-
摘要:
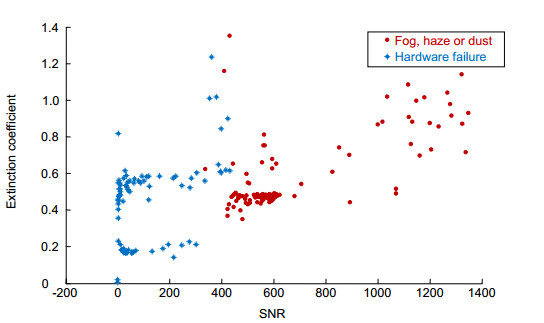
激光雷达出现硬件故障时,会使回波数据的质量变差。目前,对由硬件故障造成的错误回波还缺乏比较有效的识别方法。对中国科学院安徽光学精密机械研究所自主研发的大气颗粒物监测激光雷达有硬件故障出现时的回波数据进行分析,根据硬件故障对雷达的回波波形、强度等回波信号信息的影响,采用模糊逻辑算法对大气颗粒物雷达的硬件故障数据进行识别检验。同时,为了降低对无故障数据的误判,分析被误判数据的回波特征,比较硬件故障数据和被误判数据在300 m~500 m高度上对应的消光系数和信噪比均值,通过设置信噪比阈值来降低误判率。实验结果表明:应用此方法对外场运行的大气颗粒物监测激光雷达硬件故障数据进行识别,识别率为94.6%,而误判率仅为1.5%,证明该算法对硬件故障数据的识别有很好的效果。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The hardware fault of the LiDAR will make the quality of the echo data worse. However, there is still a lack of effective identification methods for the error data caused by the hardware failure. Analysis of echo characteristics of atmospheric particulate matter monitoring when LiDAR has hardware failure, according to the echo signal information of the echo shape and intensity of the LiDAR, the fuzzy logic algorithm is used to identify the fault data. The hardware fault data of the atmospheric particulate LiDAR is identified and tested. At the same time, in order to reduce the false positive rate of data without hardware failures, the mean values of extinction coefficient and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at the height of 300 meters to 500 meters were compared between the data of hardware failures and the data was misjudged, reduced the false positive rate by setting the signal to noise ratio threshold. The experimental results show that this method is used to identify the hardware fault data of the LiDAR monitoring of the external field, the recognition rate is 94.6%, and the false positive rate is only 1.5%. This method has a good recognition effect on hardware fault data.
-
Key words:
- LiDAR /
- fuzzy logic /
- membership function /
- signal to noise ratio /
- extinction coefficient
-

Overview: Particle LiDAR is a high-precision instrument with laser as the emitter. It continuously monitors the temporal and spatial evolution and characteristics of aerosol, boundary layer, cloud height and multi-layer cloud structure, thus obtaining the three-dimensional structure of atmospheric aerosol distribution with detailed changes, which has strong ability and high degree of automation. The particulate matter LiDAR is fully covered in the area to achieve high-temporal resolution air pollution monitoring, combined with the application of informational big data to achieve pollution source tracking, early warning, forecasting functions, etc., to provide more timely and effective decision support for environmental pollution prevention and control. However, when the hardware of the radar's transmitting unit, receiving unit, etc. fails, there will often be abnormal echo data generated, which will directly affect the subsequent inversion results and have a great influence on the accuracy of the above applications. As a long-term, high-intensity, continuous operation high-precision equipment, atmospheric particulate matter monitoring LiDAR affected by factors such as working environment and accessory quality, and hardware failure is difficult to avoid.
The hardware fault of the LiDAR will make the quality of the echo data worse. However, there is still a lack of effective identification methods for the error data caused by the hardware failure. Analysis of echo characteristics of atmospheric particulate matter monitoring when LiDAR has hardware failure, according to the echo signal information of the echo shape and intensity of the radar, the fuzzy logic algorithm is used to identify the fault data. The hardware fault data of the atmospheric particulate radar is identified and tested. At the same time, in order to reduce the false positive rate of data without hardware failures, the mean values of extinction coefficient and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at the height of 300 meters to 500 meters were compared between the data of hardware failures and the data was misjudged, reducing the false positive rate by setting the signal to noise ratio threshold. The experimental results show that this method is used to identify the hardware fault data of the LiDAR monitoring of the external field, the recognition rate is 94.6%, and the false positive rate is only 1.5%. This method has a good recognition effect on hardware fault data.
The method adopted in this paper can also realize the real-time monitoring of the LiDAR operating state and achieve real-time warning of the LiDAR running state, which provides a reference for us to find faults in time and ensures the normal operation of the equipment.
-

-
表 1 大气颗粒物监测激光雷达硬件故障数据识别表
Table 1. Identification of hardware failure data of atmospheric particulates monitor LiDAR
数据类型 判别为故障数据 判别为无故障数据 故障数据(1470) 1390(NTN) 80(NFP) 无故障数据(7226) 1228(NFN) 5998(NTP) 表 2 误判校正后颗粒物监测激光雷达硬件故障数据识别表
Table 2. Identification of the hardware failure data of atmospheric particulates monitor LiDAR after misjudgment correction
数据类型 判别为故障数据 判别为无故障数据 故障数据(1470) 1390(NTN) 80(NFP) 无故障数据(7226) 109(NFN) 7117(NTP) 表 3 颗粒物激光雷达硬件故障数据的识别表
Table 3. Identification of the hardware failure data of particle LiDAR
数据类型 判别为故障数据 判别为无故障数据 故障数据(185) 173(NTN) 12(NFP) 无故障数据(489) 11(NFN) 478(NTP) -
[1] 窦振中.模糊逻辑控制技术及其应用[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 1996.
Dou Z Z. Fuzzy Logic Control Technology and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1995.
[2] 董德保, 张统明, 翁宁泉, 等.基于模糊逻辑的风廓线雷达功率谱数据质量控制研究[J].高原气象, 2015, 34(2): 568-574. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyqx201502028
Dong D B, Zhang T M, Weng N Q, et al. Power spectrum data quality control method of wind profile radar based on fuzzy logic[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2015, 34(2): 568-574. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyqx201502028
[3] 刘黎平, 吴林林, 杨引明.基于模糊逻辑的分步式超折射地物回波识别方法的建立和效果分析[J].气象学报, 2007, 65(2): 252-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2007.02.011
Liu L P, Wu L L, Yang Y M. Development of fuzzy-logical two-step ground clutter detection algorithm[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2007, 65(2): 252-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2007.02.011
[4] 刘增良, 刘有才.模糊逻辑与神经网络:理论研究与探索[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 1996.
Liu Z L, Liu Y C. Fuzzy Logic and Neural Network: Theoretical Research and Exploration[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1996.
[5] 张秉祥, 李国翠, 刘黎平, 等.基于模糊逻辑的冰雹天气雷达识别算法[J].应用气象学报, 2014, 25(4): 415-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.04.004
Zhang B X, Li G C, Liu L P, et al. Identification method of hail weather based on fuzzy-logical principle[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2014, 25(4): 415-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.04.004
[6] 庄薇, 刘黎平, 余燕群, 等.雷达地物回波模糊逻辑识别法的改进及效果检验[J].气象学报, 2012, 70(3): 576-584. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qxxb201203018
Zhuang W, Liu L P, Yu Y Q, et al. Improvement of the fuzzy logic technique for identifying ground clutter and its verification[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2012, 70(3): 576-584. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qxxb201203018
[7] 赵瑞金, 刘黎平, 张进.硬件故障导致雷达回波错误数据质量控制方法[J].应用气象学报, 2015, 26(5): 578-589. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyqxxb201505007
Zhao R J, Liu L P, Zhang J. The quality control method of erroneous radar echo data generated by hardware fault[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2015, 26(5): 578-589. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyqxxb201505007
[8] 马中元, 朱春巧, 刘熙明, 等. CINRAD雷达数据质量控制方法初探[J].气象, 2010, 36(8): 134-141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qx201008019
Ma Z Y, Zhu C Q, Liu X M, et al. Study on CINRAD radar data quality control methods[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2010, 36(8): 134-141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qx201008019
[9] 江源.天气雷达观测资料质量控制方法研究及其应用[D].南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2013.
Jiang Y. Meteorological radar data quality control studay and application[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2013.
[10] 邹强.多普勒天气雷达数据质量控制方法探讨[J].西南科技大学学报, 2009, 24(1): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2009.01.011
Zou Q. Discussion of doppler weather radar data quality control[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2009, 24(1): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2009.01.011
[11] 朱睿.多普勒雷达观测资料质量控制方法研究及其应用[J].科技创新与应用, 2014(27): 291. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qgsj201427272
Zhu R. Research and application of doppler radar observation data quality control method[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2014(27): 291. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qgsj201427272
[12] 郑佳锋, 刘黎平, 曾正茂, 等. Ka波段毫米波云雷达数据质量控制方法[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2016, 35(6): 748-757. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201606018
Zheng J F, Liu L P, Zeng Z M, et al. Ka-bard millimeter wave cloud radar data quality control[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(6): 748-757. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201606018
[13] 周芯玉, 廖菲.利用中位数方法对风廓线雷达数据质量控制的研究[J].热带气象学报, 2015, 31(6): 804-810. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdqxxb201506008
Zhou X Y, Liao F. A study on the quality control of wind profiler data by using the median method[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 2015, 31(6): 804-810. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdqxxb201506008
[14] 刘志青, 李鹏程, 陈小卫, 等.基于信息向量机的机载激光雷达点云数据分类[J].光学精密工程, 2016, 24(1): 210-219. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201601027
Liu Z Q, Li P C, Chen X W, et al. Classification of airborne LiDAR point cloud data based on information vector machine[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(1): 210-219. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201601027
[15] 马超杰, 杨华, 李晓霞, 等.复杂场景下应用成像Ladar的自动目标识别[J].光学精密工程, 2009, 17(7): 1714-1721. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2009.07.034
Ma C J, Yang H, Li X X, et al. Implementation of automatic target recognition by imaging Ladar in complex scenes[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2009, 17(7): 1714-1721. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2009.07.034
[16] 潘新民, 柴秀梅, 崔柄俭, 等. CINRAD/SB雷达回波强度定标调校方法[J].应用气象学报, 2010, 21(6): 739-746. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.06.011
Pan X M, Chai X M, Cui B J, et al. The method of CINRAD/SB radar echo intensity calibration and adjustment[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2010, 21(6): 739-746. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.06.011
[17] 胡东明, 刘强, 程元慧, 等. CINRAD/SA天线伺服系统轴角箱多次故障的分析[J].气象, 2007, 33(10): 114-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qx200710017
Hu D M, Liu Q, Cheng Y H, et al. Analysis of the multi-fault in conder of servo about CINRAD/SA radar[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2007, 33(10): 114-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qx200710017
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: