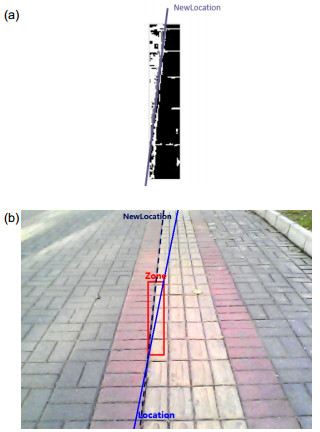
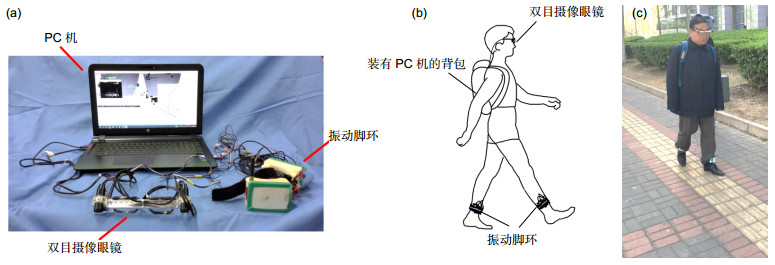
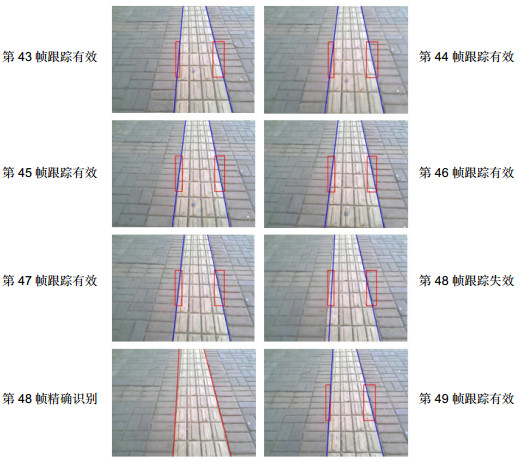
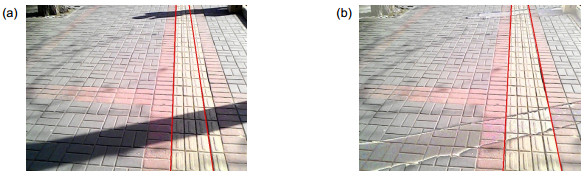
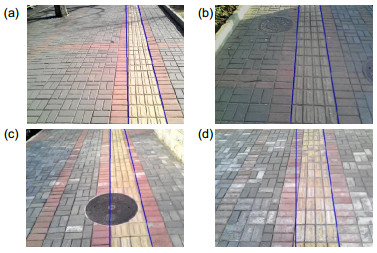
-
摘要:
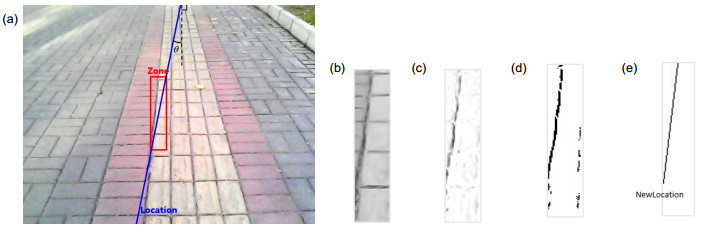
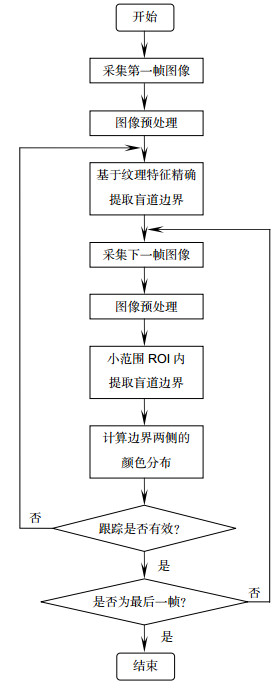
针对现有盲道识别算法实时性较差的问题,提出一种基于边界跟踪的高实时性盲道识别算法,主要包括精确识别和跟踪识别两个步骤。精确识别步骤主要计算初始帧的灰度共生矩阵,并通过聚类和Hough变换提取图像中盲道的边界直线。之后的跟踪识别步骤利用前一帧盲道边界位置估计当前帧边界所处的小范围ROI(感兴趣区域),在该区域中利用图像灰度梯度特征提取盲道边界位置,并通过判断前后帧盲道边界两侧颜色分布一致性检验跟踪的有效性:一致则有效,继续进行跟踪识别;反之转向精确识别步骤。对该算法进行多次实验,正常光照下每帧图像中盲道的精确识别和跟踪识别时间分别约为0.8 s和0.1 s,综合平均每帧识别时间显著降低,且盲道识别率达到90%以上,同时在阴影环境下的适应性良好。实验结果表明本文算法在保证识别率的前提下可显著提高盲道识别的实时性。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to solve the problem that existing blind sidewalk recognition algorithms have bad real-time performance, a highly real-time blind sidewalk recognition algorithm based on boundary tracking is proposed, mainly including accurate recognition and tracking recognition. First, accurate recognition step mainly calculates gray level co-occurrence matrix of the initial frame, and uses clustering and Hough transform to find the boundary lines of blind sidewalk in image. Then tracking recognition step takes over next frame. The location of blind sidewalk's boundary in previous frame is used to predict the small-scale region of interest (ROI) of the boundary in current frame, and boundary lines in that region are extracted based on gray gradient feature. After that, the algorithm checks up the validity of tracking by estimating the consistency of color distribution on both sides of the boundary in previous and current frames: tracking is considered to be valid if the consistency is high, and tracking recognition step continues, otherwise accurate recognition step restarts. In many experiments, the time of accurate recognition and tracking recognition in each image frame under normal illumination are about 0.8 s and 0.1 s, respectively, and the average time of recognition per frame decreases significantly while the recognition rate of blind sidewalk is more than 90%. Meanwhile, the adaptability is good in shadow environment. Experimental results indicate that the algorithm can significantly enhance the real-time performance of blind sidewalk recognition in the premise of ensuring the recognition rate.
-
Key words:
- blind sidewalk recognition /
- highly real-time /
- boundary tracking /
- visual travel aids
-

Abstract: Computer visual travel aids (VTA) are effective means to assist the blind, while blind sidewalk recognition is an important function of VTA. The so-called blind sidewalk recognition is a method that segments blind sidewalk and detects boundary lines via image processing technology. After blind sidewalk recognition, VTA locate the boundary based on stereo vision and then guide the blind to sidewalk by control signal. In order to solve the problem that existing blind sidewalk recognition algorithms have bad real-time performance, a highly real-time blind sidewalk recognition algorithm based on boundary tracking is proposed, mainly including accurate recognition and tracking recognition. First, the preprocessing of shadow removal is performed for each frame image before recognition, which calculates a residual model based on the Retinex theory to detect shadow and uses regional color compensation to remove shadow. Next, accurate recognition step mainly calculates gray level co-occurrence matrix of the initial frame, and uses clustering and Hough transform to find the boundary lines of blind sidewalk in image. Then tracking recognition step takes over next frame. The location of blind sidewalk’s boundary in previous frame is used to predict the small-scale region of interest (ROI) of the boundary in current frame, and boundary lines in that region are extracted based on gray gradient feature. After that, the algorithm checks up the validity of tracking by estimating the consistency of color distribution on both sides of the boundary in previous and current frames: tracking is considered to be valid if the consistency is high, and tracking recognition step continues, otherwise accurate recognition step restarts. We apply our algorithm on binocular VTA and the blind wear the VTA to walk along blind sidewalk for the algorithm performance test. In many experiments, the time of accurate recognition and tracking recognition in each image frame under normal illumination are about 0.8 s and 0.1 s, respectively, and the average time of recognition per frame decreases significantly while the recognition rate of blind sidewalk is more than 90%. Meanwhile, the adaptability is good in shadow environment and is acceptable in other environment, including strong and weak light, damage of blink sidewalk, and blurring. Experimental results indicate that the algorithm can significantly enhance the real-time performance of blind sidewalk recognition in the premise of ensuring the recognition rate. Therefore, our algorithm is more suitable for real-time visual navigation than traditional ones.
-

-
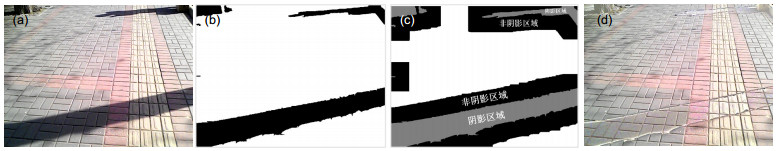
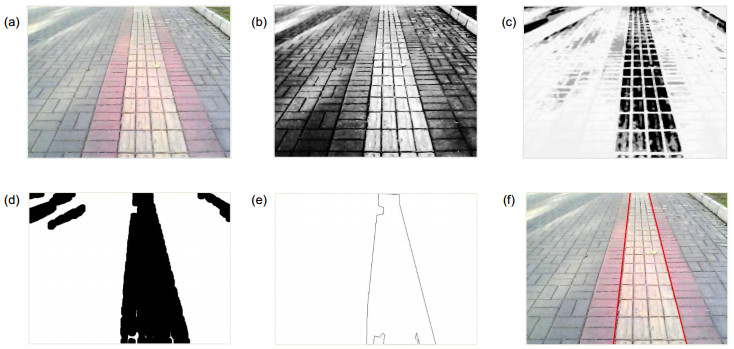
图 3 盲道精确识别的分步处理结果. (a) RGB图像. (b)直方图均衡化. (c)盲道特征的提取. (d)盲道特征的聚类分割. (e)盲道区域轮廓的提取. (f)盲道边界直线的检测.
Figure 3. Step processing results of accurate recognition of blind sidewalk. (a) RGB image. (b) Histogram equalization. (c) Feature extraction of blind sidewalk. (d) Feature clustering and segmentation of blind sidewalk. (e) Contour extraction of blind sidewalk region. (f) Boundary lines detection of blind sidewalk.
表 1 实验中算法的参数列表.
Table 1. List of parameters in experiments.
图像大小/pixel×pixel Zone最小宽度Wmin/pixel Zone最小高度Hmin/pixel VL调整阈值set1 VR调整阈值set2 640×480 15 15 30 45 表 2 不同算法的对比结果.
Table 2. Comparison results of different algorithms.
实验序号 1 2 3 4 5 测试环境 阴影环境 阴影环境 正常光照 正常光照 正常光照 处理帧数 132 128 136 106 267 精确识别次数 42 37 46 6 3 精确识别平均每帧时间/s 0.98 0.94 0.85 0.88 0.82 跟踪识别平均每帧时间/s 0.22 0.21 0.11 0.10 0.09 综合平均每帧识别时间/s 0.46 0.42 0.36 0.14 0.10 识别率/% 85.58 86.46 90.44 97.17 96.63 表 3 不同算法的对比结果.
Table 3. Comparison results of different algorithms.
阴影环境 正常光照 识别率/% 平均识别时间/s 识别率/% 平均识别时间/s 文献[6]算法 70.75 0.88 91.37 0.87 本文算法 86.46 0.42 90.44 0.36 表 4 算法适应性测试结果.
Table 4. Adaptability test results of the algorithms.
测试场景 识别率/% 平均识别时间/s 强光环境 91.21 0.22 弱光环境 91.45 0.18 盲道缺损 84.57 0.35 盲道模糊 73.41 0.52 -
[1] Pradeep V, Medioni G, Weiland J. A wearable system for the visually impaired[C]. Proceedings of 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2010: 6233–6236.
[2] Pradeep V, Medioni G, Weiland J. Robot vision for the visually impaired[C]. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2010: 15–22.
[3] Kammoun S, Parseihian G, Gutierrez O, et al. Navigation and space perception assistance for the visually impaired: The NAVIG project[J]. IRBM, 2012, 33(2): 182–189. doi: 10.1016/j.irbm.2012.01.009
[4] Leung T S, Medioni G. Visual navigation aid for the blind in dynamic environments[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2014: 579–586.
https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_workshops_2014/W16/papers/Leung_Visual_Navigation_Aid_2014_CVPR_paper.pdf [5] 柯剑光. 基于图像处理的盲道识别系统[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2008.
Ke Jianguang. The recognition system for the blind way based on image processing[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2008.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10248-2008053311.htm [6] 彭玉青, 薛杰, 郭永芳.基于颜色纹理信息的盲道识别算法[J].计算机应用, 2014, 34(12): 3585–3588, 3604. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSJY201412047.htm
Peng Yuqing, Xue Jie, Guo Yongfang. Blind road recognition algorithm based on color and texture information[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2014, 34(12): 3585–3588, 3604. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSJY201412047.htm
[7] 周毅, 赵群飞.基于颜色信息的盲道区域检测与跟随算法[J].微型电脑应用, 2010, 26(8): 47–50. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/wxdnyy201008016
Zhou Yi, Zhao Qunfei. Detecting and tracing algorithm of blind sidewalk based on color information[J]. Microcomputer Appli-cations, 2010, 26(8): 47–50. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/wxdnyy201008016
[8] 柯剑光, 赵群飞, 施鹏飞.基于图像处理的盲道识别算法[J].计算机工程, 2009, 35(1): 189–191, 197. http://www.docin.com/p-9379792.html
Ke Jianguang, Zhao Qunfei, Shi Pengfei. Blind way recognition algorithm based on image processing[J]. Computer Engineering, 2009, 35(1): 189–191, 197. http://www.docin.com/p-9379792.html
[9] Jung C, Kim W, Kim C. Detecting shadows from a single image[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(22): 4428–4430. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.004428
[10] 杨俊, 赵忠明.基于归一化RGB色彩模型的阴影处理方法[J].光电工程, 2007, 34(12): 92–96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2007.12.019
Yang Jun, Zhao Zhongming. Shadow processing method based on normalized RGB color model[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2007, 34(12): 92–96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2007.12.019
[11] Rampun A, Strange H, Zwiggelaar R. Texture segmentation using different orientations of GLCM features[C]. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Vi-sion/Computer Graphics Collaboration Techniques and Applications, 2013: 17.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237089640_Texture_Segmentation_Using_Different_Orientations_of_GLCM_Features [12] 桑庆兵, 李朝锋, 吴小俊.基于灰度共生矩阵的无参考模糊图像质量评价方法[J].模式识别与人工智能, 2013, 26(5): 492–497. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_mssbyrgzn201305012
Sang Qinbing, Li Chaofeng, Wu Xiaojun. No-reference blurred image quality assessment based on gray level co-occurrence matrix[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 26(5): 492–497. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_mssbyrgzn201305012
[13] Guerreiro R F C, Aguiar P M Q. Connectivity-enforcing Hough transform for the robust extraction of line segments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(12): 4819–4829. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2202673
[14] 钟权, 周进, 吴钦章, 等.基于Hough变换和边缘灰度直方图的直线跟踪算法[J].光电工程, 2014, 41(3): 89–94. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_gdgc201403014
Zhong Quan, Zhou Jin, Wu Qinzhang, et al. A method of line tracking based on Hough transforms and edge histogram[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2014, 41(3): 89–94. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_gdgc201403014
[15] Kim J, Lee S. Extracting major lines by recruiting ze-ro-threshold canny edge links along sobel highlights[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(10): 1689–1692. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2400211
[16] 袁小翠, 吴禄慎, 陈华伟.基于Otsu方法的钢轨图像分割[J].光学精密工程, 2016, 24(7): 1772–1781. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gxjm201607028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Yuan Xiaocui, Wu Lushen, Chen Huawei. Rail image segmentation based on Otsu threshold method[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(7): 1772–1781. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gxjm201607028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[17] Aznaveh M M, Mirzaei H, Roshan E, et al. A new and improves skin detection method using RGB vector space[C]. Proceed-ings of the 5th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices, 2008: 1–5.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4632786/ -


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: