-
摘要:
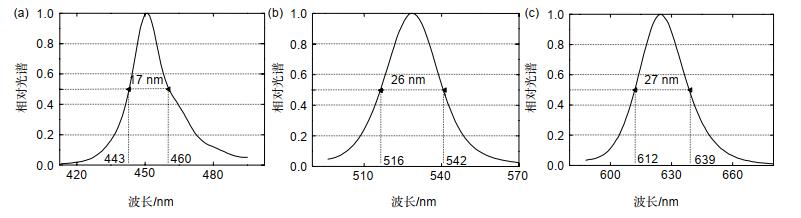
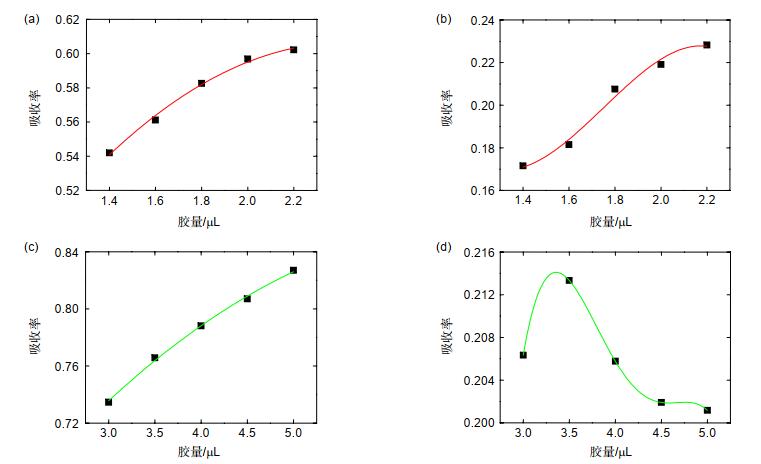
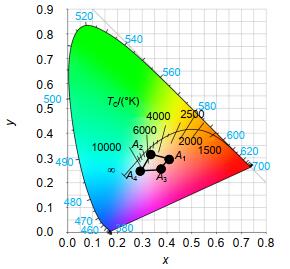
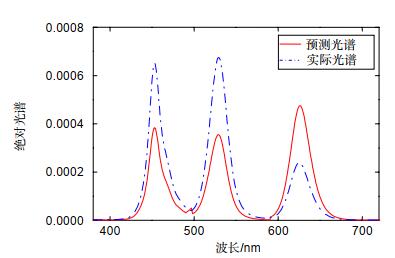
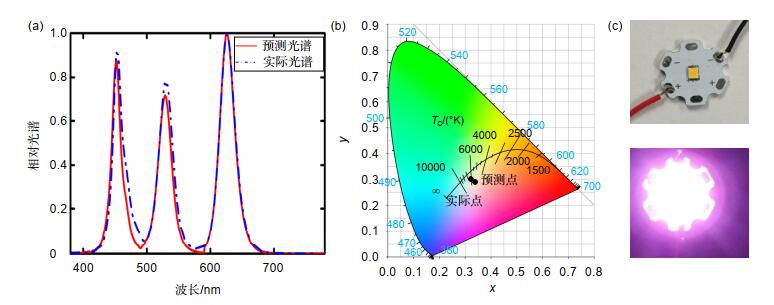
量子点材料具有发光光谱窄、发光波长可调及荧光量子产率高等特点,其制成的发光器件在提升色域方面更具潜力。本文介绍了一种由蓝光LED激发CdSe红、绿光量子点并结合表色系统计算方法配得白光的计算方法。经多次实验确定,红、绿光量子点与胶水配比为(1:60)和(1:10),胶量测试范围为1.4 μL~2.2 μL和3.0 μL~5.0 μL。采用传统LED制作方式和分层结构制得样品,测试此胶量范围对蓝光的吸收、转化比率,经Matlab拟合得到胶量与吸收、转化率的函数关系。取上述测试胶量范围形成的白光区域点(0.34,0.3),得到红、绿光量子点胶量为1.9 μL和4.55 μL,根据光谱计算公式得到对应的理论光谱。再根据上述胶量制作验证样品,测试得到色坐标点为(0.3409, 0.2992)且对应的光谱与理论光谱也基本重合。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Quantum dot materials have the characteristics of narrow luminescence spectrum, adjustable luminescence wavelength and high fluorescence quantum yield. The quantum dot LEDs have more potential in improving color gamut. In this paper, a method of white light generation by blue LED excited CdSe red and green quantum dots is introduced. The ratio of red and green quantum dots to glue was (1:60) and (1:10), and the test range of glue content was 1.4 μL~2.2 μL and 3.0 μL~5.0 μL. The samples were prepared by traditional method and layered structure. The absorption and conversion ratio of blue light in the range of glue amount were tested. The function relationship between glue amount and absorption and conversion was obtained by Matlab fitting. When taking the dots (0.34, 0.3) in white light region formed in the above test glue amount range, the red and green quantum dots were calculated with glue amount of 1.9 μL and 4.55 μL, and the corresponding theoretical spectrum was established according to the spectral calculation formula. According to the above glue amount, the verification samples were made and tested the color coordinates (0.3409, 0.2992) and the homologous spectra were basically coincident with the theoretical spectra.
-
Key words:
- quantum dots /
- white LED /
- Matlab /
- spectral fitting
-

Overview: Quantum dot material is a new semiconductor luminescent material which has the characteristics of narrow luminescent spectrum, adjustable luminescent wavelength and high quantum yield. Because of its narrow fluorescence spectrum, the light-emitting device is very helpful to improve the color gamut and saturation in the backlight field. Quantum dot materials are used as backlight devices to improve the color gamut and saturation which need to match the white light to meet the requirements through the principle of three primary colors. At present, there are many studies on the fitting method of white light spectrum, but it is not verified by the quality ratio of fluorescent materials in actual production. Based on the CIE 1931 XYZ surface color system, a new white light spectrum fitting method is developed in this paper.
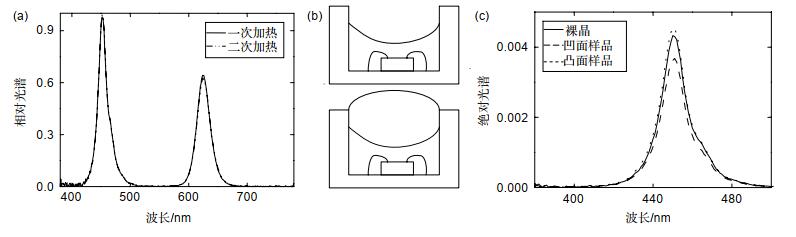
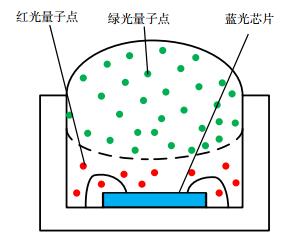
The ratio of red and green QDs to glue was (1: 60) and (1: 10). The test range of the glue content was 1.4 μL~2.2 μL and 3.0 μL~5.0 μL. In the experiment, the traditional LED manufacturing method is used and the red green quantum dots are excited by the characteristics of blue light short wavelength and high energy to obtain the red green blue three colors which are mixed into white light. At the same time, due to the more stable nature of red quantum dots, the layered structure of red quantum dots under green quantum dots is adopted. Make samples according to the above-mentioned manufacturing method, test the absorption and conversion ratio of different samples to blue light, get the functional relationship between glue amount and absorption and conversion ratio through Matlab fitting, and then substitute it into the calculation formula to get the white light area. In the experiment, it is found that the amount of red-green quantum dots with layered structure will affect each other's absorption conversion; therefore, when fitting the functional relationship between the amount of glue and the absorption conversion, it is necessary to take the amount of red-green quantum dots as an independent variable at the same time.
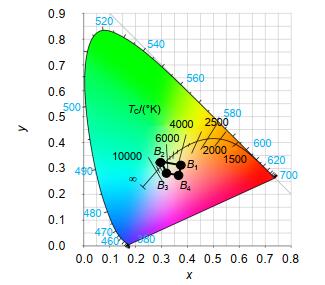
According to the spectral fitting method, the white light region of each sample in the color coordinate is calculated, and a point (0.34, 0.3) in the region is taken. The corresponding red and green quantum dots are 1.9 μL and 4.55 μL by the inverse use of the spectral fitting method, so the corresponding theoretical spectrum is obtained. Then, according to the above-mentioned amount of glue, the white light spectrum is obtained, which basically coincides with the theoretical spectrum, and the color coordinate points (0.3409, 0.2992) obtained from the actual spectrum are also basically close. The fitting method of white light spectrum introduced in this paper is combined with the actual production and verified, which has a certain reference value for the preparation of white light of photoluminescent products.
-

-
表 1 不同量子点胶量的吸收和转化率
Table 1. Absorption and conversion of different quantum dot gels
红光量子点胶量/μL 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 红光量子点吸收率 0.5420 0.5611 0.5826 0.5968 0.6022 红光量子点转化率 0.1715 0.1815 0.2075 0.2191 0.2282 绿光量子点胶量/μL 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 绿光量子点吸收率 0.7327 0.7639 0.7865 0.8055 0.8257 绿光量子点转化率 0.2085 0.21543 0.2077 0.2038 0.2030 -
[1] 季洪雷, 周青超, 潘俊, 等.量子点液晶显示背光技术[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(5): 666-680. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201705013
Ji H L, Zhou Q C, Pan J, et al. Advances and prospects in quantum dots based backlights[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(5): 666-680. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201705013
[2] Smet P F, Parmentier A B, Poelman D. Selecting conversion phosphors for white light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(6): R37-R54. doi: 10.1149/1.3568524
[3] 王巍, 李一, 宁平凡, 等.广色域钙钛矿量子点/荧光粉转换白光LED[J].发光学报, 2018, 39(5): 627-632. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fgxb201805004
Wang W, Li Y, Ning P F, et al. Perovskite quantum dot/powder phosphor converted white light LEDs with wide color gamut[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(5): 627-632. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fgxb201805004
[4] 柳杨, 刘志伟, 卞祖强, 等.高效、稳定Ⅱ-Ⅵ族量子点发光二极管(LED)的研究进展[J].无机化学学报, 2015, 31(9): 1751-1760. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjhxxb201509007
Liu Y, Liu Z W, Bian Z Q, et al. Research progress on high-efficiency and stable Ⅱ-Ⅵ groug quantum-dot light-emitting diodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 31(9): 1751-1760. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjhxxb201509007
[5] Wang R F, Zhang J L, Xu X M, et al. White LED with high color rendering index based on Ca8Mg(SiO4)4Cl2: Eu2+ and ZnCdTe/CdSe quantum dot hybrid phosphor[J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 84(1): 24-26. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257009866_White_LED_with_high_color_rendering_index_based_on_Ca8MgSiO44Cl2Eu2_and_ZnCdTeCdSe_quantum_dot_hybrid_phosphor?_sg=a8rqpXXU5qKatzJC6BNbuUrp2xF_EjgCIsG2zfdcOAsAOvXHk2Clg0dIQzNzAiVeONQMhDLSQel1Iu8
[6] Valcheva E, Yordanov G, Yoshimura H, et al. Low temperature studies of the photoluminescence from colloidal CdSe nanocrystals prepared by the hot injection method in liquid paraffin[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 461: 158-166. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=94d26cebbe25449c5df0672ac1ec5f94
[7] Shirasaki Y, Supran G J, Bawendi M G, et al. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(1): 13-23. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.328
[8] Ning P F, Zhang C Y, Liu J G, et al. Photoluminescence and thermal stability of Mn2+-doped CdSe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 13th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting, 2016: 63-65.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312114505_Photoluminescence_and_thermal_stability_of_Mn_2_-doped_CdSeCdSZnS_quantum_dots [9] Jain A, Voznyy O, Hoogland S, et al. Atomistic design of CdSe/CdS core-shell quantum dots with suppressed auger recombination[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(10): 6491-6496. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03059
[10] Gutsev L G, Ramachandran B R, Gutsev G L. Pathways of growth of CdSe nanocrystals from nucleant (CdSe)34 clusters[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(5): 3168-3175. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12716
[11] Kurochkin N S, Katsaba A V, Ambrozevich S A, et al. Energy transfer in hybrid systems composed of TPD and CdSe/CdS/ZnS colloidal nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 194: 530-534. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.11.001
[12] 齐永莲, 王丹, 邱云, 等.超高色域图案化量子点彩膜的研究[J].液晶与显示, 2017, 32(3): 169-176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201703002
Qi Y L, Wang D, Qiu Y, et al. Ultro-high color gamut and patterned color filter based on quantum dot photoresist[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2017, 32(3): 169-176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201703002
[13] Wang Y, Li X M, Song J Z, et al. All-inorganic colloidal perovskite quantum dots: a new class of lasing materials with favorable characteristics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(44): 7101-7108. doi: 10.1002/adma.201503573
[14] Song J Z, Li J H, Li X M, et al. Quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on inorganic perovskite cesium lead halides (CsPbX3)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(44): 7162-7167. doi: 10.1002/adma.201502567
[15] 刘选福.蓝光光谱宽度及荧光粉配比对白光性能的影响研究[D].大连: 大连工业大学, 2017.
Liu X F. Research on the effect of spectral width of blue light and phosphor ratios on the optical performance of white light[D]. Dalian: Dalian Polytechnic University, 2017.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10152-1018021091.htm [16] 唐爱伟, 滕枫, 王元敏, 等. Ⅱ-Ⅵ族半导体量子点的发光特性及其应用研究进展[J].液晶与显示, 2005, 20(4): 302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2005.04.008
Tang A W, Teng F, Wang Y M, et al. Luminescent characteristics and applied research progress of Ⅱ-Ⅵ semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2005, 20(4): 302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2005.04.008
[17] Fang Z L. Semiconductor Lighting Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009: 19-26.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: