-
摘要:
自适应共焦检眼镜以其高分辨率、动态成像等光学特性,已经在生物医学和临床医学的多个领域得到了广泛而具体的应用。为了能够将非圆形光瞳滤波器等瞳面调制技术运用于其中,并不对波前探测产生影响,系统需要利用两个光源分别进行成像和波前校正。本文首先设计了一套基于双光源的自适应共焦检眼镜,对不同光源的人眼像差进行测量,分析了其主要差异。然后对双光源系统的像差校正能力和高分辨成像能力进行了验证,系统闭环后的图像的亮度、对比度和分辨率都有了显著的提高。最后验证了使用半圆形光瞳实现暗场成像的可行性,并得到了模拟人眼的明暗场图像。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Adaptive confocal laser ophthalmoscope with the high-resolution and dynamic imaging ability has been widely applied in specific biomedical and clinical medical fields. In order to apply the noncircular pupil filter and other pupil modulation technology without influence in wavefront detection, the system needs two light sources for imaging and aberration correction respectively. This paper has designed an adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy with two sources, and then analyzed the differences of the aberration of the two light sources. Then, the aberration correction and high-resolution imaging ability of the system have been verified, and the brightness, contrast and resolution of the image have been significantly improved after close-loop. Finally, we have studied the feasibility of realizing the dark field imaging by semi-circular pupil and obtained the bright and dark field images of the artificial eye.
-
Key words:
- adaptive optics /
- confocal laser ophthalmoscope /
- two sources
-

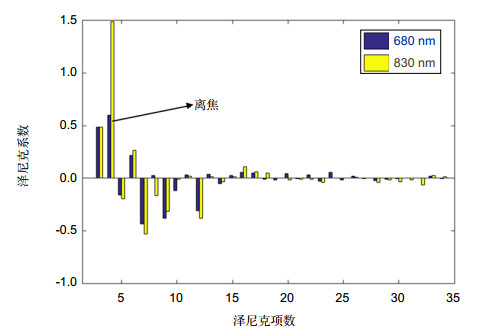
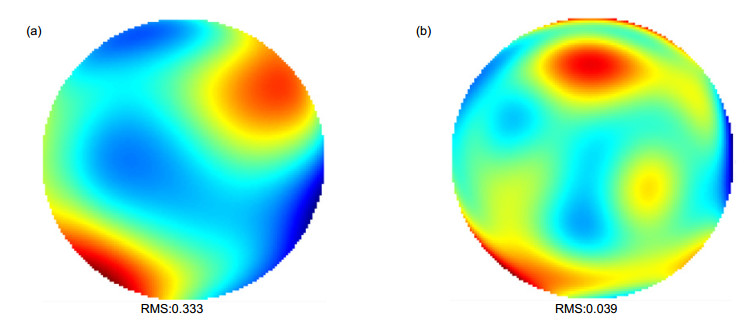
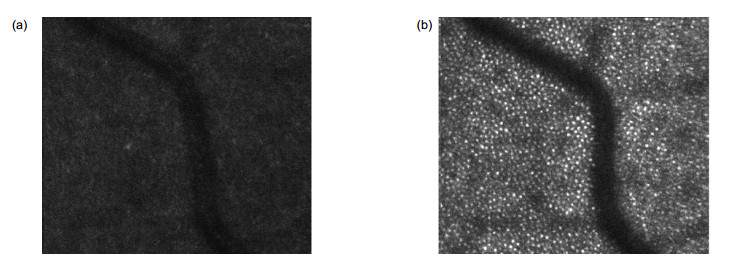
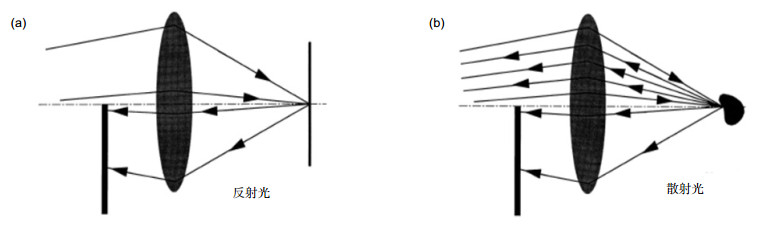
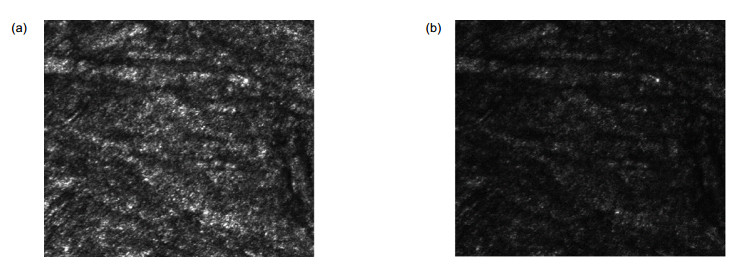
Overview: Adaptive confocal laser ophthalmoscope with the high-resolution and dynamic imaging ability has been widely applied in specific biomedical and clinical medical fields. In order to get more information of the retina, the noncircular pupil filter and other pupil modulation technology should be applied in the adaptive confocal laser ophthalmoscope without influence in wavefront detection, so two light sources are need for imaging and aberration correction respectively. We have designed an adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy with infrared and visible light sources. The principle of the system and some parameters of optical elements have been introduced. The two beams with different wavelengths are combined and separated by dichroic mirrors. The pupil filter could be utilized in entrance and exit of imaging optical path and it could not make an impact on the wavefront detection. Since two different light beams are used at the same time, we should consider the chromatic dispersion effect of human eye. By measuring the human eye aberrations made by the two light sources, it could be found that the biggest difference is in the defocus and the other high-order aberrations are almost same. We have calculated the difference of the defocus of the two sources by empirical formulas and finally compensated it by moving the pinhole that is in front of PMT. Then, the aberration correction and high-resolution imaging ability of the system have been verified through the experiments in human retina. Wavefronts before and after close-loop have been obtained, which proves that the system has realized the diffraction limit after the close-loop. We have found from the image that both brightness and contrast of the image have been significantly improved. In addition, the spectra of the retinal image have also showed that the intensities of almost whole the spatial frequency components are increased, so that more details could be observed. Finally, we studied the feasibility of realizing the dark field imaging by semi-circular pupil, which could block the reflected light and let some of the scattered light pass through, and thus the dark filed image can be obtained. We have inserted two semi-circular pupils in entrance and exit pupils of the adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy and obtained the dark field image of the artificial eye. By comparing the bright and dark field images, it could be seen that the main information are different, which may help us obtain more details of the retina based on the multi-layer structure of the retina.
-

-
表 1 闭环前后视网膜图像的平均强度、均方根值和对比度
Table 1. Mean intensity, root mean square and contrast of the retinal image before and after close-loop
平均强度 均方根值 对比度/% 开环 36.41 11.91 32.71 闭环 85.71 37.07 43.24 -
[1] Cathey W T Jr, Hayes C L, Davis W C, et al. Compensation for atmospheric phase effects at 10.6 μm[J]. Applied Optics, 1970, 9(3): 701–707. doi: 10.1364/AO.9.000701
[2] Rao X, Li X, Jiang W. Small tabletop adaptive optical systems for human retinal imaging[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4825: 99–108. doi: 10.1117/12.451982
[3] 姜文汉.自适应光学发展综述[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 170489. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170489
Jiang W H. Overview of adaptive optics development[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(3): 170489. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170489
[4] Gliss C, Parel J M, Flynn J T, et al. Toward a miniaturized fundus camera[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2004, 9(1): 126–131. doi: 10.1117/1.1631313
[5] Huang D, Swanson E A, Lin C P, et al. Optical coherence tomography[J]. Science, 1991, 254(5035): 1178–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.1957169
[6] 孔文, 郎婷婷, 高峰, 等.高分辨率大视场线扫描共焦显微镜的设计与研制[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(6): 616–620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.06.007
Kong W, Lang T T, Gao F, et al. Design of high-resolution wide field of view conf ocal line scanning laser microscopy[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(6): 616–620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.06.007
[7] 伍春荣, 马志中, 胡莲娜, 等.糖尿病视网膜病变相关因素的因子分析[J].国际眼科杂志, 2007, 7(4): 1056–1059. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5123.2007.04.050
Wu C R, Ma Z Z, Hu L N, et al. Analysis of systemic factors associated with diabetic retinopathy[J]. International Journal of Ophthalmology, 2007, 7(4): 1056–1059. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5123.2007.04.050
[8] Sheppard C J R, Campos J, Escalera J C, et al. Two-zone pupil filters[J]. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(5): 913–922. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2007.10.050
[9] Sheppard C J R, Campos J, Escalera J C, et al. Three-zone pupil filters[J]. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(14): 3623–3630. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2008.03.047
[10] Sales T R M, Morris G M. Axial superresolution with phase-only pupil filters[J]. Optics Communications, 1998, 156(4–6): 227–230. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(98)00455-6
[11] Gong W, Si K, Sheppard C J. Optimization of axial resolution in a confocal microscope with D-shaped apertures[J]. Applied Optics, 2009, 48(20): 3998–4002. doi: 10.1364/AO.48.003998
[12] Ma Y, Kuang C F, Gong W, et al. Improvements of axial resolution in confocal microscopy with fan-shaped apertures[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(6): 1354–1362. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.001354
[13] Liang J Z, Williams D R. Aberrations and retinal image quality of the normal human eye[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 1997, 14(11): 2873–2883. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.14.002873
[14] Thibos L N, Ye M, Zhang X X, et al. The chromatic eye: a new reduced-eye model of ocular chromatic aberration in humans[J]. Applied Optics, 1992, 31(19): 3594–3600. doi: 10.1364/AO.31.003594
[15] 戴云, 肖飞, 赵军磊, 等.自适应光学人眼像差调控及其应用[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 170703. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170703
Dai Y, Xiao F, Zhao J L, et al. Ocular aberrations manipulation with adaptive optics and its application[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(3): 170703. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170703
[16] Wang J Y, Candy T R, Teel D F W, et al. Longitudinal chromatic aberration of the human infant eye[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2008, 25(9): 2263–2270. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.25.002263
[17] Fernández E J, Artal P. Ocular aberrations up to the infrared range: from 632.8 to 1070 nm[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(26): 21199–21208. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.021199
[18] Manzanera S, Canovas C, Prieto P M, et al. A wavelength tunable wavefront sensor for the human eye[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(11): 7748–7755. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.007748
[19] Marcos S, Burns S A, Moreno-Barriusop E, et al. A new approach to the study of ocular chromatic aberrations[J]. Vision Research, 1999, 39(26): 4309–4323. doi: 10.1016/S0042-6989(99)00145-5
[20] 程少园.视网膜血管的液晶自适应光学成像系统设计[D].长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2010.
Cheng S Y. Design of liquid crystal adaptive optical system for fundus blood vessel imaging[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mehcanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010.
http://ir.ciomp.ac.cn/handle/181722/27141 [21] 田雨.波前解卷积及自适应光学图像事后处理技术研究[D].成都: 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 2009.
http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1623526 [22] Török P, Laczik Z, Sheppard C J. Effect of half-stop lateral misalignment on imaging of dark-field and stereoscopic confocal microscopes[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(34): 6732–6739. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.006732
[23] Scoles D, Sulai Y N, Dubra A. In vivo dark-field imaging of the retinal pigment epithelium cell mosaic[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2013, 4(9): 1710–1723. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001710
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: