-
摘要:
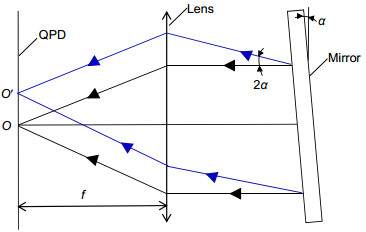
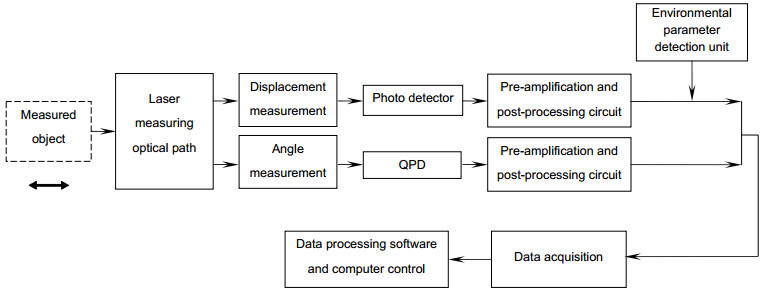
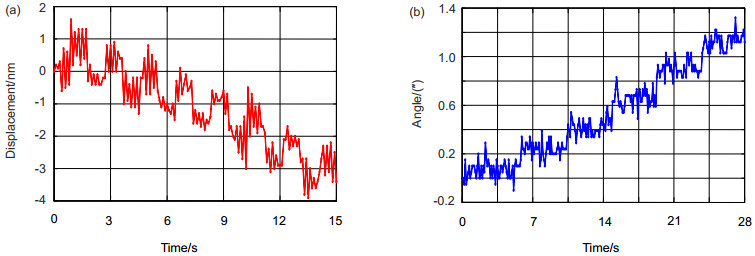
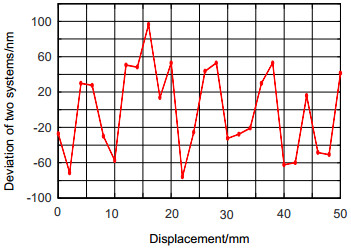
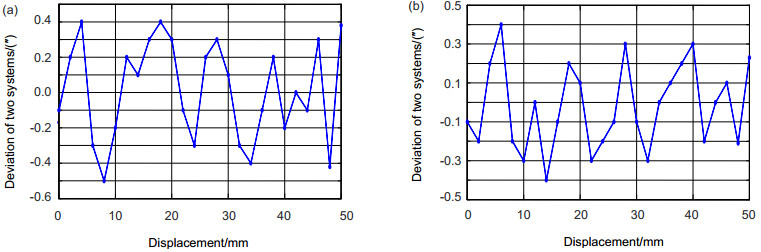
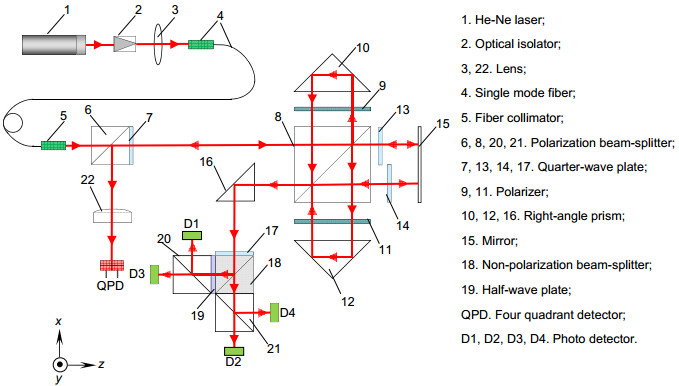
基于迈克尔逊干涉原理和激光自准直原理,采用共光路布局,研制了能对运动工作台同时进行一维位移和二维角度测量的三自由度激光测量系统。在位移测量中,采用光程差放大技术,并结合偏振干涉技术和信号差分处理,得到高质量的位移输出信号和高分辨力的位移测量结果。在角度测量中,运动工作台的偏摆和俯仰运动会引起固定在工作台上的反射镜位置变化。入射光被反射镜反射,并被四象限探测器探测,根据四象限探测器上的光斑位置变化,获得偏摆角和俯仰角的变化值。对研制的系统进行稳定性和分辨力测试,同时与英国雷尼绍XL-80激光干涉仪进行比对实验。实验结果表明:测量系统的位移分辨力为0.8 nm,角度分辨力为0.2″;在50 mm的测量范围内,与雷尼绍XL-80激光干涉仪测量值相比,系统的位移最大偏差小于100 nm,偏摆角最大偏差为0.5″,俯仰角最大偏差为0.4″。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Common optical path arrangement was adopted to design a three-degree-of-freedom laser measurement system for measuring 1D displacement and 2D angles of a moving stage simultaneously on the basis of the principles of Michelson interference and laser auto-collimation. In the displacement measurement, the fine resolution of displacement measurement was achieved by using optical path difference doubling technique. Combined with polarization interference technology and signal differential processing, high-quality displacement output signal was obtained. In the angle measurement, changes in yaw and pitch of a moving stage caused the position change of the mirror which was mounted on the stage. The incident beam was reflected by the mirror and detected by a four-quadrant detector. According to the position change of the spot, yaw and pitch angles were obtained. The stability, resolution tests and the comparison experiments with the British Renishaw XL-80 laser interferometer were done. Experimental results show that the system has the resolution of 0.8 nm for displacement measurement and 0.2″ for angle measurement. Compared with the results of Renishaw XL-80 laser interferometer, the maximum deviation of displacement is less than 100 nm within the measurement range of 50 mm. The maximum deviations of yaw and pitch are 0.5″ and 0.4″.
-
Key words:
- common optical path /
- laser /
- polarization interference /
- auto-collimation /
- simultaneous measurement
-

In the field of advanced processing and manufacturing, precision guide and stage are the important moving parts, which ensure the accuracy of machine tool manufacturing and instrument measurement. The precise installation and adjustment of guide and stage, the detection and control of their location and motion, need to measure multiple spatial parameters of the moving object simultaneously. The traditional commercial measurement instruments, such as the HP5529A Dynamic Calibrator and the Renishaw laser interferometer, can only measure one parameter at a time, and the measurement process is very complicated. Therefore, multi-parameter measurement has become one of the research focuses. At present, domestic and foreign research institutions and manufacturers have developed some measurement devices, but they have the disadvantages of complex structure, uneasy adjustment, small measurement range and low measurement accuracy.
In order to simplify the measurement structure, expand the measurement range and improve the measurement accuracy, a three-degree-of-freedom common-path laser measurement system, which is a combination of the laser interferometer with the auto-collimator, can realize the measurement of three parameters of displacement, yaw and pitch angles simultaneously with the advantages of large stroke, high precision and non-contact.
Common optical path arrangement was adopted to design the three-degree-of-freedom laser measurement system for measuring 1D displacement and 2D angles of a moving stage simultaneously on the basis of the principles of Michelson interference and laser auto-collimation. In the displacement measurement, the fine resolution of displacement measurement was achieved by using polarization interference and optical path difference doubling technique. Adopting four-beam-signal detection technique and signal differential processing, high-quality displacement output signals were obtained. In the angle measurement, changes in yaw and pitch of a moving stage caused the position change of the mirror which was mounted on the stage. The incident beam was reflected by the mirror and detected by a four-quadrant detector. According to the position change of the spot, yaw and pitch angles were detected precisely. In order to verify the effectiveness of the system, the stability and resolution tests and the comparison experiments with the British Renishaw XL-80 laser interferometer were done. Experimental results show that the system has the resolution of 0.8 nm for displacement measurement and 0.2″ for angle measurement. Compared with the results of XL-80 laser interferometer, the maximum deviation of displacement measurement is less than 100 nm within the measurement range of 50 mm. The maximum deviations of yaw and pitch are 0.5″ and 0.4″.
-

-
-
[1] 陈强华, 吴健, 殷纯永.双频激光远程直线度/同轴度测量系统[J].中国激光, 2002, 29(7): 625-630. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2002.07.013
Chen Qianghua, Wu Jian, Yin Chunyong. Long range straightness/coaxiality measurement system using dual-frequency laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2002, 29(7): 625-630. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2002.07.013
[2] 匡萃方, 冯其波, 张斌, 等.直线导轨四自由度同时测量方法的研究[J].中国激光, 2005, 32(9): 1266-1270. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zgjg200509024.aspx
Kuang Cuifang, Feng Qibo, Zhang Bin, et al. Study of the method for measuring four-degree-of-freedom geometric errors of a linear stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2005, 32(9): 1266-1270. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zgjg200509024.aspx
[3] 上海耶葛精密仪器有限公司. SP-15000TR三光束激光干涉仪[EB/OL]. (2014-01) [2017-04]. http://www.shjaeger.com/product/128.html.
Shanghai Jaeger Precision Instrument Co., Ltd. SP-15000TR three-beam laser interferometer[EB/OL]. (2014-01) [2017-04]. http://www.shjaeger.com/product/128.html.
[4] Kim J W, Kang C S, Kim J A, et al. A compact system for simultaneous measurement of linear and angular displacements of nano-stages[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(24): 15759-15766. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.015759 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8b5856476e2457a85a7401171af3e016&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] 吕勇, 冯其波, 刘立双, 等.基于多准直光的六自由度测量方法[J].红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(11): 3597-3602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.11.016 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hwyj201411016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Lü Yong, Feng Qibo, Liu Lishuang, et al. Six-degree-of-freedom measurement method based on multiple collimated beams[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(11): 3597-3602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.11.016 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hwyj201411016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[6] Sutton A J, Gerberding O, Heinzel G, et al. Digitally enhanced homodyne interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(20): 22195-22207. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.022195 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e01cd9a90b8998c0c19352ce8c6ac151&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] 段小艳, 任冬梅.激光干涉法微位移测量技术综述[J].计测技术, 2012, 32(6): 1-5, 13. doi: 10.12060/j.issn.1000-7202.2012.06.01 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hkjc201206003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Duan Xiaoyan, Ren Dongmei. Review of high-resolution measuring method of displacement using laser interferometer[J]. Metrology & Measurement Technology, 2012, 32(6): 1-5, 13. doi: 10.12060/j.issn.1000-7202.2012.06.01 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hkjc201206003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[8] Wu Wanduo, Huang Qiangxian, Wang Chaoqun, et al. The analysis and design of a large stroke with high-precision polarized laser interferometer system[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2016, 679: 129-134. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.679
[9] 程晓锋, 蒋晓东, 郑万国, 等. KDP晶体光学均匀性检测实验研究[J].光电工程, 2008, 35(2): 25-28. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gdgc200802008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Cheng Xiaofeng, Jiang Xiaodong, Zheng Wanguo, et al. Measurement of optical uniformity of KDP crystals[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2008, 35(2): 25-28. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gdgc200802008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[10] 韩旭东, 艾华.共光路移相单频激光干涉测长系统[J].光学技术, 2004, 30(2): 195-198. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjs200402007
Han Xudong, Ai Hua. Common-path and phase-shifting single frequency laser interferometer for length measurement[J]. Optical Technique, 2004, 30(2): 195-198. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjs200402007
[11] 刘壮, 李英博, 张浩钧, 等.菲涅尔透镜激光四象限定位系统光学设计[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(9): 62-66, 71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GDGC201609012.htm
Liu Zhuang, Li Yingbo, Zhang Haojun, et al. Optical design for laser four-quadrant location system based on Fresnel Lens[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(9): 62-66, 71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GDGC201609012.htm
[12] Keem T, Gonda S, Misumi I, et al. Simple, real-time method for removing the cyclic error of a homodyne interferometer with a quadrature detector system[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(17): 3492-3498. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.003492 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3b8492686b4b23591a66a4091e2ceec6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] 胡红波, 于梅.零差激光干涉仪正交相位误差的分析[J].光电工程, 2012, 39(12): 55-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdgc201212012
Hu Hongbo, Yu Mei. Analysis of quadrature phase-shift error for homodyne interferometer[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2012, 39(12): 55-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdgc201212012
[14] Hu Pengcheng, Zhu Jinghao, Zhai Xiaoyu, et al. DC-offset-free homodyne interferometer and its nonlinearity compensation[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(7): 8399-8408. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.008399 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4b0e2b382e99007fb5657ed71418a5f9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: