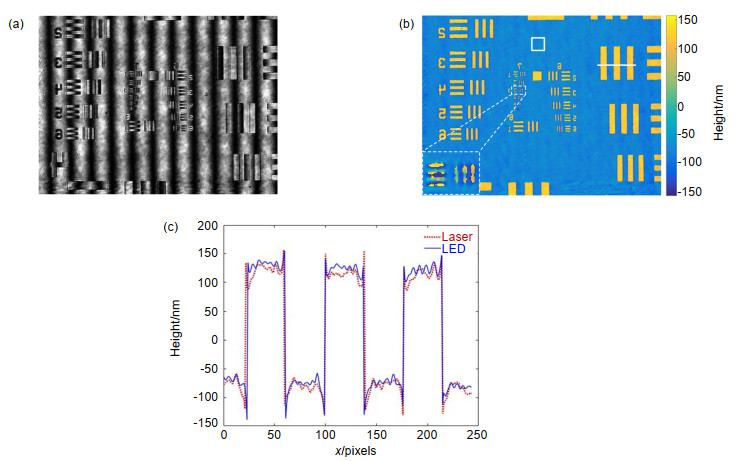
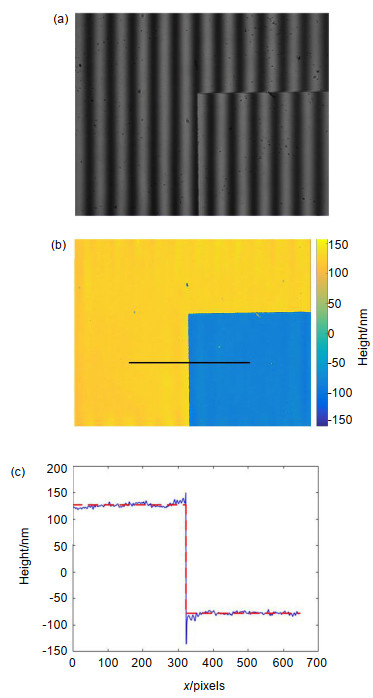
Several experiments were conducted to verify the correctness and effectiveness of the system. In the experiments, we measured samples respectively under LED illumination and laser illumination and compared the phase noise level of phase images under different illuminating sources. In the first experiment, the sample is a reflective USAF 1951 resolution target and the experimental results demonstrate that the noise in the phase map with LED illumination is reduced by 70% when compared with that of laser illumination. At the same time, there is no significant difference in system resolution between two reconstructed phase maps corresponding to LED and laser illumination, respectively. Consequently, the proposed scheme can effectively reduce the phase noise and improve the quality of reconstructed phase image. In the second experiment, the device was used to measure a micro-nano step. The measured height was in good agreement with its nominal value. The experimental results show that the system can be potentially applied in the precise measurement of the three-dimensional topography of the micro-structure surface and other related fields.
-

-
-
[1] Zhang Y Y, Zhao J L, Di J L, et al. Real-time monitoring of the solution concentration variation during the crystallization process of protein-lysozyme by using digital holographic interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(16):18415-18421. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.018415
[2] Min J W, Yao B L, Ketelhut S, et al. Simple and fast spectral domain algorithm for quantitative phase imaging of living cells with digital holographic microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(2):227-230. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.000227
[3] 周战荣.单次相移数字全息中相移值的提取[J].光电工程, 2009, 36(7):117-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2009.07.022
Zhou Z R. Phase-shifting value extraction on digital holography with single phase-shifting operation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2009, 36(7):117-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2009.07.022
[4] Zheng J J, Zuo C, Gao P, et al. Dual-mode phase and fluorescence imaging with a confocal laser scanning microscope[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(22):5689-5692. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.005689
[5] Yue Q Y, Cheng Z J, Han L, et al. One-shot time-resolved holographic polarization microscopy for imaging laser-induced ultrafast phenomena[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(13):14182-14191. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.014182
[6] Xue L, Wang S Y, Yan K D, et al. Fast pixel shifting phase unwrapping algorithm in quantitative interferometric microscopy[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2014, 12(7):071801. doi: 10.3788/COL201412.071801
[7] 范锋, 栗军香, 宋修法, 等.基于Hilbert变换实现数字全息高精度相位重建[J].物理学报, 2014, 63(19):194207. doi: 10.7498/aps.63.194207
Fan F, Li J X, Song X F, et al. High accuracy phase reconstruction of digital hologram by Hilbert transform[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(19):194207. doi: 10.7498/aps.63.194207
[8] 田鹏, 严伟, 李凡星, 等.均匀球面波数字同轴全息生物显微方法[J].光电工程, 2019, 46(1):180110. http://www.oejournal.org/J/OEE/Article/Details/A181222000004/CN
Tian P, Yan W, Li F X, et al. Biology microscopy using well-distributed sphere digital in-line holography[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2019, 46(1):180110. http://www.oejournal.org/J/OEE/Article/Details/A181222000004/CN
[9] 王云新, 王大勇, 赵洁, 等.基于数字全息显微成像的微光学元件三维面形检测[J].光学学报, 2011, 31(4):0412003. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7492216
Wang Y X, Wang D Y, Zhao J, et al. 3D profile measurement for micro-optical component by using digital holographic microscopy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2011, 31(4):0412003. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7492216
[10] 张倩, 徐先锋, 袁红光, 等.四步相移数字全息干涉术相移提取和物光重建[J].光电工程, 2011, 38(8):139-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2011.08.023
Zhang Q, Xu X F, Yuan H G, et al. Phase-shift extraction and wave reconstruction in four-step phase-shifting interferometry[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2011, 38(8):139-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2011.08.023
[11] 王凤鹏, 邓世桂, 张选洲, 等.同轴数字全息视频动态跟踪处理实验[J].光电工程, 2014, 41(6):81-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.06.014
Wang F P, Deng S G, Zhang X Z, et al. Processing experiments of digital in-line holographic video[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2014, 41(6):81-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.06.014
[12] 邓慧, 张蓉竹, 孙年春.激光光束非相干叠加对散斑噪声抑制情况[J].光学学报, 2016, 36(1):0129002. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201601035
Deng H, Zhang R Z, Sun N C. Suppression situation of incoherent superposition of laser beams on speckle noise[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(1):0129002. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201601035
[13] 肖文, 王庆伍, 潘锋.小波结合双边滤波抑制全息相干噪声[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(8):39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.08.007
Xiao W, Wang Q W, Pan F. Suppression of coherent noise by wavelet combined with bilateral filtering in digital holography[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(8):39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.08.007
[14] Rong L, Xiao W, Pan F, et al. Speckle noise reduction in digital holography by use of multiple polarization holograms[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2010, 8(7):653-655. doi: 10.3788/COL20100807.0653
[15] 王大勇, 王云新, 郭莎, 等.基于多角度无透镜傅里叶变换数字全息的散斑噪声抑制成像研究[J].物理学报, 2014, 63(15):154205. doi: 10.7498/aps.63.154205
Wang D Y, Wang Y X, Guo S, et al. Research on speckle denoising by lensless Fourier transform holographic imaging with angular diversity[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(15):154205. doi: 10.7498/aps.63.154205
[16] Aum J H, Kim J H, Jeong J. Effective speckle noise suppression in optical coherence tomography images using nonlocal means denoising filter with double Gaussian anisotropic kernels[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(13):D43-D50. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.000D43
[17] Uzan A, Rivenson Y, Stern A. Speckle denoising in digital holography by nonlocal means filtering[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(1):A195-A200. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.00A195
[18] 秦怡, 钟金钢.基于发光二极管的弱相干光数字全息理论与实验研究[J].光学学报, 2010, 30(8):2236-2241. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201008012
Qin Y, Zhong J G. Theoretical and experimental research of digital holography with partially coherent light based on light-emitting diode[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(8):2236-2241. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201008012
[19] Monemhaghdoust Z, Montfort F, Emery Y, et al. Dual wavelength full field imaging in low coherence digital holographic microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(24):24005-24022. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.024005
[20] 巩琼, 秦怡. LED光源数字全息技术研究[J].应用光学, 2010, 31(2):237-241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2010.02.016
Gong Q, Qin Y. LED-based digital holography[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2010, 31(2):237-241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2010.02.016
[21] 王海珊, 史铁林, 廖广兰, 等.基于干涉显微原理的表面形貌测量系统[J].光电工程, 2008, 35(7):84-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2008.07.017
Wang H S, Shi T L, Liao G L, et al. Profilometer based on interferometry and micro vision system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2008, 35(7):84-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2008.07.017
[22] Kemper B, Sturwald S, Remmersmann C, et al. Characterisation of light emitting diodes (LEDs) for application in digital holographic microscopy for inspection of micro and nanostructured surfaces[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2008, 46(7):499-507. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2008.03.007
[23] Dubois F, Yourassowsky C. Full off-axis red-green-blue digital holographic microscope with LED illumination[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(12):2190-2192. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.002190
[24] 李勇, 吴奎, 卢荣胜, 等. Linnik白光干涉仪自动对焦及光程差最小化[J].光电工程, 2012, 39(11):8-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.11.002 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GDGC201211006.htm
Li Y, Wu K, Lu R S, et al. Automated method of focusing and minimizing OPD in Linnik white light interferometry[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2012, 39(11):8-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.11.002 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GDGC201211006.htm
[25] Guo R L, Yao B L, Gao P, et al. Off-axis digital holographic microscopy with LED illumination based on polarization filtering[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(34):8233-8238. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.008233
[26] Zhao J L, Di J L, Zhang J W, et al. Common-path digital holographic microscopy and its applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 10022:1002202.
[27] Di J L, Wang K Q, Zhang J W, et al. Quasicommon-path digital holographic microscopy with phase aberration compensation based on a long-working distance objective[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57(2):024108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c5c4b70b69fba695f460a9ee20b10cb3
[28] Guo R L, Wang F. Compact and stable real-time dual-wavelength digital holographic microscopy with a long-working distance objective[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(20):24512-24520. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.024512
[29] Sinclair M B, de Boer M P, Corwin A D. Long-working-distance incoherent-light interference microscope[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(36):7714-7721. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.007714
[30] Guo R L, Yao B L, Min J W, et al. LED-based digital holographic microscopy with slightly off-axis interferometry[J]. Journal of Optics, 2014, 16(12):125408. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/16/12/125408
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: