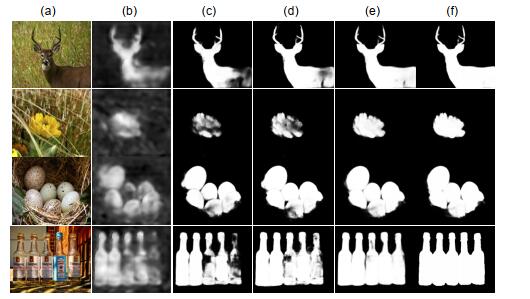
-
摘要:
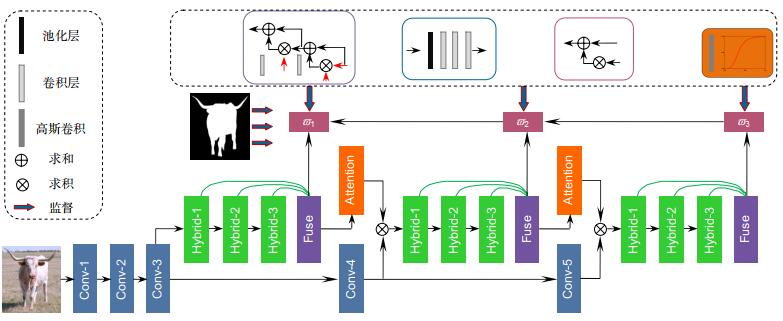
针对现有显著性检测算法在复杂场景下细节特征丢失的问题,本文提出了一种多层子网络级联式混合信息流的融合方法。首先使用FCNs骨干网络学习多尺度特征。然后通过多层子网络分层挖掘构建级联式网络框架,充分利用各层次特征的上下文信息,将检测与分割任务联合处理,采用混合信息流方式集成多尺度特性,逐步学习更具有辨别能力的特征信息。最后,嵌入注意力机制将显著性特征作为掩码有效地补偿深层语义信息,进一步区分前景和杂乱的背景。在6个公开数据集上与现有的9种算法进行对比分析,经实验验证,本文算法运行速度可达20.76帧/秒,并且实验结果在5个评价指标上普遍达到最优,即使对于挑战性很强的全新数据集SOC。本文方法明显优于经典的算法,其测试结果F-measure提升了1.96%,加权F-measure提升了3.53%,S-measure提升了0.94%,E-measure提升了0.26%。实验结果表明,提出的模型有效提高了显著性检测的正确率,能够适用于各种复杂的环境。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In view of the detail feature loss issue existing in the complex scenario of existing saliency detection algorithms, a fusion method of multi-layer sub-network cascade hybrid information flows is proposed in this paper. We first use the FCNs backbone network to obtain multi-scale features. Through the multi-layer sub-network layering mining to build a cascading network framework, the context information of the characteristic of each level is fully used. The detection and segmentation tasks are processed jointly. Multi-scale features are integrated by hybrid information flows, and more characteristic information with discernment is learned step by step. Finally, the embedded attention mechanism effectively compensates the deep semantic information as a mask, and further distinguishes the foreground and the messy background. Compared with the existing 9 algorithms on the basis of the 6 public datasets, the running speed of the proposed algorithm can reach 20.76 frames and the experimental results are generally optimal on 5 evaluation indicators, even for the challenging new dataset SOC. The proposed method is obviously better than the classic algorithm. Experimental results were improved by 1.96%, 3.53%, 0.94%, and 0.26% for F-measure, weighted F-measure, S-measure, and E-measure, respectively. These experimental results show that the demonstrating the proposed model has higher accuracy and robustness and can be suitable for more complex environments, the proposed framework improves the performance significantly for state-of-the-art models on a series of datasets.
-
Key words:
- saliency detection /
- cascade /
- hybrid information flows /
- attention mechanism
-

Overview: Saliency detection (SOD) is to detect and segment most important foreground objects that are modeled to accurately locate the mechanism of human visual attention. It has many types, including RGB SOD, light field SOD, RGB-D SOD, and high-resolution SOD. In the video scene, there are object SOD and fixation SOD, while the specific task is broken down into object-level saliency detection and instance-level significance detection. In view of the multi-scale feature fusion problem existing in the complex scenario of the existing saliency object detection algorithms, a fusion method of multi-layer sub-network cascade hybrid information flows is proposed in this paper. First of all, the FCNs backbone network and feature pyramid structure are used to learn multi-scale features. Then, through the multi-layer sub-network layering mining to build a cascading network framework, the context information of the characteristic of each level is fully used. The method of information extraction and flows determines the effect of final feature fusion, so we use the hybrid information flows to integrate multi-scale characteristics and learn more characteristic information with discernment. In order to solve the problem of semantic information fusion, high-level semantic information is used to guide the bottom layer, obtaining more effective context information. In this paper, we adopt the way of channel combination fusion, and the sampling processing is accompanied by the convolution layer smoothing the fusion feature map, making the next fusion more effective. Finally, the effective saliency feature is transmitted as mask information, which realizes the efficient transmission of information flows and further distinguishes the foreground and messy background. Finally, the multi-stage saliency mapping nonlinear weighted fusion is combined to complement the redundant features. Compared with the existing 9 algorithms on the basis of the 6 public datasets, the run speed of the proposed algorithm can reach 20.76 frames and the experimental results are generally optimal on 5 evaluation indicators, even for the challenging new dataset SOC. The proposed method is obviously better than the classic algorithm. Experimental results were improved by 1.96%, 3.53%, 0.94%, and 0.26% for F-measure, weighted F-measure, S-measure, and E-measure, respectively, effectively demonstrating the accuracy and robustness of the proposed model. Through the visual qualitative analysis verification, the correlation analysis and running speed analysis of different indicators are carried out, which further highlights the superior performance of the proposed model. In addition, this paper verifies the effectiveness of each module, which further explains the efficiency of the proposed cascading framework that mixes information flow and attention mechanisms. This model may provide a new way for multi-scale integration, which is conducive to further study.
-

-
表 1 ξ(·)函数参数选择
Table 1. Parameter selection of function ξ(·)
表 2 在5个基准数据集的Fβ评分结果(越高越好)
Table 2. Fβ score of five benchmark datasets (the higher the better)
Methods/Datasets ECSSD[15] DUT-OMRON[19] PASCAL-S[18] HKU-IS[15] DUTS[20] DRFI[34] 0.6899 0.6237 0.6382 0.7177 0.5857 DCL[27] 0.8820 0.6993 0.8220 0.8849 0.782 DSS[28] 0.9062 0.7369 0.8111 0.9011 0.7773 DHS[29] 0.8937 -TR- 0.7984 0.8772 0.7813 Amulet[30] 0.9050 0.7154 0.8165 0.8888 0.7504 DLS[31] 0.8257 0.6448 0.7200 0.8074 -TR- NLDF[32] 0.8887 0.6993 0.8027 0.8876 0.8120 SRM[33] 0.9048 0.7253 0.8250 0.8915 0.7976 Proposed 0.9332 0.7892 0.8692 0.9236 0.8643 表 3 在5个基准数据集的MAE评分结果(越低越好)
Table 3. MAE score of five benchmark datasets (the lower the better)
Methods/Datasets ECSSD[15] DUT-OMRON[19] PASCAL-S[18] HKU-IS[15] DUTS[20] DRFI[34] 0.1639 0.1554 0.2034 0.1394 0.1453 DCL[27] 0.0679 0.0797 0.1080 0.0481 0.0880 DSS[28] 0.0517 0.0628 0.0977 0.0401 0.0618 DHS[29] 0.0588 -TR- 0.0959 0.0519 0.0651 Amulet[30] 0.0589 0.0976 0.0992 0.0501 0.0841 DLS[31] 0.0859 0.0894 0.1328 0.0696 -TR- NLDF[32] 0.0626 0.0796 0.1007 0.0480 0.0660 SRM[33] 0.0543 0.0694 0.0867 0.0457 0.0583 Proposed 0.0402 0.0572 0.0715 0.0327 0.0431 表 4 在5个基准数据集的Fβw评分结果(越高越好)
Table 4. Fβw score of five benchmark datasets (the higher the better)
Methods/Datasets ECSSD[15] DUT-OMRON[19] PASCAL-S[18] HKU-IS[15] DUTS[20] DRFI[34] 0.4629 0.3720 0.4695 0.5284 0.3261 DCL[27] 0.8387 0.6392 0.7332 0.8411 0.6927 DSS[28] 0.8928 0.7118 0.7815 0.8891 0.7377 DHS[29] 0.8422 -TR- 0.7397 0.8411 0.6965 Amulet[30] 0.8321 0.5928 0.7174 0.8022 0.6306 DLS[31] 0.7933 0.5966 0.6734 0.7750 -TR- NLDF[32] 0.8547 0.6407 0.7484 0.8502 0.7103 SRM[33] 0.8628 0.6622 0.7617 0.8455 0.7252 Proposed 0.8839 0.7112 0.7987 0.8815 0.7957 表 5 在5个基准数据集的Sα和Em评分结果(越高越好)
Table 5. Sα and Em score of five benchmark datasets (the higher the better)
Methods/Datasets ECSSD[15] DUT-OMRON[19] PASCAL-S[18] HKU-IS[15] DUTS[20] Sα Em Sα Em Sα Em Sα Em Sα Em DRFI[34] 0.7202 0.7631 0.6978 0.7938 0.6487 0.7450 0.7277 0.8329 0.6725 0.7620 DCL[27] 0.8684 0.9163 0.7710 0.8261 0.7855 0.8490 0.8770 0.9318 0.7891 0.8448 DSS[28] 0.8821 0.9306 0.7899 0.8450 0.7926 0.8560 0.8783 0.9414 0.8106 0.8717 DHS[29] 0.8842 0.9279 -TR- -TR- 0.8045 0.8592 0.8698 0.9311 0.8201 0.8802 Amulet[30] 0.8941 0.9315 0.7805 0.8339 0.8193 0.8653 0.8860 0.9344 0.8039 0.8507 DLS[31] 0.8066 0.8726 0.7250 0.7978 0.7198 0.7941 0.7986 0.8769 -TR- -TR- NLDF[32] 0.8747 0.9221 0.7704 0.8200 0.8012 0.8591 0.8782 0.9344 0.8163 0.8716 SRM[33] 0.8952 0.9371 0.7977 0.8438 0.8306 0.8787 0.8871 0.9442 0.8356 0.8910 Proposed 0.9125 0.9512 0.8188 0.8566 0.8562 0.8876 0.9089 0.9498 0.8707 0.9110 表 6 在SOC基准数据集的测试结果
Table 6. SOC benchmark data set scoring
Methods Fβ MAE Fβw Sα Em DCL[28] 0.6440 0.1373 0.5570 0.6960 0.7712 DSS[28] 0.6284 0.1411 0.5625 0.6726 0.7593 DHS[29] 0.6844 0.1123 0.6103 0.7354 0.8005 RFCN[35] 0.6581 0.1276 0.5797 0.7180 0.7811 NLDF[32] 0.6663 0.1285 0.5774 0.7234 0.7843 SRM[33] 0.7071 0.1074 0.6147 0.7632 0.8184 Proposed 0.7268 0.0975 0.6500 0.7726 0.8210 -
[1] 张学典, 汪泓, 江旻珊, 等.显著性分析在对焦图像融合方面的应用[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(4): 435-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.008
Zhang X D, Wang H, Jiang M S, et al. Applications of saliency analysis in focus image fusion[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(4): 435-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.008
[2] Piao Y R, Rong Z K, Zhang M, et al. Deep light-field-driven saliency detection from a single view[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019: 904-911.
[3] Zhao J X, Cao Y, Fan D P, et al. Contrast prior and fluid pyramid integration for RGBD salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019: 3927-3936.
[4] Zeng Y, Zhang P P, Lin Z, et al. Towards high-resolution salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 7233-7242.
[5] Fan D P, Wang W G, Cheng M M, et al. Shifting more attention to video salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 8554-8564.
[6] Shen C, Huang X, Zhao Q. Predicting eye fixations on webpage with an ensemble of early features and high-level representations from deep network[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimedia, 2015, 17(11): 2084-2093. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d4dd0064b0cceab0d89477cbd7a796a4
[7] Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254-1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558
[8] Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, et al. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection[C]//2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2012: 733-740.
[9] 赵宏伟, 何劲松.基于贝叶斯框架融合深度信息的显著性检测[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(2): 170341. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170341
Zhao H W, He J S. Saliency detection method fused depth information based on Bayesian framework[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(2): 170341. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170341
[10] Wei Y C, Wen F, Zhu W J, et al. Geodesic saliency using background priors[C]//Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2012: 29-42.
[11] Liu J J, Hou Q, Cheng M M, et al. A Simple Pooling-Based Design for Real-Time Salient Object Detection[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 3917-3926.
[12] Liu N, Han J W, Yang M H. PiCANet: Learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 3089-3098.
[13] Chen K, Pang J M, Wang J Q, et al. Hybrid task cascade for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019: 4974-4983.
[14] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015: 3431-3440.
[15] Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J P, et al. Hierarchical saliency detection[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2013: 1155-1162.
[16] Li G B, Yu Y Z. Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015: 5455-5463.
[17] Xi X Y, Luo Y K, Wang P, et al. Salient object detection based on an efficient end-to-end saliency regression network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 323: 265-276. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.002
[18] Li Y, Hou X D, Koch C, et al. The secrets of salient object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 280-287.
[19] He X M, Zemel R S, Carreira-Perpinan M A. Multiscale conditional random fields for image labeling[C]//Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2004: II.
[20] Wang L J, Lu H C, Wang Y F, et al. Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 136-145.
[21] Fan D P, Cheng M M, Liu J J, et al. Salient objects in clutter: bringing salient object detection to the foreground[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 186-202.
[22] Cheng M M, Mitra N J, Huang X L, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569-582. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401
[23] Cheng M M, Warrell J, Lin W Y, et al. Efficient salient region detection with soft image abstraction[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer vision, 2013: 1529-1536.
[24] Margolin R, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A. How to evaluate foreground maps[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 248-255.
[25] Fan D P, Cheng M M, Liu Y, et al. Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 4548-4557.
[26] Fan D P, Gong C, Cao Y, et al. Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018: 698-704.
[27] Li G B, Yu Y Z. Deep contrast learning for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 478-487.
[28] Hou Q B, Cheng M M, Hu X W, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 3203-3212.
[29] Liu N, Han J W. DHSNet: deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 678-686.
[30] Zhang P P, Wang D, Lu H C, et al. Amulet: aggregating multi-level convolutional features for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 202-211.
[31] Hu P, Shuai B, Liu J, et al. Deep level sets for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 2300-2309.
[32] Luo Z M, Mishra A, Achkar A, et al. Non-local deep features for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 6609-6617.
[33] Wang T T, Borji A, Zhang L H, et al. A stagewise refinement model for detecting salient objects in images[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 4039-4048.
[34] Jiang H D, Wang J D, Yuan Z J, et al. Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2013: 2083-2090.
[35] Wang L Z, Wang L J, Lu H C, et al. Saliency detection with recurrent fully convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 825-841.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: