-
Abstract:
Beam deflectors are important optical elements which can control the propagation direction of the beam in free space. However, with the development of miniaturization of the optical systems, conventional reflector-based mechanical beam deflectors confront a huge challenge due to their large sizes and incompatibility to the device integration. Here we propose an all-dielectric flat metasurface beam deflector which is composed of a single layer array of TiO2 nanoantennas resting on a fused-silica substrate. Numerical simulations are performed to demonstrate that the proposed deflectors are able to efficiently deflect the incident beam for different angles with transmission efficiency higher than 80% at visible frequencies. This ultrathin all-dielectric metasurface deflector may have great potential applications in integrated optics.

-
Key words:
- metasurfaces /
- beam deflector /
- nanoantenna /
- integrated optics
-

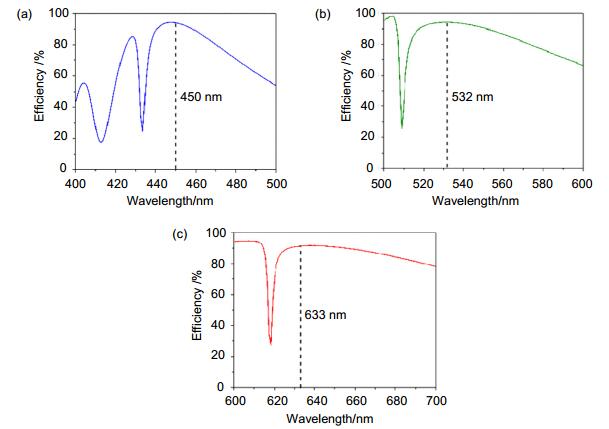
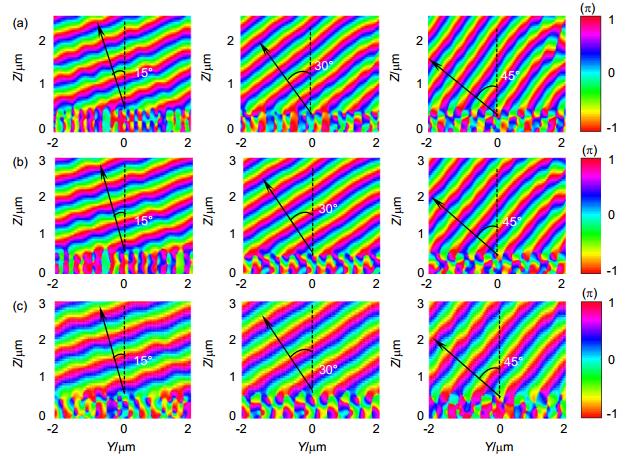
Abstract: Beam deflectors, which are able to change or control the propagation direction of the beam in free space, are important optical components in integrated optical circuit and optical communication systems. However, with the development of miniaturization of the optical systems, conventional reflector-based mechanical beam deflectors confront a huge challenge due to their large size and incompatible to the device integration. Recently, metasurfaces, also known as two-dimensional metamaterials, have attracted significant attentions due to their ultrathin thicknesses and perfect controlling of amplitude, phase and polarization of the beams. On account of full 2p phase control, metasurfaces are widely used in lensing, holograms, wave plates and other applications. The original metasurfaces are mainly designed using metallic resonant structures. However, metallic metasurfaces always have large ohmic losses, which are similar to the plasmonic structures. To overcome the loss issue, metasurfaces using dielectrics, such as silicon and titanium dioxide (TiO2), appear and are widely employed in the novel optical devices' design. Here we propose and design an all-dielectric flat metasurface beam deflector which is composed of a single layer array of TiO2 nanoantennas resting on a fused-silica substrate. The TiO2 nanoantennas are considered as birefringent elements and the Jones transfer matrix can be used to model electrometric response of each TiO2 nanoantenna. Based on the phase discontinuity principle, we design the beam deflectors that operate at the wavelengths of 450 nm, 532 nm, and 633 nm, respectively. For the circularly polarized incident light, the polarization conversion efficiencies of the designed beam deflectors are all higher than 90% at the operation wavelength. Numerical simulations based on the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) algorithm show that deflecting behaviors of the proposed devices with deflection angles of 15°, 30° and 45° are all in excellent agreement with our theoretical predictions. The simulated optical transmissions of the designed deflectors are 88.2%, 86.8% and 71.3% for 15°, 30° and 45° at wavelength of 450nm; 86.7%, 86.4%, 69.7% for 15°, 30° and 45° at wavelength of 532nm and 89.3%, 80.6%, 62.0% for 15°, 30° and 45° at wavelength of 633nm, respectively. Compared with other thin-film plasmonic beam deflectors using metallic nanoslits, the transmission efficiencies of the metasurface beam deflectors are much higher. The all-dielectric metasurface beam deflector may have potential applications for manipulation of the light propagation in the high-integration optical systems.
-

-
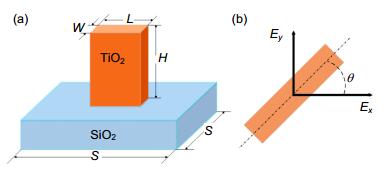
Figure 1. (a) Front view of the beam deflector unit cell, showing unit cell periodicity S, nanoantenna width W, length L and height H. At the wavelength of 450 nm, S=230 nm, L=145 nm, W=60 nm, H=500 nm; At the wavelength of 532 nm, S=270 nm, L=210 nm, W=70 nm, H=550 nm; At the wavelength of 633 nm, S=320 nm, L=270 nm, W=105 nm, H=600 nm. (b) Cross-section of single nanoantenna with rotation angle θ.
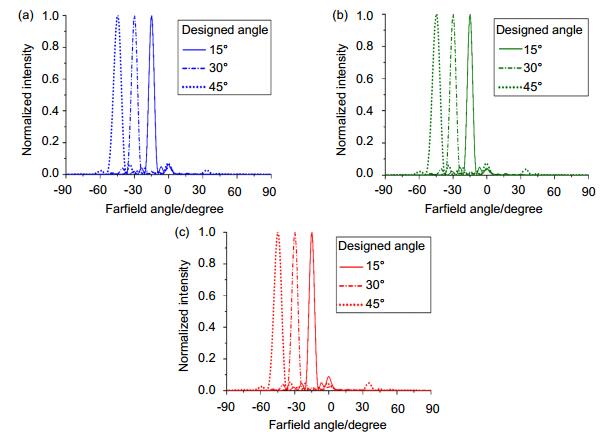
Figure 4. Simulated far-field transmitted power distributions as the functions of angle at the three wavelengths. (a) Blue lines at the wavelength of 450 nm. (b) Green lines at the wavelength of 532nm and (c) red lines at the wavelength of 633 nm. Solid lines, short dash dot lines and short dot lines represent the deflection angles designed for 15°, 30° and 45°, respectively.
-
[1] Xu Ting, Wang Changtao, Du Chunlei, et al. Plasmonic beam deflector[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(7): 4753-4759. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.004753
[2] Wang Y, Wang L L, Liu J Q, et al. Plasmonic surface-wave bidirectional splitter in different angles of incident light[J]. Optics Communications, 2010, 283(9): 1777-1779. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.12.072
[3] Yu Nanfang, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333-337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713
[4] Yu Nanfang, Capasso F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces[J]. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(2): 139-150. doi: 10.1038/nmat3839
[5] Kildishev A V, Boltasseva A, Shalaev V M. Planar photonics with metasurfaces[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6125): 1232009. doi: 10.1126/science.1232009
[6] Qin Fei, Ding Lu, Zhang Lei, et al. Hybrid bilayer plasmonic metasurface efficiently manipulates visible light[J]. ScienceAdvances, 2016, 2(1): e1501168. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016SciA....2E1168Q
[7] West P R, Stewart J L, Kildishev A V, et al. All-dielectric subwavelength metasurface focusing lens[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(21): 26212-26221. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.026212
[8] Hasman E, Kleiner V, Biener G, et al. Polarization dependent focusing lens by use of quantized Pancharatnam-Berry phase diffractive optics[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 82(3): 328-330. doi: 10.1063/1.1539300
[9] Khorasaninejad M, Aieta F, Kanhaiya P, et al. Achromatic metasurface lens at telecommunication wavelengths[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(8): 5358-5362. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01727
[10] Khorasaninejad M, Chen W T, Zhu A Y, et al. Multispectral chiral imaging with a metalens[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(7): 4595-4600. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01897
[11] Ni Xingjie, Kildishev A V, Shalaev V M. Metasurface holograms for visible light[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2807. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3807
[12] Zheng Guoxing, Mühlenbernd H, Kenney M, et al. Metasurface holograms reaching 80% efficiency[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(4): 308-312. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.2
[13] Huang Lingling, Chen Xianzhong, Mühlenbernd H, et al. Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2808. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3808
[14] Li Xiong, Chen Lianwei, Li Yang, et al. Multicolor 3D meta-holography by broadband plasmonic modulation[J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(11): e1601102. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601102
[15] Yu Nanfang, Aieta F, Genevet P, et al. A broadband, background-free quarter-wave plate based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(12): 6328-6333. doi: 10.1021/nl303445u
[16] Chen Weiting, Török P, Foreman M R, et al. Integrated plasmonic metasurfaces for spectropolarimetry[J]. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(22): 224002. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/27/22/224002
[17] Arbabi A, Arbabi E, Kamali S M, et al. Miniature optical planar camera based on a wide-angle metasurface doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 13682. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13682
[18] Ma Xiaoliang, Pu Mingbo, Li Xiong, et al. A planar chiral meta-surface for optical vortex generation and focusing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 10365. doi: 10.1038/srep10365
[19] Aieta F, Kats M A, Genevet P, et al. Multiwavelength achromatic metasurfaces by dispersive phase compensation[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6228): 1342-1345. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa2494
[20] Yang Yuanmu, Wang Wenyi, Moitra P, et al. Dielectric meta-reflectarray for broadband linear polarization conversion and optical vortex generation[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(3): 1394-1399. doi: 10.1021/nl4044482
[21] Lin Dianmin, Fan Pengyu, Hasman E, et al. Dielectric gradient metasurface optical elements[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6194): 298-302. doi: 10.1126/science.1253213
[22] Sun Shulin, Yang Kuangyu, Wang C M, et al. High-efficiency broadband anomalous reflection by gradient meta-surfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(12): 6223-6229. doi: 10.1021/nl3032668
[23] Pors A, Bozhevolnyi S I. Plasmonic metasurfaces for efficient phase control in reflection[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(22): 27438-27451. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.027438
[24] Khorasaninejad M, Chen Weiting, Devlin R C, et al. Metalenses at visible wavelengths: diffraction-limited focusing and subwavelength resolution imaging[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6290): 1190-1194. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf6644
[25] Liu Zhaocheng, Li Zhancheng, Liu Zhe, et al. Beam Deflectors: high-performance broadband circularly polarized beam deflector by mirror effect of multinanorod metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(34): 5567. doi: 10.1002/adfm.v25.34
[26] Su Xiaoqiang, Ouyang Chunmei, Xu Ningning, et al. Active metasurface terahertz deflector with phase discontinuities[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(21): 27152-27158. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.027152
[27] Shalaev M I, Sun Jingbo, Tsukernik A, et al. High-efficiency all-dielectric metasurfaces for ultracompact beam manipulation in transmission mode[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(9): 6261- 6266. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02926
[28] Khorasaninejad M, Crozier K B. Silicon nanofin grating as a miniature chirality-distinguishing beam-splitter[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5386. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6386
[29] Ding Xumin, Monticone F, Zhang Kuang, et al. Ultrathin pancharatnam-berry metasurface with maximal cross-polarization efficiency[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(7): 1195- 1200. doi: 10.1002/adma.201405047
[30] Zhao Wenyu, Jiang Huan, Liu Bingyi, et al. High-efficiency beam manipulation combining geometric phase with anisotropic Huygens surface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(18): 181102. doi: 10.1063/1.4948518
[31] DeVore J R. Refractive indices of rutile and sphalerite[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1951, 41(6): 416-419. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.41.000416
[32] Zhang Xueqian, Tian Zhen, Yue Weisheng, et al. Broadband terahertz wave deflection based on C-shape complex metamaterials with phase discontinuities[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(33): 4567-4572. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204850
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: