-
摘要:
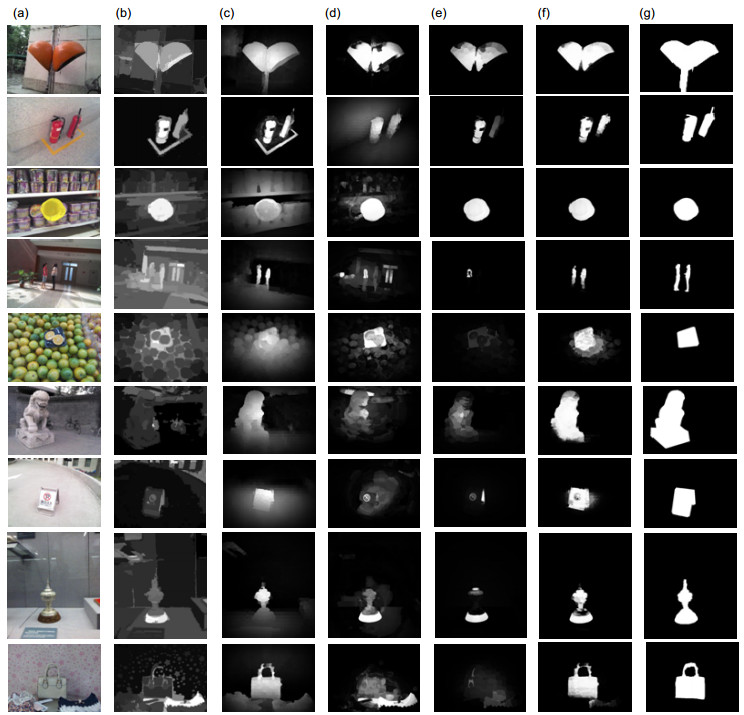
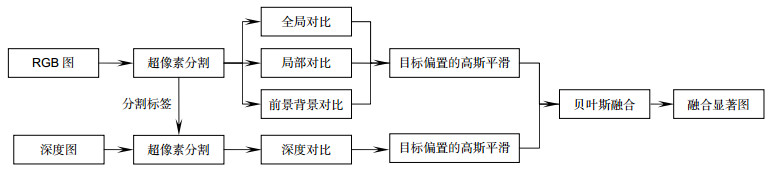
复杂背景下,传统显著性检测方法经常遭遇检测结果不稳定和准确率低的问题。针对这些问题,提出一种基于贝叶斯框架融合深度信息的显著性检测方法。首先利用全局对比、局部对比和前景背景对比方法获取颜色显著图,并利用非均质中心-邻居差异的深度对比方法获取深度显著图。其次采用贝叶斯模型融合颜色显著图和深度显著图,获得输出显著图。实验结果表明,本文的方法能有效检测出复杂背景下的显著目标,并在公开的NLPR-RGBD数据集和NJU-DS400数据集上取得较高检测精确度。
Abstract:In the complex background, the traditional saliency detection methods often encounter the problems of unstable detection results and low accuracy. To address this problem, a saliency detection method fused depth information based on Bayesian framework is proposed. Firstly, the color saliency map is obtained by using a variety of contrast methods which includes global contrast, local contrast and foreground-background contrast, and the depth saliency map is obtained by using the depth contrast method based on the anisotropic center-surround difference. Secondly, using the Bayesian model to fuse the color-based saliency map and the depth-based saliency map. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively detect the salient targets under complex background and achieve higher detection accuracy on the published NLPR-RGBD dataset and NJU-DS400 dataset.
-
Key words:
- saliency detection /
- color contrast /
- depth contrast /
- Bayesian fusion
-

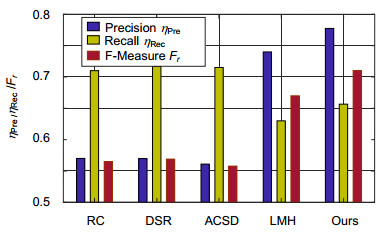
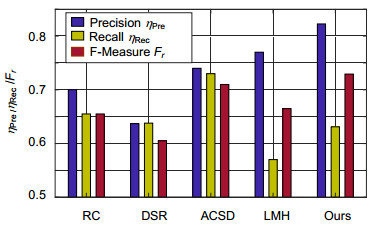
Overview: Saliency detection aims to detect salient objects in an image and filter out background noise by simulating human visual attention mechanism. Most current methods for saliency detection rely on the color-difference between salient object and background while ignoring depth information, which has been proven to be important in the human cognitive system. This leads to not good enough saliency detection results especially when the salient object presents in a low-contrast background with confusing visual appearance. To address this problem, we present a saliency detection method fused depth information based on the Bayesian framework. Firstly, in order to reduce the computational complexity, we use SLIC algorithm on the RGB images and depth image. Secondly, we extract the tinctorial information and spatial information of the superpixel from the input RGB picture, and obtain the color-based saliency map using a variety of contrast methods which includes global contrast, local contrast and foreground-background contrast method. Meanwhile, extracting the depth information of the superpixel from the input depth picture, and obtaining the depth-based saliency map based on anisotropic center-surround difference. Third, an object-biased Gaussian model acts on color-based saliency map and depth-based saliency map for the purpose of filtering out background noise further. Finally, we fuse the color-based saliency map and the depth-based saliency map based on the Bayesian framework. Specifically, depth-based saliency map is used as the prior probability, and calculate the likelihood probability using color-based saliency map, then obtain a posterior probability based on the Bayesian formula. Exchanging the role of depth-based saliency map and color-based saliency map in the Bayesian framework could obtain another posterior probability. The finally saliency map is defined as the product of two posterior probability in this paper. Our approach is evaluated on the published NLPR-RGBD dataset and the NJU-DS400 dataset, and experimental results show that our approach can effectively detect the salient object in a low-contrast background with a confusing visual appearance by filtering tinctorial information and deep information. Furthermore, compared with other four prevailing methods by precision score and the F-measure score, our approach is superior to the other four prevailing methods.
-

-
表 1 在2个标准数据集上三种显著图融合方法的平均性能比较
Table 1. Average performance comparison of three notable image fusion methods on two standard datasets
融合策略 准确率/(%) 召回率/(%) F-measure/(%) 直接相加 0.6201 0.7454 0.6132 直接相乘 0.7773 0.6566 0.7103 贝叶斯相乘 0.8138 0.6097 0.7162 -
[1] 李萌, 陈恳, 郭春梅, 等.融合显著性信息和社会力模型的人群异常检测[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12): 193-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.029 http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1864.shtml
Li M, Chen K, Guo C M, et al. Abnormal crowd event detection by fusing saliency information and social force model[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 193-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.029 http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1864.shtml
[2] 张学典, 汪泓, 江旻珊, 等.显著性分析在对焦图像融合方面的应用[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(4): 435-441. http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1970.shtml
Zhang X D, Wang H, Wang M S, et al. Applications of saliency analysis in focus image fusion[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(4): 435-441. http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1970.shtml
[3] Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254-1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558
[4] Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, et al. Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 2009: 1597-1604.
[5] Hou X D, Zhang L Q. Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2007: 1-8.
[6] Zhai Y, Shah M. Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues[C]//Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Santa Barbara, CA, 2006: 815-824.
[7] Harel J, Koch C, Perona P. Graph-based visual saliency[C]//Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Canada, 2006: 545-552.
[8] Cheng M M, Zhang G X, Mitra N J, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[C]//Proceedings of 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado, CO, USA, 2011: 409-416.
[9] Cheng M M, Mitra N J, Huang X L, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569-582. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401
[10] Lu H C, Li X H, Zhang L H, et al. Dense and sparse reconstruction error based saliency descriptor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1592-1603. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2524198
[11] Desingh K, Madhava Krishna K, Rajan D, et al. Depth really matters: improving visual salient region detection with depth[C]//Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, 2013.
[12] Peng H W, Li B, Xiong W H, et al. RGBD salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Switzerland, 2014: 92-109.
[13] Ren J Q, Gong X J, Yu L, et al. Exploiting global priors for RGB-D saliency detection[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 25-32.
[14] 林昌, 何炳蔚, 董升升.融合深度信息的室内RGB图像视觉显著物体快速检测方法[J].中国激光, 2014, 41(11): 1108005. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jjzz201411035&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Lin C, He B W, Dong S S. An indoor object fast detection method based on visual attention mechanism of fusion depth information in RGB image[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(11): 1108005. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jjzz201411035&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[15] Zhang Y, Jiang G Y, Yu M, et al. Stereoscopic visual attention model for 3D video[C]//Proceedings of the 16th International Multimedia Modeling Conference on Advances in Multimedia Modeling, Chongqing, China, 2010: 314-324.
[16] Shen X H, Wu Y. A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 2012: 853-860.
[17] Borji A, Itti L. Exploiting local and global patch rarities for saliency detection[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 2012: 478-485.
[18] Perazzi F, KrähenbÜHl P, Pritch Y, et al. Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 2012: 733-740.
[19] Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274-2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120
[20] Wolfe J M, Horowitz T S. What attributes guide the deployment of visual attention and how do they do it?[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2004, 5(6): 495-501. doi: 10.1038/nrn1411
[21] Ju R, Ge L, Geng W J, et al. Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 2014: 1115-1119.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: