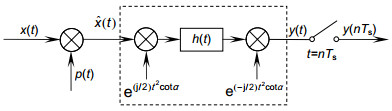
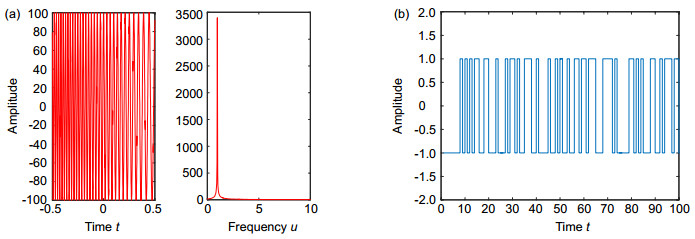
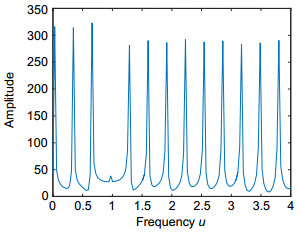
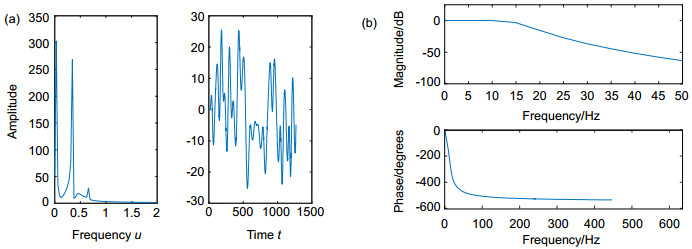
Analog to information conversion for sparse signals band-limited in fractional Fourier transform domain
-
摘要:
经典香农采样定理在信号处理和通信领域有着深远的影响, 随着高速率采样与转换精度矛盾的日益突出, 基于香农采样定理的传统模拟数字转换技术面临严峻的挑战, 尤其是在降低采样率问题上存在着瓶颈效应的制约。近年来, 在信号处理领域诞生的基于压缩感知理论的模拟信息转换技术为解决这一问题提供了一种有效的办法。然而, 现有模拟信息转换的信号模型仅适合频域带限的多音和多带信号。在通信、雷达等电子信息系统广泛存在的线性调频信号就不满足这一模型。鉴于此, 本文提出了基于分数傅里叶变换的模拟信息转换, 不仅对现有模拟信息转换在分数傅里叶变换域进行了推广, 更重要的是解决了其前述面临的问题。本文给出了相应的理论推导, 并进行了仿真分析, 仿真结果与理论分析一致。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The classical Shannon sampling theorem has a profound influence on signal processing and communication. With the increasing contradiction between high rate sampling and conversion accuracy, the traditional analog to digital conversion technology, which is based on the Shannon sampling theorem, is facing a great challenge, especially for the bottleneck effect on reducing the sampling rate. In recent years, the analog-to-information conversion (AIC) technology, which is based on the theory of compressive sensing, provides an effective method to solve this problem. However, the signal model of the existing AIC is only suitable for sparse signals band-limited in the Fourier transform (FT) domain. It cannot be applied to non-bandlimited chirp signals which is widely used in electronic information systems, including radar and communications. Towards this end, we propose a new AIC based on the fractional Fourier transform (FRFT), which is not only the extension of the traditional AIC in the FRFT domain, but also can solve the problem as mentioned above. The theoretical derivation is presented, and the corresponding simulation analysis is also given. The simulation results are consistent with the theoretical analysis.
-

Overview:The classical Shannon sampling theorem has a profound influence on signal processing and communication. For an analog signal f(x) contains no frequencies higher than W/2 Hz, we can sample the signal uniformly at the rate of the W Hz, as prescribed by the theorem. Although the Shannon sampling theory is elegant and has proven to be fruitful, because of the constraints in hardware condition, it is difficult to sample radio frequency signals of very high bandwidth with analog-to-digital converter. As the development of sampling theorem, there are various extensions of the Shannon sampling theorem in the literature. Including sampling for functions of more than one variable, random processes, non-uniform sampling, generalized functions, and so on. In recent years, the Shannon sampling theorem has also been extended to the fractional Fourier transform (FRFT) which is a more general integral transform than the usual Fourier transform (FT).
The fractional sampling theorem is similar to the Shannon sampling theorem, which is concise and widely recognized. For an Wα band-limited signal whose fractional spectrum is at[-um, um], we sample the signal at the fractional sampling rate us satisfied us> 2um. Then we can realize the non-aliasing sampling and could represent exactly using the uniform samples of signal. However, the similar problem also exists just like Shannon sampling theorem, this fractional sampling theorem becomes impractical when the band limit of signal is very large because of the hardware cannot meet its demand.
With the increasing contradiction between high rate sampling and conversion accuracy, the traditional analog to digital conversion technology, which is based on the Shannon sampling theorem, is facing a great challenge, especially for the bottleneck effect on reducing the sampling rate. In recent years, the analog-to-information conversion (AIC) technology, which is based on the theory of compressive sensing, provides an effective method to solve this problem. However, the signal model of the existing AIC is only suitable for sparse signals band-limited in the Fourier transform (FT) domain. It cannot be applied to non-bandlimited chirp signals which are widely used in electronic information systems, including radar and communications.
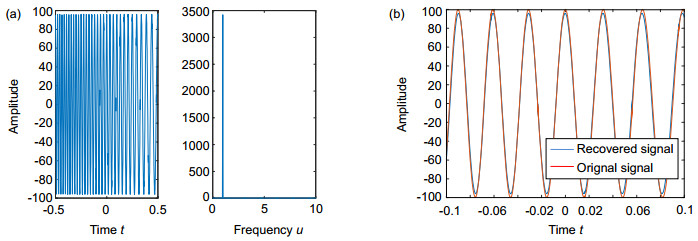
Towards this end, we propose a new AIC based on the fractional Fourier transform (FRFT), which is not only the extension of the traditional AIC in the FRFT domain, but also can solve the problem as mentioned above. This novel sampling structure can greatly reduce the high sampling rate of signals, which has sparsity in fractional domain and especially for chirp signal. The theoretical derivation is presented, and the corresponding simulation analysis is also given. The simulation results are consistent with the theoretical analysis.
-

-
-
[1] Unser M. Sampling-50 years after Shannon[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2000, 88(4):569-587. doi: 10.1109/5.843002
[2] Xia X G. On bandlimited signals with fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 1996, 3(3):72-74. doi: 10.1109/97.481159
[3] 石光明, 刘丹华, 高大化, 等.压缩感知理论及其研究进展[J].电子学报, 2009, 37(5):1070-1081. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXU200905027.htm
Shi G M, Liu D H, Gao D H, et al. Advances in theory and application of compressed sensing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(5):1070-1081. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXU200905027.htm
[4] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4):1289-1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582
[5] Eldar Y C, Kutyniok G. Compressed Sensing:Theory and Applications[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2012.
[6] Kirolos S, Laska J, Wakin M, et al. Analog-to-information conversion via random demodulation[C]//Proceedings of 2006 IEEE Dallas/CAS Workshop on Design, Applications, Integration and Software, 2007: 71-74.
https://www.ece.rice.edu/~jnl5066/papers/DCAS2006_randmod.pdf [7] Tropp J A, Laska J N, Duarte M F, et al. Beyond Nyquist:efficient sampling of sparse bandlimited signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 56(1):520-544. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1fe761793f5aa7b61daba1401f559d96&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[8] Mishali M, Eldar Y C. From theory to practice:sub-Nyquist sampling of sparse wideband analog signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2):375-391. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2042414
[9] Mishali M, Elron A, Eldar Y C. Sub-Nyquist processing with the modulated wideband converter[C]//Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, 2010: 3626-3629.
http://webee.technion.ac.il/Sites/People/YoninaEldar/Info/SUB-NYQUIST%20PROCESSING%20WITH%20THE%20MODULATED%20WIDEBAND%20CONVERTER.pdf [10] 赵贻玖. 稀疏模拟信号压缩采样与重构算法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2012.
Zhao Y J. Study on compressive sampling and recovery algorithm of sparse analog signal[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10614-1012473969.htm [11] 姚婷婷. 基于MWC的模拟信息转换技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.
Yao T T. Research on analog to information conversion technology based on modulated wideband converter[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1015980170.htm [12] 张弓, 方青, 陶宇, 等.模拟信息转换器研究进展[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(2):229-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.02.01
Zhang G, Fang Q, Tao Y, et al. Advances in analog-to-information convertor[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(2):229-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.02.01
[13] 贺继渊, 田松, 王星, 等.模拟信息转换处理高带宽稀疏信号的噪声分析[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(10):637-643. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1014084891.htm
He J Y, Tian S, Wang X, et al. Noise analysis of high bandwidth sparse signals processed by AIC[J]. Editorial Office of Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(10):637-643. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1014084891.htm
[14] Namias V. The fractional order Fourier transform and its application to quantum mechanics[J]. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics, 1980, 25(3):241-265. doi: 10.1093/imamat/25.3.241
[15] 沙学军, 史军, 张钦宇.分数傅里叶变换原理及其在通信系统中的应用[M].北京:人民邮电出版社, 2013.
Sha X J, Shi J, Zhang Q Y. Fractional Fourier Transform Theory and Its Applications in Communication Systems[M]. Beijing:Posts and Telecom Press, 2013.
[16] Shi J, Sha X J, Song X C, et al. Generalized convolution theorem associated with fractional Fourier transform[J]. Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing, 2015, 14(13):1340-1351. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7e73ecf46640d2c6fe3d9f99eadfa605&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] Candès E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing[J]. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9-10):589-592. doi: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014
[18] Baraniuk R G. A lecture on compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(4):118-121. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.4286571
[19] Ramani S, Fessler J A. An accelerated iterative reweighted least squares algorithm for compressed sensing MRI[C]//Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 2010: 257-260.
http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9e2588012ccb791747f5a286e8c35562&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] Tropp J, Gilbert A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12):4655-4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108
[21] Wang J, Kwon S, Shim B. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12):6202-6216. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2218810
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: