-
摘要:
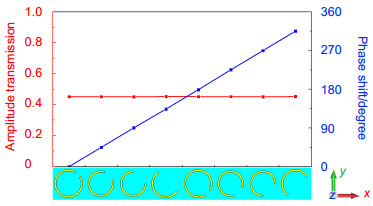
设计了一种在远红外波段基于超表面全息的宽频带多焦点透镜。通过设计8个C型谐振环单元,当以线极化波垂直入射到该组单元上时,其透射的交叉极化波产生0到2π范围的相位突变,同时透过率保持不变。利用全波仿真验证了该组谐振单元对垂直入射线极化波的异常折射特性,并采用计算全息的方法获得了多焦点透镜上的相位分布,根据相位分布对所设计的天线单元进行排列,得到了方形的超表面多焦点透镜。对该透镜进行仿真,结果显示在中心频率28 THz、焦距108 μm处有良好的多点聚焦效果。
 Abstract:
Abstract:A broadband multi-focus lens based on metasurface holography in the far-infrared region is designed. By designing 8 C-shaped resonant rings, when linearly polarized light waves are incident normally to this set of resonators, cross-polarized component of transmitted light will form the phase shift from 0 to 2π, meanwhile the amplitude transmittance remains constant. Full-wave simulation was utilized to verify anomalous refraction properties when linearly polarized light waves irradiated this set of resonators vertically. The phase distribution of multi-focus lens was obtained by adopting the computer-generated hologram (CGH) method. According to arranged resonant rings based on the calculated phase distribution, a squared multi-focus lens based on metasurface was obtained. Simulation for the designed lens was conducted. Results show a good multi-focusing performance at the central frequency 28 THz in the focal length of 108 μm.
-
Key words:
- metasurface /
- hologram /
- multi-focus lens /
- phase shift
-

Abstract: Multi-focus lens is applied widely as an important optical element, but it has stringent requirements for manufacturing and assembling micro-lens array which is used for multi-focusing in traditional methods. So tiny error is inevitable, which may affect the usage performance. Therefore, it is necessary to design a new type of multi-focus optical device. Metasurface is a kind of artificial surface which consists of many subwavelength antenna units different from traditional optical element. Metasurface utilizes the anomalous refraction properties that subwavelength antenna units response to the electromagnetic wave to modulate wave front. Subwavelength scale antennas with different structural parameters are arranged according to certain rules, so it can realize flexible modulation to amplitude and phase of electromagnetic wave. Metasurface has been widely used in the designing of various new optical components in recent years. Compared to the conventional multi-focus lens, metasurface is used to design multi-focus lens with its unique advantages. In finished works, when designing the multi-focus lens based on metasurface, the phase retrieval algorithm is used to obtain the phase distribution of lens commonly, and multiple iterations are performed between metasurface and the focusing surface. However, this method for phase calculation is of great computation load, and sometimes it is easy to fall into local optima. Meanwhile, metasurface-based flat-lens array also be proposed. It consists a number of regularly arranged lenslets to achieve multi-focusing function, but the array structure is not favorable to be integrated. Computer-generate holography (CHG) method to design multi-focus lens based on metasurface has been proposed in far-infrared region. This method is simple, straightforward, accurate, and easily implemented and realized. Firstly, 8 C-shaped resonant rings aimed at central frequency 28 THz(wavelength 10.71 μm) were designed, which was able to modulate the phase of transmitted cross-polarized wave from 0 to 2π and amplitude transmittance remains constant, that can be used in the design of multi-focus lens. Secondly, the anomalous refraction functions of this set of resonators were verified by full-wave simulation when linearly polarized light waves were irradiated normally. It can be seen that the wavefronts of the deflected waves with cross-polarization are well deflected, further demonstrating the broadband property of the resonators. Finally, the four spot light source in focusing plane were set as certain distance away from the plane where metasurface located. The phase distribution of multi-focus lens at metasurface was calculated by the method of complex amplitude superposition. Then, according to arranged C-shaped resonators based on obtained phase distribution, a square metasurface-based lens was got, and the structure was simulated as a integer by CST Microwave Stdio. Simulation results show a good multi-focus performance at 28 THz while the focal length is 108 μm, as certain broadband response characteristics in 27.6 THz ~28.5 THz.
-

-
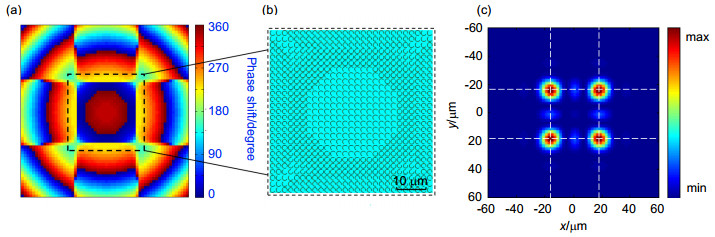
图 4 多焦点透镜的设计. (a)在28 THz处用复振幅叠加方法得到的超表面上量化后的相位分布. (b)图(a)中心区域单元结构排列情况. (c)用Matlab对图(a)进行衍射计算得到的电场分布.
Figure 4. Design of multi-focus lens. (a) Quantized phase distribution in metasurface at 28 THz calculated by complex amplitude superposition. (b) Central part of the C-shaped units arrangement in (a). (c) The electric field intensity distribution simulated by Matlab diffraction calculation to (a).
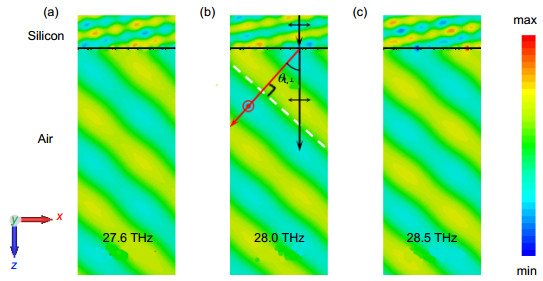
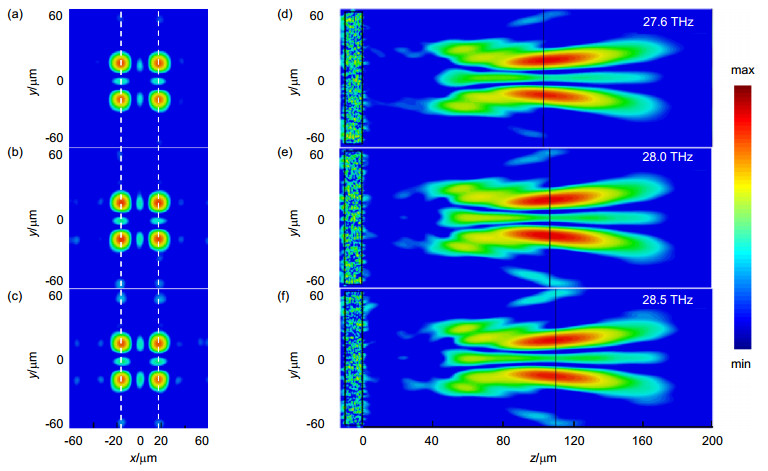
图 5 仿真得到的不同频率处的电场强度分布. (a)~(c) 27.6 THz, 28 THz, 28.5 THz各频点处焦平面上y极化电场强度分布. (d)~(f) 27.6 THz, 28 THz, 28.5 THz各频点处yoz截面上y极化电场强度分布,入射波为x极化平面波.
Figure 5. Simulated results of the electric field Intensity distribution at different frequencies. (a)~(c) Electric field Intensity distributions of y-polarized in focal planes at 27.6 THz, 28 THz, 28.5 THz, respectively. (d)~(f) Electric field Intensity distributions of y-polarized in the yoz section at 27.6 THz, 28 THz, 28.5 THz, respectively, at x-polarized normal incidence.
-
[1] Luo Xiangang. Principles of electromagnetic waves in metasurfaces[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2015, 58(9): 594201. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11433-015-5688-1
[2] 李雄, 马晓亮, 罗先刚.超表面相位调控原理及应用[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(3): 255–275. https://wuxizazhi.cnki.net/qikan-GDGC201703005.html
Li Xiong, Ma Xiaoliang, Luo Xiangang. Principles and applications of metasurfaces with phase modulation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(3): 255–275. https://wuxizazhi.cnki.net/qikan-GDGC201703005.html
[3] Yu Nanfang, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333–337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713
[4] Genevet P, Yu Nanfang, Aieta F, et al. Ultra-thin plasmonic optical vortex plate based on phase discontinuities[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(1): 013101. doi: 10.1063/1.3673334
[5] Aieta F, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Aberration-free ultrathin flat lenses and axicons at telecom wavelengths based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano letters, 2012, 12(9): 4932–4936. doi: 10.1021/nl302516v
[6] Blanchard R, Aoust G, Genevet P, et al. Modeling nanoscale V-shaped antennas for the design of optical phased arrays[J]. Physical Review B, 2012, 85(15): 155457. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.155457
[7] Cong Longqing, Xu Ningning, Gu Jianqiang, et al. Highly flexible broadband terahertz metamaterial quarter‐wave plate[J]. Laser & Photonics Review, 2014, 8(4): 626–632. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261141747_Highly_flexible_broadband_terahertz_metamaterial_quarter-wave_plate
[8] Yu Nanfang, Aieta F, Genevet P, et al. A broadband, back-ground-free quarter-wave plate based on plasmonic metasur-faces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(12): 6328–6333. doi: 10.1021/nl303445u
[9] Lin Jiao, Mueller J P B, Wang Qian, et al. Polarization-controlled tunable directional coupling of surface plasmon polaritons[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6130): 331–334. doi: 10.1126/science.1233746
[10] Huang Lingling, Chen Xianzhong, Bai Benfeng, et al. Helicity dependent directional surface plasmon polariton excitation using a metasurface with interfacial phase discontinuity[J]. Light Science & Applications, 2013, 2(3): e70. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Benfeng_Bai/publication/236002864_Helicity_Dependent_Directional_Surface_Plasmon_Polariton_Excitation_Using_A_Metasurface_with_Interfacial_Phase_Discontinuity/links/00b4953c5c7b88faca000000.pdf
[11] Ni Xingjie, Kildishev A V, Shalaev V M, et al. Metasurface holograms for visible light[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2807.
[12] Huang Lingling, Chen Xianzhong, Mühlenbernd H, et al. Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2808. https://www.ece.nus.edu.sg/stfpage/eleqc/holography-metasurface-nc13.pdf
[13] Wang Qiu, Zhang Xueqian, Xu Yuehong, et al. Broadband metasurface holograms: toward complete phase and amplitude engineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32867. doi: 10.1038/srep32867
[14] Montelongo Y, Tenorio-Pearl J O, Williams C, et al. Plasmonic nanoparticle scattering for color holograms[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(35): 12679–12683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405262111
[15] Li Xiong, Chen Lianwei, Li Yang, et al. Multicolor 3D me-ta-holography by broadband plasmonic modulation[J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(11): e1601102. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601102
[16] Fan Qingbin, Huo Pengcheng, Wang Daopeng, et al. Visible light focusing flat lenses based on hybrid dielectric-metal metasurface reflector-arrays[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 45044. doi: 10.1038/srep45044
[17] Fan Qingbin, Wang Daopeng, Huo Pengcheng, et al. Autofo-cusing airy beams generated by all-dielectric metasurface for visible light[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(8): 9285–9294. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.009285
[18] Wang Qiu, Zhang Xueqian, Xu Yuehong, et al. A broadband metasurface‐based terahertz flat‐lens array[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2015, 3(6): 779–785. doi: 10.1002/adom.v3.6
[19] Chen Xianzhong, Zhang Yan, Huang Lingling, et al. Ultrathin metasurface laser beam shaper[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2014, 2(10): 978–982. doi: 10.1002/adom.v2.10
[20] He Jingwen, Ye Jiasheng, Wang Xinke, et al. A broadband terahertz ultrathin multi-focus lens[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 28800. doi: 10.1038/srep28800
[21] Li Xin, Xiao Shiyi, Cai Bengeng, et al. Flat metasurfaces to focus electromagnetic waves in reflection geometry[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(23): 4940–4942. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004940
[22] Hu Dan, Wang Xinke, Feng Shengfei, et al. Ultrathin terahertz planar elements[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2013, 1(2): 186–191. doi: 10.1002/adom.201200044
[23] Jiang Xiaoyan, Ye Jiasheng, He Jingwen, et al. An ultrathin terahertz lens with axial long focal depth based on metasurfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(24): 30030–30038. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.030030
[24] Aieta F, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Aberration-free ultrathin flat lenses and axicons at telecom wavelengths based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(9): 4932–4936. doi: 10.1021/nl302516v
[25] Pu Mingbo, Li Xiong, Ma Xiaoliang, et al. Catenary optics for achromatic generation of perfect optical angular momentum[J]. Science Advances, 2015, 1(9): e1500396. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500396
[26] Li Xiong, Pu Mingbo, Zhao Zeyu, et al. Catenary nanostructures as compact Bessel beam generators[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 20524. doi: 10.1038/srep20524
[27] 刘德森.微小光学与微透镜阵列[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013: 5–6.
Liu Desen. Micro optics and lens array[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013: 5–6.
[28] Gu Benyuan, Yang Guozhen, Dong Bizhen, et al. General theory for performing an optical transform[J]. Applied Optics, 1986, 25(18): 3197–3206. doi: 10.1364/AO.25.003197
[29] Zhang Xueqian, Tian Zhen, Yue Weisheng, et al. Broadband terahertz wave deflection based on C‐shape complex met-amaterials with phase discontinuities[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(33): 4567–4572. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204850
[30] Liu Lixiang, Zhang Xueqian, Kenney M, et al. Broadband metasurfaces with simultaneous control of phase and ampli-tude[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(29): 5031–5036. doi: 10.1002/adma.201401484
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: