-
摘要:
针对部分对比度低、噪声大的图像,提出一种基于大脑内部生成机制(IGM)和改进脉冲耦合神经网络(PCNN)的图像增强方法。首先,根据IGM有关理论将原始图像分解为细节子图与粗糙子图;然后,采用改进的PCNN增强方法对粗糙子图进行处理,以提高整体对比度,采用PCNN与模糊集理论结合的增强方法对细节子图进行处理,增强边缘等细节信息并去除部分噪声;最后,将处理后的细节子图与粗糙子图重构,得到最终的增强图像。实验结果表明,该方法能够有效增强图像的对比度和纹理细节,减少部分噪声,较好地保留原图细节信息。
 Abstract:
Abstract:To deal with low-contrast and high-noisy natural images, an image enhancement method based on internal generative mechanism (IGM) and improved pulse coupled neural network (PCNN) is proposed. First, the original image is decomposed into rough sub-graph and detail sub-graph by the theory of IGM. And then, an improved PCNN method is adopted to make the rough sub-graph more clearly. At the same time, the enhancement method which PCNN incorporates with fuzzy sets is introduced for the detail sub-graph so as to sharpen the image edge and remove outliers. Finally, the final image is reconstructed by processed rough sub-graph and detail sub-graph. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively enhance the image contrast and image contour, as well as filter out some noise without any loss of image edges.
-

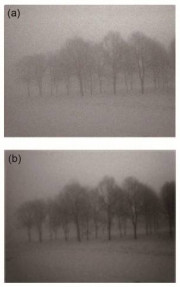
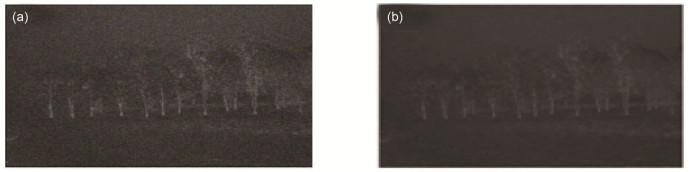
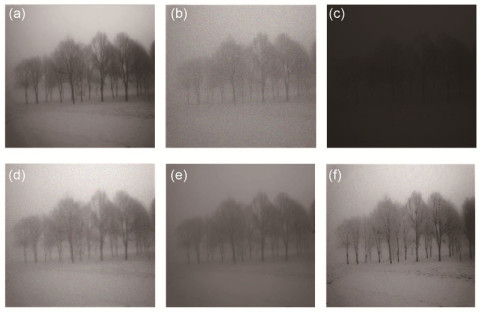
Abstract: Image enhancement is an important and fundamental problem for image processing. However, there are some images that the visual system obtained with a mass of effective features loss, appearing to be low contrast and high noise, which will affect the image enhancement and the subsequent processing of computer vision applications. To deal with the low-contrast and high-noisy natural images, an image enhancement method based on internal generative mechanism (IGM) and improved pulse coupled neural network (PCNN) is proposed. First, in the division operation, an image is segmented into two parts using the theory of IGM. One part is a rough sub-graph, which contains the basic information of the images, and the other is a detail sub-graph, which contains the image details. Second, in order to make the rough sub-graph more clearly, an improved PCNN enhancement method with fuzzy sets is adopted. As we all know, the lij in PCNN represents the working state of each neuron and every neuron has its own lij. So we use the lij as the input of the fuzzy function to obtain the fuzzy membership. Subsequently, through the successive iteration of the fuzzy membership, we have achieved the purpose of using this information to non- linearly extend the lij, and then, the image contrast of the target and background is enhanced accordingly. At the same time, βij in PCNN affects the ignition cycle between the central neuron and the neighborhood neurons, which in turn affects the gray value of the pixels. By improving the calculation method of βij in PCNN, we have achieved the purpose of sharpening the image edge and removing the noises of the detail sub-graph. Finally, the final image is reconstructed by the processed rough sub-graph and detail sub-graph. To verify the effectiveness and superiority, we design three sets of controlled experiments which are performed on some PCNN enhancement algorithms, including the original PCNN method in Ref.[7], the improved PCNN methods in Ref.[8] and Ref.[9]. Meanwhile, we choose three classic images to show the experiment results qualitatively, and the results are shown in Fig. 4, Fig. 5 and Fig. 6. After that, in order to show the quantitative experiment results, we also chose five reference and no-reference image quality assessment methods, such as the DV/BV, SSIM, entropy, SNR, and EPI, to compare the effect of various image enhancement methods. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively enhance the image contrast and image contour, as well as filter out some noise without any loss of image edges.
-

-
表 1 不同增强方法的定量评价结果.
Table 1. Performance comparison of different enhancement methods.
图像 参数 原始图像 降质图像 传统PCNN[7] 文献[8] 文献[9] 本文算法 Tree DV/BV 13.145 8.381 3.520 9.342 7.551 11.681 SSIM 1 0.621 0.506 0.719 0.632 0.769 信息熵 5.119 4.012 3.461 4.334 4.260 4.819 SNR 21.688 12.428 13.825 17.643 16.267 18.764 EPI 1 0.671 0.701 0.742 0.713 0.817 People DV/BV 8.492 4.113 2.583 5.219 4.763 8.313 SSIM 1 0.617 0.592 0.716 0.691 0.812 信息熵 5.337 4.405 3.933 4.863 4.361 5.105 SNR 22.183 14.064 13.651 17.971 16.539 21.001 EPI 1 0.611 0.653 0.732 0.709 0.841 Barbara DV/BV 9.328 5.194 4.360 6.256 7.633 9.194 SSIM 1 0.602 0.551 0.468 0.632 0.627 信息熵 5.629 3.370 4.338 4.459 5.012 5.410 SNR 19.865 11.306 14.467 10.465 15.871 16.306 EPI 1 0.642 0.659 0.583 0.816 0.831 -
[1] Magudeeswaran V, Ravichandran C G, Thirumurugan P. Brightness preserving bi-level fuzzy histogram equalization for MRI brain image contrast enhancement[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2017, 27(2): 153–161. doi: 10.1002/ima.v27.2
[2] Xu F Y, Zeng D G, Zhang J, et al. Detail enhancement of blurred infrared images based on frequency extrapolation[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2016, 76: 560-568. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2016.04.008
[3] 吴燕燕, 王亚杰, 石祥滨, 等.结合NSST和颜色对比度增强的彩色夜视方法[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(11): 88–94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.11.014
Wu Yanyan, Wang Yajie, Shi Xiangbin, et al. Color night vision method combing NSST with color contrast enhancement[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(11): 88–94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.11.014
[4] Kaur A, Singh C. Contrast enhancement for cephalometric images using wavelet-based modified adaptive histogram equalization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 51: 180–191. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.11.046
[5] Bai T B, Zhang L B, Duan L X, et al. NSCT-based infrared image enhancement method for rotating machinery fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(10): 2293–2301. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2579440
[6] Wang Y F, Wang H Y, Yin C L, et al. Biologically inspired image enhancement based on Retinex[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 177: 373–384. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.124
[7] Johnson J L, Ritter D. Observation of periodic waves in a pulse-coupled neural network[J]. Optics Letters, 1993, 18(15): 1253–1255. doi: 10.1364/OL.18.001253
[8] Xu G Z, Li C L, Zhao J J, et al. Multiplicative decomposition based image contrast enhancement method using PCNN fac-toring model[C]// Proceedings of the 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 2014: 1511–1516.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7052943/?reload=true&arnumber=7052943 [9] 苏娟, 李冰, 王延钊.结合PCNN分割和模糊集理论的红外图像增强[J].光学学报, 2016, 36(9): 0910001. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ160909000192DaGcJf
Su Juan, Li Bing, Wang Yanzhao. Infrared image enhancement based on PCNN segmentation and fuzzy set theory[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(9): 0910001. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ160909000192DaGcJf
[10] Peter D, Geoffrey E H, Radford M N, et al. The Helmholtz machine[J]. Neural computation, 1995, 7(5): 889–904. doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.5.889
[11] Wu J J, Lin W S, Shi G M, et al. Perceptual quality metric with internal generative mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(1): 43–54 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214048
[12] Zhang K H, Zhang L, Yang X. Infrared image adaptive en-hancement based on fuzzy sets theory[C]// Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Asia Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, 2010, 2: 242–245
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224134784_Infrared_image_adaptive_enhancement_based_on_fuzzy_sets_theory [13] Li C F, Bovik A C, Wu X J. Blind image quality assessment using a general regression neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(5): 793–799. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2120620
[14] 毛瑞全, 宫霄霖, 刘开华.基于PCNN区域分割的图像邻域去噪算法[J].光电工程, 2010, 37(2): 122–127. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90982A/201002/32957176.html
Mao Ruiquan, Gong Xiaolin, Liu Kaihua. Image de-noising algorithm with neighborhood based on PCNN segmentation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2010, 37(2): 122–127. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90982A/201002/32957176.html
[15] 何胜宗, 刘映杰, 马义德, 等.基于PCNN图像因子分解的X线医学图像增强[J].中国图象图形学报, 2011, 16(1): 21–26. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4484019
He Shengzong, Liu Yingjie, Ma Yide, et al. Medical X-ray image enhancement based on PCNN image factorization[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2011, 16(1): 21–26. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4484019
[16] Wang Z, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
[17] Gupta S, Kaur L, Chauhan R C, et al. A versatile technique for visual enhancement of medical ultrasound images[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2007, 17(3): 542–560. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2006.12.001
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: