-
摘要:
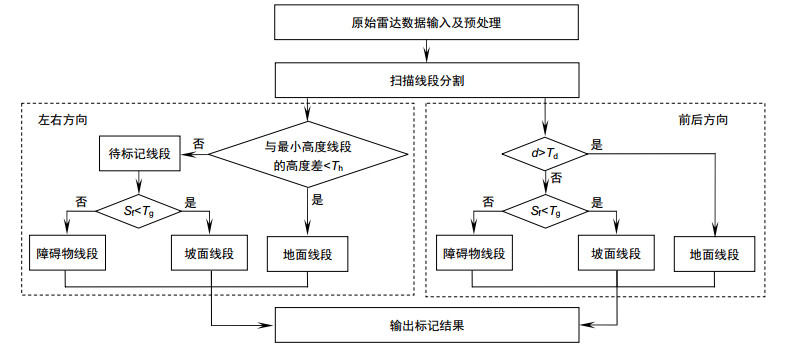
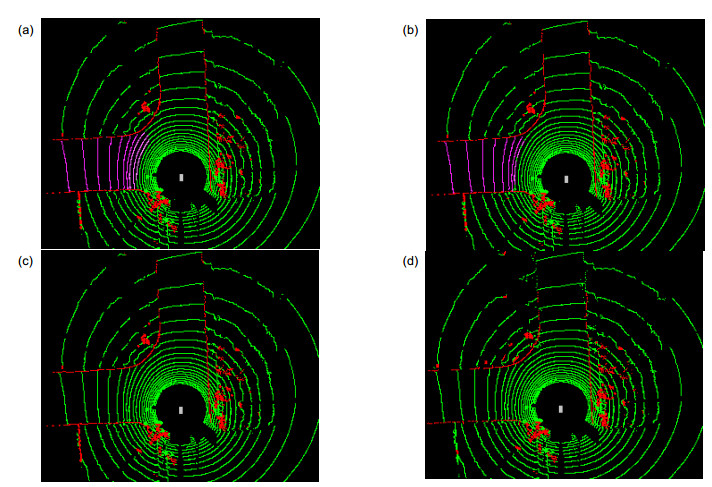
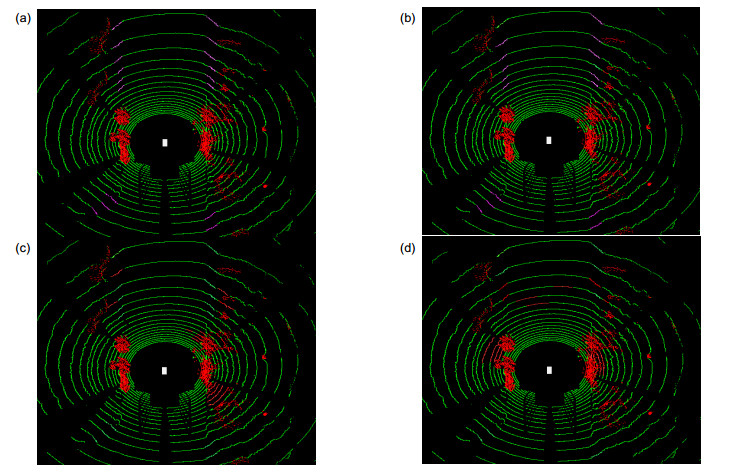
针对从三维激光雷达点云中准确实时地分割地面的问题,提出一种基于扫描线段特征的地面分割算法。算法首先对三维点云进行去噪和位姿修正,接着依据相邻点间的欧氏距离和绝对高度差分割扫描线,然后对扫描线段的相邻线段间距、倾斜度、绝对高度差等特征进行分析,采用最大似然估计法求解特征阈值函数,提高了阈值的自适应性;最后综合考虑起伏、倾斜等复杂地形,通过制定横、纵向分类策略将扫描线标记为平坦地面线段、坡面线段和障碍物线段。本算法已成功应用在地面无人平台上,使用情况和对比试验表明,在城市和野外场景中,本算法都能够稳定高效地分割地面。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of accurately segmenting the ground in real-time from 3D LiDAR point cloud, a ground segmentation algorithm based on the features of scanning line segments is proposed. The algorithm first performs de-noising and pose correction on the 3D point cloud, then divides the scanning line according to the Euclidean distance and absolute height difference between adjacent points. Next, the characteristics of the adjacent line segments such as spacing, slope, and absolute height difference are analyzed. The maximum likelihood estimation is used to solve the feature threshold function, which improves the adaptability of threshold. Finally, comprehensively considering the undulating and inclined complex terrain, the scanning line segments are marked as segments of flat ground, segments of slope and segments of obstacle by formulating the new horizontal and vertical classification strategies. This algorithm has been successfully applied to the unmanned ground platform. The usage and comparative test show that the algorithm can detect the ground stably and efficiently in both urban and field scenarios.
-
Key words:
- 3D LiDAR /
- ground segmentation /
- segment features /
- complex terrain /
- real-time
-

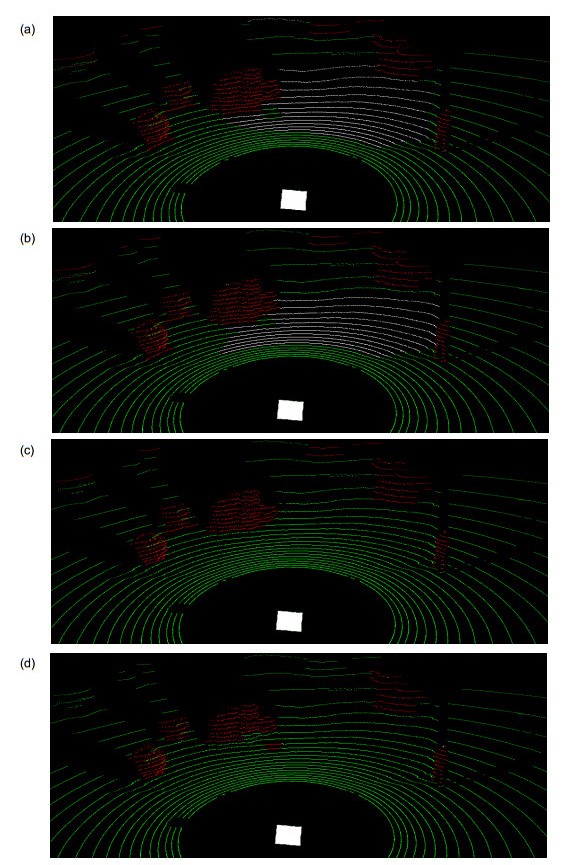
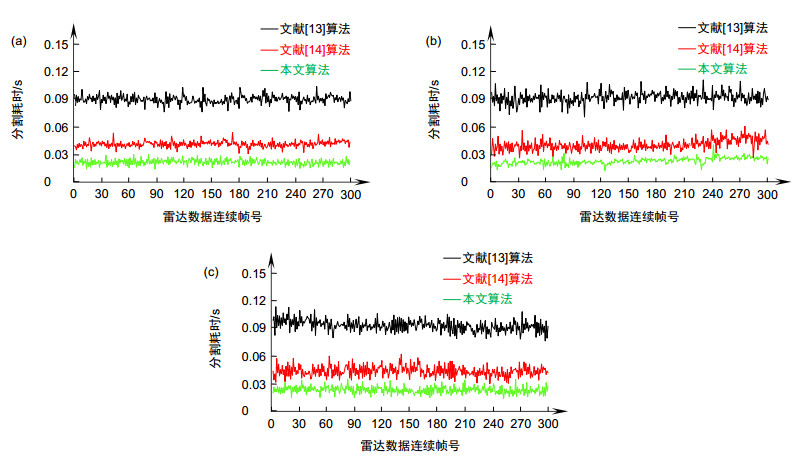
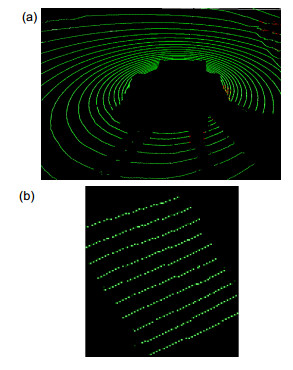
Overview: The development of unmanned vehicles is very rapid, but most of the studies are based on the urban environment, while the ground segmentation in the complex environment still faces many challenges. The problems include: 1) in the bumpy terrain, the platform will have changes in pitch, roll and suspension; 2) the LiDAR points are unevenly distributed, such as the measurement points in the area close to the LiDAR are densely distributed relatively, while the distribution of measurement points in the area away from the LiDAR is sparse, which results in a large range of gaps between different scanning lines; 3) in the case of processing a few millions of points, the accuracy and real-time of the segmentation are difficult to balance. This article conducts research aiming at the problem of accurately segmenting the ground in real-time from 3D point cloud in various environments. Considering that the existing methods are complex, long time consuming, or selected features are not universal, a ground segmentation algorithm based on the features of scanning line segments is proposed. The algorithm first performs de-noising and pose correction on the 3D point cloud, then divides the scanning line according to the Euclidean distance and absolute height difference between adjacent points. Next, the characteristics of the adjacent line segments such as spacing, slope, and absolute height difference are analyzed. The maximum likelihood estimation is used to solve the feature threshold function, which improves the adaptability of threshold. Finally, comprehensively considering the undulating and inclined complex terrain, combining the distribution characteristics of the features of scanning line segments, the scanning line segments are marked as segments of flat ground, segments of slope and segments of obstacle by formulating the new horizontal and vertical classification strategies: firstly select the line segment with the smallest height from the scanning line closest to the radar origin and mark it as the initial ground scanning line segment. Then determine the line segments type in the scanning line closest to the radar origin horizontally and determine the segments type in other scanning lines vertically. This algorithm has been successfully applied to the unmanned ground platform. The effect of the actual engineering application indicates that, the features selected in this paper have high sensitivity and easy extraction, which are less affected by noise than single point features. The segmentation algorithm is highly efficient and robust, which can detect the ground stably and efficiently in structured road scene, wild undulating road scene and complex undulating scene. And the comparative test results of the algorithm in this paper with the local elevation estimation algorithm in Ref. [13] and the feature fusion algorithm in Ref. [14] show that the segmentation effect of this algorithm is superior to the other two algorithms in accuracy and time-consuming.
-

-
表 1 不同场景中分割算法的效果对比
Table 1. Result comparison of segmentation algorithms in different scenes
-
[1] 龚友平, 金涛, 童水光.点云数据区域分割方法[J].工程图学学报, 2006, 27(4): 8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0158.2006.04.002
Gong Y P, Jin T, Tong S G. Segmentation method for point cloud data[J]. Journal of Engineering Graphics, 2006, 27(4): 8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0158.2006.04.002
[2] 吴禄慎, 俞涛, 陈华伟.基于自适应椭圆距离的点云分区精简算法[J].计算机应用与软件, 2016, 33(2): 42-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2016.02.010
Wu L S, Yu T, Chen H W. Reduction algorithm of point cloud segmentation based on adaptive elliptical distance[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2016, 33(2): 42-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2016.02.010
[3] Huangfu Z M, Yan L, Zhang S. A new method for estimation of normal vector and curvature based on scattered point cloud[J]. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 2012, 8(19): 7937-7945.
[4] Klasing K, Wollherr D, Buss M. A clustering method for efficient segmentation of 3D laser data[C]//Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2008: 4043-4048.
[5] Rabbani T, Van den Heuvel F A, Vosselman M G. Segmentation of point clouds using smoothness constraints, international archives of photogrammetry[J]. Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2006, 36(5): 248-253.
[6] Vo A V, Truong-Hong L, Laefer D F, et al. Octree-based region growing for point cloud segmentation[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 104: 88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.01.011
[7] 郭保青, 余祖俊, 张楠, 等.铁路场景三维点云分割与分类识别算法[J].仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(9): 2103-2111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.09.002
Guo B Q, Yu Z J, Zhang N, et al. 3D point cloud segmentation, classification and recognition algorithm of railway scene[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(9): 2103-2111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.09.002
[8] Hoffman R, Jain A K. Segmentation and classification of range images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1987, PAMI-9(5): 608-620. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1987.4767955
[9] Zhang X M, Wan W G, Xiao L, et al. Mean shift clustering segmentation and RANSAC simplification of color point cloud[C]//Proceedings of 2014 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, 2014: 837-841.
[10] Kisner H, Thomas U. Segmentation of 3D point clouds using a new spectral clustering algorithm without a-priori knowledge[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, 2018: 315-322.
[11] Kuçak R A, Özdemir E, Erol S. The segmentation of point clouds with k-means and ANN (artifical neural network)[J]. ISPRS-International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2017, XLⅡ-1/W1: 595-598.
[12] 王晓辉, 吴禄慎, 陈华伟, 等.应用改进的粒子群优化模糊聚类实现点云数据的区域分割[J].光学精密工程, 2017, 25(4): 1095-1105. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172504.1095
Wang X H, Wu L S, Chen H W, et al. Region segmentation of point cloud data based on improved particle swarm optimization fuzzy clustering[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(4): 1095-1105. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172504.1095
[13] Rummelhard L, Paigwar A, Nègre A, et al. Ground estimation and point cloud segmentation using SpatioTemporal conditional random field[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2017: 1105-1110.
[14] 樊丽, 刘晋浩, 黄青青.基于特征融合的林下环境点云分割[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(5): 133-138. doi: 10.13332/j.1000--1522.20150332
Fan L, Liu J H, Huang Q Q. Point cloud segmentation algorithm based on feature fusion used for understory environments[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(5): 133-138. doi: 10.13332/j.1000--1522.20150332
[15] Moosmann F, Pink O, Stiller C. Segmentation of 3D Lidar data in non-flat urban environments using a local convexity criterion[C]//Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2009: 215-220.
[16] Hernandez J, Marcotegui B. Point cloud segmentation towards urban ground modeling[C]//Proceedings of 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, 2009: 1-5.
[17] Himmelsbach M, Hundelshausen F V, Wuensche H J. Fast segmentation of 3D point clouds for ground vehicles[C]//Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2010: 560-565.
[18] 朱株, 刘济林.基于马尔科夫随机场的三维激光雷达路面实时分割[J].浙江大学学报(工学版), 2015, 49(3): 464-469. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2015.03.010
Zhu Z, Liu J L. Real-time Markov random field based ground segmentation of 3D Lidar data[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2015, 49(3): 464-469. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2015.03.010
[19] 赵凯, 徐友春, 王任栋.一种城市环境三维点云配准的预处理方法[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(12): 180266. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180266
Zhao K, Xu Y C, Wang R D, et al. A preprocessing method of 3D point clouds registration in urban environments[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(12): 180266. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180266
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: