-
摘要:
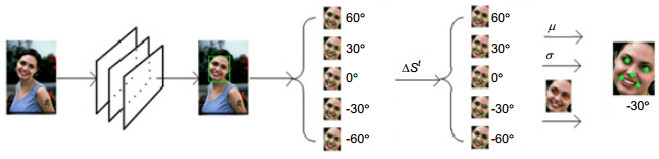
针对人脸关键点检测(人脸对齐)在应用场景下的速度和精度需求, 首先在SSD基础之上融合更多分布均匀的特征层, 对人脸框坐标进行级联预测, 形成对于多尺度人脸信息均具有更加鲁棒响应的深度学习检测器MR-SSD。其次在局部二值特征LBF的级联形状回归方法基础上, 提出了基于面部像素差值的多角度初始化算法。采用端正人脸正负90°倾斜范围内的五组特征点形状进行初始化, 求取每组回归后形状的眼部特征点像素均方差值并以最大者对应方案作为最终回归形状, 从而实现对多角度倾斜人脸优异的拟合效果。本文所提出的最优架构可以实时获得极具鲁棒性的人脸框坐标并且可实现对于多角度倾斜人脸的关键点检测。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to meet the speed and accuracy requirements of face key point detection (face alignment) in application scenarios, firstly, cascaded prediction is carried out on the basis of SSD (single shot multibox detector), which combines more uniformly distributed feature layers to form MR-SSD (more robust SSD), a deep learning detector with more robust response to multi-scale faces. Secondly, based on the cascade shape regression method of local binary feature (LBF), a multi-angle initialization algorithm based on the difference between the facial pixels is proposed. Five groups of feature points in the 90 degree inclination range of positive and negative face are initialized to achieve excellent fitting effect for inclined face under multi angles. The mean square deviation of each group of feature points after regression is calculated and the maximum corresponding shape is used as the final regression shape. The optimal architecture proposed in this paper can obtain robust face bounding box and face alignment schemes against multi-angle tilt in real time.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- machine learning /
- face keypoint detection /
- face alignment /
- pixel difference
-

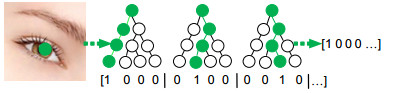
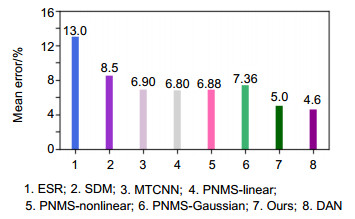
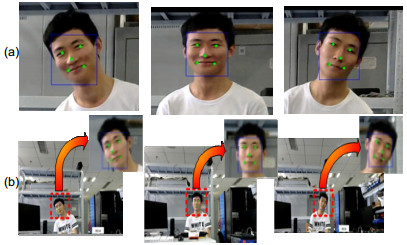
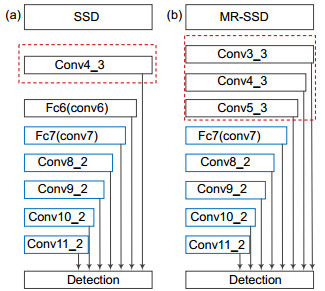
Overview: The introduction and maturity of deep learning technology greatly promote the development of object detection and key point detection technology. Face alignment, as an extension of the task of face detection, as well as the basis of face calibration and face recognition, is of great significance. For example, in expression recognition, face alignment provides possibilities for the research of emotion recognition. In addition, many applications with the function of beautifying pictures, including face polishing, dynamic face changing effects and so on, need face alignment technology to get facial feature points or feature areas for related operations. There are many methods for realizing face alignment algorithm. Cao et al. put forward ESR (explicit shape regression) scheme to regress the display shape. SDM algorithm uses supervised descent method to achieve the objective function of non-linear least squares, so that it converges to the minimum at a very fast speed. The LBF scheme uses the method of extracting local binary features for regression, which greatly improves the speed of location of key points. In the PNMS scheme, discontinuous linear functions and continuous functions based on Gauss distribution are introduced to improve the non-maximum suppression algorithm, and the candidate windows are re-scored to improve the accuracy and speed. In the scheme of deep learning architecture, Zhang et al. proposed the representative MTCNN (multi-task convolutional neural network) architecture using the deep cascade network, which improves the performance of tasks by utilizing the intrinsic relationship between face detection and face alignment. The unified three-stage cascade CNN is used to advance from coarse-grained to fine-grained step by step. Later, DAN (deep alignment network) used in-depth learning scheme to extract key points of human face. DAN contains many stages, each stage is to modify the position of key points of human face estimated in the previous stage. Based on the requirement of speed and accuracy, the paper uses deep learning architecture to provide accurate regression of face bounding box, and then a multi-angle initialization algorithm is proposed to achieve fast face key point location. This paper makes the following two tasks: 1) On the basis of one-stage network SSD, cascaded regression prediction is carried out by fusing eight feature layers with uniform distribution, and a robust model MR-SSD is formed by choosing the scale of accurate prediction which accords with the proportion of faces, and can make better response to multi-scale face information and save time. 2) A cascade regression scheme based on LBF binary feature is proposed, and a multi-angle initialization algorithm based on pixel difference is proposed. Five groups of uniformly separated initial shapes are used for each image to be fed into the model regression. Then the mean square deviation of the pixels is calculated for the key areas of the eye, and the regression shape with the largest jitter is obtained as the final regression shape of points. Compared with the traditional face alignment scheme based on machine learning, the architecture can obtain more accurate facial feature points regression and faster real-time speed.
-

-
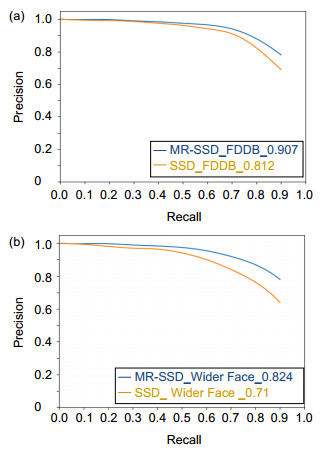
表 1 精度与速度的比较
Table 1. Comparison between accuracy and speed
Network Mean accuracy Speed/(f/s) FDDB Wide Face SSD 0.812 0.71 42 MR-SSD 0.907 0.824 41 表 2 平均人脸检测速度的比较
Table 2. Comparison of detection speed
Architecture GPU Real-time speed/(f/s) MTCNN GeForce GTX TITAN X 50 PNMS-linear GeForce GTX TITAN X 40 PNMS-nonlinear GeForce GTX TITAN X 71 PNMS-Gaussian GeForce GTX TITAN X 83 Ours NVIDIA 1060Ti 66 表 3 平均对齐速度的比较
Table 3. Comparison of alignment speed
Architecture Real-time speed/(f/s) SDM 40 LBF 3000 DAN 73 Ours 76 表 4 测试图片关键点检测平均误差
Table 4. Mean error of key point detection on test image
Architecture Mean error/% LBF 7.9 Multi-angle key point detection algorithm 5.4 表 5 变化倾斜角下不同算法的效果对比
Table 5. Different algorithm comparison upon variable angle
Architecture Error/% Inclination angle/(°) HELEN LFPW LBF 5.41 3.35 ±10 MR-SSD+multi-angle key point detection algorithm 3.61 2.17 ±50 -
[1] Wang Y M, Pan G, Wu Z H. A survey of 3D face recognition[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2008, 20(7): 819–829. doi: 10.3745/JIPS.2009.5.2.041
[2] Peng M C, Bao J, Ye M, et al. Face alignment algorithm based on shape parameter regression[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 29(1): 63–71. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201601008
[3] Zhu C R, Wang R S. Adaptive facial feature selection algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2002, 14(1): 26–30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2002.01.007
[4] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 580–587.
[5] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2015: 1440–1448.
[6] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 91–99.
[7] Uijlings J R R, van de Sande K E A, Gevers T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154–171. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3216de1927eb16418ad3bdf8d4bcd8bd
[8] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 21–37.
[9] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016: 779–788.
[10] Cao X D, Wei Y C, Wen F, et al. Face alignment by explicit shape regression[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 107(2): 177–190. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.201711
[11] Xiong X H, De la Torre F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2013: 532–539.
[12] Ren S Q, Cao X D, Wei Y C, et al. Face alignment at 3000 FPS via regressing local binary features[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 1685–1692.
[13] 李振东, 钟勇, 陈蔓, 等.基于惩罚因子的PNMS算法的人脸检测和对齐[J].工程科学与技术, 2018, 50(6): 225–231. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.201701086
Li Z D, Zhong Y, Chen M, et al. PNMS algorithm based on penalty factors for face detection and alignment[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2018, 50(6): 225–231. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.201701086
[14] Zhang K P, Zhang Z P, Li Z F, et al. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(10): 1499–1503. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2603342
[15] Jiao F, Shan S G, Cui G Q, et al. Face recognition based on local feature analysis[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2003, 15(1): 53–58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_ec6b86e81d73524c4bee848acd29070c
[16] Song H, Shi F. Multi-view face detection and pose discrimination in video[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2007, 19(1): 90–95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2007.01.017
[17] Zhang S F, Zhu X Y, Lei Z, et al. S3FD: single shot scale-invariant face detector[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017: 192–201.
[18] Wan J, Li J, Chang J, et al. Face alignment on local-shape-based combined model[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(9): 2162–2174. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.02162
[19] Bodini M. A review of facial landmark extraction in 2D images and videos using deep learning[J]. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 2019, 3(1): 14. doi: 10.3390/bdcc3010014
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: