-
摘要:
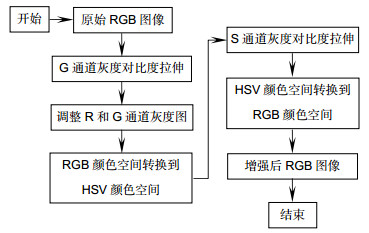
为了提高医用电子内窥镜所获图像的血管与组织的对比度, 针对内窥镜血管图像的特点, 提出了一种基于多颜色空间非线性对比度拉伸的血管增强处理方法。首先在RGB颜色空间利用非线性映射函数对绿色(G)分量进行自适应对比度拉伸;接着依据G分量的拉伸结果, 相应地调整红色(R)和蓝色(B)两个分量的灰度值;然后将图像转换到HSV颜色空间, 并对图像的饱和度(S)分量进行自适应对比度拉伸;最后将图像转换回RGB颜色空间, 最终达到血管增强的目的。在本文中, 利用所提出的算法对多幅电子内窥镜图像进行处理, 结果表明, 算法对于原始特征不明显的细小血管也具有较好的增强效果。通过与其它的增强方法相对比, 增强后图像的细节方差(DV)显著大于其它方法。将算法嵌入到分辨率为1280×800的内窥镜软件中, 其处理速度可达26 f/s。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to improve the contrast between the blood vessels and tissues of the images obtained by medical electronic endoscopes, a vessel enhancement method of non-linear contrast stretching in multi-color space is proposed according to the characteristics of endoscopic vascular images. Firstly, in RGB color space, stretching contrast adaptively of the green (G) component by using the nonlinear mapping function. Secondly, adjusting the gray value of the two components of red (R) and blue (B) according to the stretching result of the G component. Thirdly, converting the image to HSV color space, and stretching contrast adaptively of the saturation (S) component of the image. Finally, converting the image back to RGB color space, and the purpose of vessel enhancement is achieved. In this paper, the proposed algorithm is used to process several electronic endoscopic images with different contrast and brightness. The results show that the algorithm has better enhancement effect on small blood vessels which are not obvious in original features. Comparing to other enhancement methods, the detail variance (DV) of the enhanced image is significantly great. The algorithm is embedded in a resolution of 1280×800 endoscopic software, 26 frames can be processed per second.
-
Key words:
- contrast /
- vessel enhancement /
- color space /
- electronic endoscope
-

Overview: The vessel enhancement for medical endoscopic images can provide more details of blood vessels, which is useful for assisting doctors in diagnosis. An enhancement method based on multi-color spatial nonlinear contrast stretching is proposed in the present study, which is able to effectively perform vessel enhancement for endoscopic images in real time.
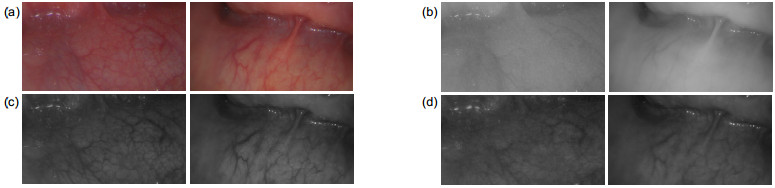
In the proposed method, the contrast stretching for enhancement is successively carried out for the G (Green) component in RGB color space and the S (Saturation) component in HSV color space. Since the details in G component are usually clearer than those in R (Red) and B (Blue) component for the endoscopic tissue images, the contrast stretching for G component only can more effectively enhance the vessels in the tissue. And the contrast stretch for S component can make the color of vessels brighter than that of tissue, which is suitable to the human visual system.
First, the G component is mapped by a nonlinear mode for contrast stretching. The mapping parameter is determined by that the value with maximum contrast stretching effect in the nonlinear mode is equal to the average value of G component of image. Then, the color space of image is converted from RGB to HSV and the S component is mapped by a nonlinear mode same to the G component. Similarly, the mapping parameter of S component is determined by that the value with maximum contrast stretching effect is equal to the average value of S component of image. Finally, the enhanced image is obtained by converting the HSV data with enhanced S component to RGB color space.
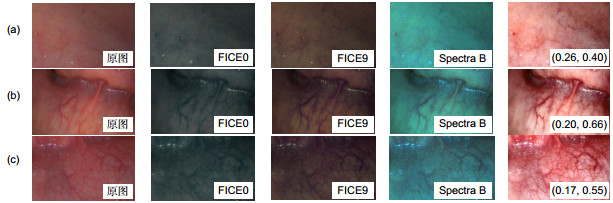
The above algorithm was implemented by a C# program and its enhancement effect was tested by multiple endoscopic vessel images. The experiment results show that even very small vessels which are almost invisible in the original images can be seen in the enhanced images under the suitable mapping parameter determined by the proposed method. The enhanced images are also compared with those obtained by FICE and Spectral-B, which are normal enhancement methods in their respective endoscopes. It is showed that only our enhancement images have consistent color tone with the original images and the DVs (detail variances) of our enhancement images are significantly larger than those obtained by FICE or Spectral-B. The enhancement algorithm was embedded in the program for an endoscope with a resolution of 1280 pixels×800 pixels, and the video speed with enhancement effect was tested to reach 26 fps on a computer with the 2.7 GHz CPU and 3.2 G memory.
-

-
表 1 不同增强方法下图像的BV和DV值
Table 1. BV and DV values of the images obtained by different enhancement methods
测试图片 评价指标 原图 FICE0 FICE9 Spectra B 本文方法 a DV 23.44 23.23 25.51 40.18 101.15 BV 11.51 12.78 11.88 20.53 30.72 DV/BV 2.04 1.82 2.15 1.96 3.29 b DV 40.31 40.77 49.46 62.93 151.40 BV 8.00 10.24 9.51 14.85 16.02 DV/BV 5.04 3.98 5.20 4.24 9.45 c DV 35.03 30.08 38.09 61.48 221.14 BV 11.65 13.88 12.84 21.36 47.57 DV/BV 3.01 2.17 2.96 2.88 4.64 -
[1] Fraz M M, Remagnino P, Hoppe A, et al. Blood vessel segmentation methodologies in retinal images–a survey[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2012, 108(1): 407–433. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2012.03.009
[2] Yang S F, Cheng C H. Fast computation of Hessian-based enhancement filters for medical images[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2014, 116(3): 215–225. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.05.002
[3] Oh J, Hwang H. Feature enhancement of medical images using morphology-based homomorphic filter and differential evolution algorithm[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2010, 8(4): 857–861. doi: 10.1007/s12555-010-0418-y
[4] Yin X X, Ng B W H, He J, et al. Accurate image analysis of the retina using Hessian matrix and binarisation of thresholded entropy with application of texture mapping[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e95943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095943
[5] Ajam A, Aziz A A, Asirvadam V S, et al. Cerebral vessel enhancement using bilateral and Hessian-based filter[C]//Proceedings of 2016 6th International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS), 2016.
[6] Kakushima N, Yoshida M, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Magnified endoscopy with narrow-band imaging for the differential diagnosis of superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 2019, 54(1): 128–134. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2018.1557740
[7] Osawa H, Yamamoto H. Present and future status of flexible spectral imaging color enhancement and blue laser imaging technology[J]. Digestive Endoscopy, 2014, 26(S1): 105–115. doi: 10.1111/den.12205
[8] Kodashima S, Fujishiro M. Novel image-enhanced endoscopy with i-scan technology[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2010, 16(9): 1043–1049. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1043
[9] 姜鸿鹏, 章科建, 袁波, 等.一种血管内窥镜图像增强算法[J].光电工程, 2019, 46(1): 28–36. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180167
Jiang H P, Zhang K J, Yuan B, et al. A vascular enhancement algorithm for endoscope image[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2019, 46(1): 28–36. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180167
[10] Hebden J C, Varela M, Magazov S, et al. Diffuse optical imaging of the newborn infant brain[C]//Proceedings of 2012 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, 2012: 503–505.
[11] Preece S J, Claridge E. Monte Carlo modelling of the spectral reflectance of the human eye[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2002, 47(16): 2863–2877. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/47/16/303
[12] Robles F E, Chowdhury S, Wax A. Assessing hemoglobin concentration using spectroscopic optical coherence tomography for feasibility of tissue diagnostics[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2010, 1(1): 310–317. doi: 10.1364/BOE.1.000310
[13] 张弘, 曹晓光, 谢凤英.数字图像处理与分析[M]. 2版.北京:机械工业出版社, 2013.
Zhang H, Cao X G, Xie F Y. Digital Image Processing and Analysis[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2013.
[14] Coriat R, Chryssostalis A, Zeitoun J D, et al. Computed virtual chromoendoscopy system (FICE): a new tool for upper endoscopy?[J]. Gastroentérologie Clinique et Biologique, 2008, 32(4): 363–369. doi: 10.1016/j.gcb.2007.11.013
[15] Kamphuis G M, de Bruin D M, Fallert J, et al. Storz professional image enhancement system: a new technique to improve endoscopic bladder imaging[J]. Journal of Cancer Science & Therapy, 2016, 8(3): 71–77. doi: 10.4172/1948-5956.1000394
[16] Xu Z Y, Liu X M, Ji N. Fog removal from color images using contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization[C]//Proceedings of 2009 2nd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2009.
[17] 张勇, 王和明, 周瑞钊, 等.一种改进的红外图像降噪算法与FPGA实现[J].火力与指挥控制, 2017, 42(6): 167–170, 174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2017.06.038
Zhang Y, Wang H M, Zhou R Z, et al. A improved infrared image noise reduction algorithm and FPGA implement[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2017, 42(6): 167–170, 174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2017.06.038
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: