-
摘要:
针对现有电力光学电流传感中法拉第旋转角的非线性测量、解调模式的光强依赖性等问题,本文设计了一种环型亚波长偏振光栅,其光栅矢量径向分布,可将偏振光的偏振分布转化为光斑强度分布并与偏振面同步旋转。应用琼斯矩阵对其偏振特性进行分析,运用严格耦合波理论对光栅进行仿真分析与优化设计,并制备了辐射状的环型铝金属光栅。测试结果表明,光栅TM光的透过率大于80%、整体消光比大于100,可实现对光偏振态的直接检测,并具有线性测量范围大、测量结果不依赖于光的绝对强度等优点,可用于基于图像分析的偏振检测技术。
 Abstract:
Abstract:A new type of radially polarized grating is designed to solve the problems of nonlinear measurement of Faraday rotation existing in the power optical sensing. The distribution of the grating vector is in accordance with the special method, so that the polarization distribution of the polarized light can be transformed into the distribution of light intensity, which rotates synchronously with polarization plane. The theory of polarization detection is analyzed by using Jones matrix, and the parameters of the grating are simulated by rigorous coupled wave theory. Finally, the grating is fabricated and tested. The results show that the TM transmittance of the grating is greater than 80%, the extinction ratio is greater than 100, and the detection of the polarization state can be realized. It has the advantages of large linear measurement range and measurement results independent on the absolute intensity, so that it will be a new detection technology of polarization based on the image method.
-

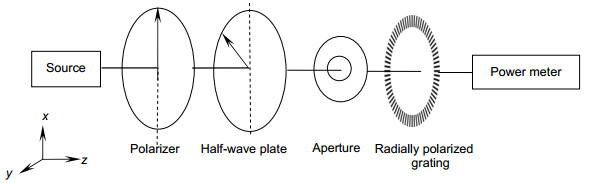
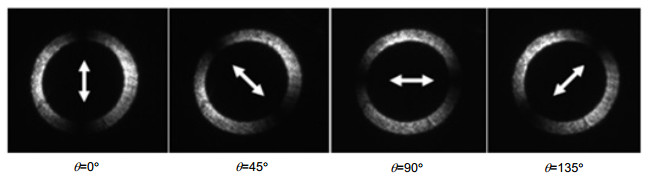
Abstract:To solve the problems of nonlinear measurement of Faraday rotation existing in the power optical sensing, a new type of circular polarization grating is designed, in which the grating grooves are arranged along the radial direction in a ring. For the polarization grating, the TE wave (parallel to the grooves) has a high reflection and the TM wave (perpendicular to the grooves) has a high transmission. Therefore, according to the Malus' law, when a linearly polarized light is transmitted through the grating, the output light gets the maximum and minimum intensities at the directions perpendicular and parallel to the polarization direction of the LP light, respectively. Because the grating is ring-shaped and the average space between adjacent grooves is in nanometer size, a linearly polarized light with any polarization direction can generate a ring-shaped intensity distribution image with dark and bright stripes after passing through the grating. In brief, the grating can be described as a radial polarizer in which the transmission axis is perpendicular to the azimuth angle that can be varied within 0~360 degree. When the azimuth angle changes, the intensity distribution will rotate accordingly, and its rotation angle is equal to the azimuth angle. Therefore, the polarization rotation can be linearly measured by detecting the rotation of the dark stripe center.
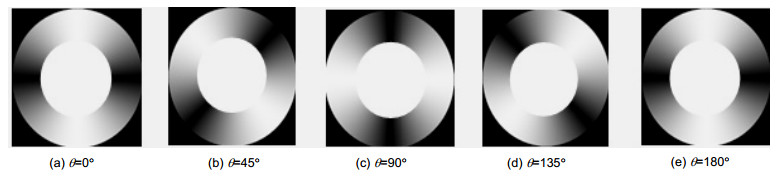
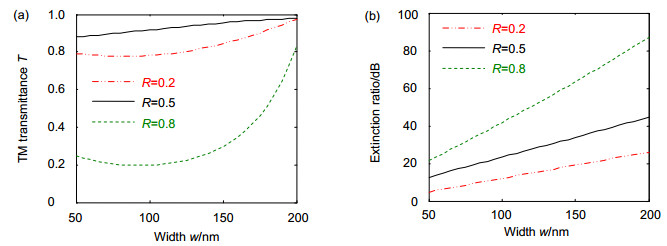
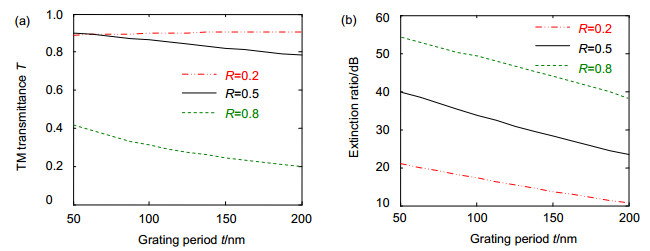
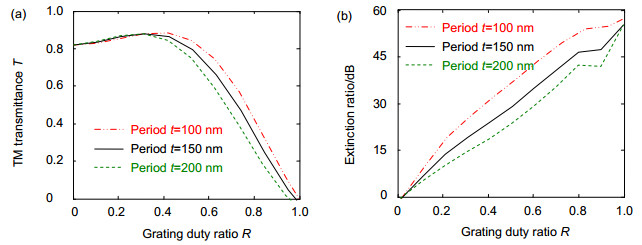
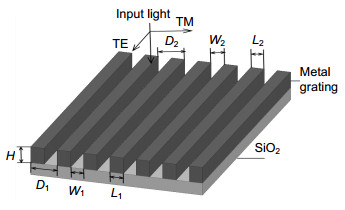
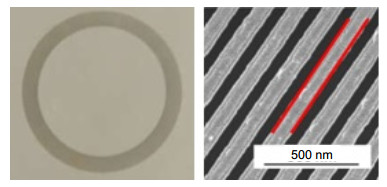
The theory of polarization detection is analyzed by using Jones matrix, and the output facula images in different azimuth angles of the linearly polarized light are given in the paper. The parameters of the grating are simulated by rigorous coupled wave theory, including the transmittance and extinction ratio under different depths, different periods and different duty radios, and then all the grating parameters are determined. The material of the grating is selected as aluminum, the width of the grooves is 50 nm, the depth is 100 nm, the inner and outer radii are 8 mm and 10 mm, respectively, the period and the duty cycle in the inner radius are 100 nm and 0.5, and the period and the duty cycle in the outer radius are 200 nm and 0.25. The polarization grating is manufactured by electron beam lithography, nanometer imprinting and plasma etching technologies.
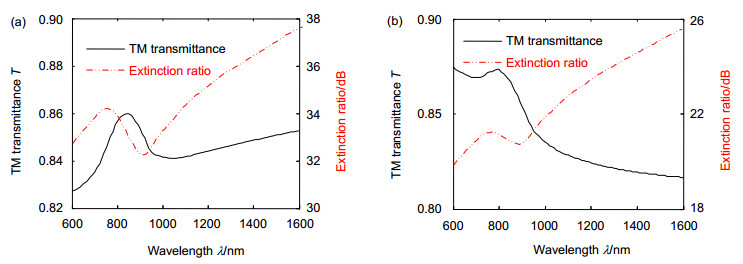
Finally, the performances of the grating are tested. When the wavelength of light varies from 600 nm to 1600 nm, the TM transmittance of the grating is greater than 80%, and the extinction ratio is greater than 100. What's more, when the incident azimuth angle changes, the output facula image detected by the grating rotates synchronously with the angle.
In a word, the new designed grating has the advantages of large linear measurement range and measurement results independent on the absolute intensity, so that it will form a new detection technology of polarization based on the image method.
-

-
表 1 光栅性能测试数据.
Table 1. Experimental data for grating performance.
Testing point I0/μW ITm/μW ITE/nW TM light transmittance Extinction ratio 1 85.20 72.45 332 0.85 218(23.4 dB) 2 85.20 69.86 213 0.82 328(25.2 dB) 3 85.20 68.14 1 45 0.80 470(26.7 dB) 4 85.20 66.47 83 0.78 800(29.0 dB) -
[1] 赵华君, 杨守良, 张东, 等.亚波长金属偏振分束光栅设计分析[J].物理学报, 2009, 58(9): 6236–6242. doi: 10.7498/aps.58.6236
Zhao Huajun, Yang Shouliang, Zhang Dong, et al. Design of polarizing beam splitters based on subwavelength metal grat-ing[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009, 58(9): 6236–6242. doi: 10.7498/aps.58.6236
[2] 郭楚才, 叶卫民, 袁晓东, 等.亚波长光栅偏振分束器的研究[J].光学学报, 2010, 30(9): 2690–2695. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?aid=OJ1009070000603y6B9E
Guo Chucai, Ye Weimin, Yuan Xiaodong, et al. Research on sub-wavelength grating polarizing beam splitter[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(9): 2690–2695. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?aid=OJ1009070000603y6B9E
[3] Bomzon Z, Kleiner V, Hasman E. Formation of radially and azimuthally polarized light using space-variant subwavelength metal stripe gratings[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 79(11): 1587–1589. doi: 10.1063/1.1401091
[4] Hasman E, Bomzon Z, Niv A, et al. Polarization beam-splitters and optical switches based on space-variant comput-er-generated sub-wavelength quasi-periodic structures[J]. Optics Communications, 2002, 209(1–3): 45–54. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(02)01598-5
[5] Mohammed W S, Mehta A, Pitchumani M, et al. Selective excitation of the TE01 mode in hollow-glass waveguide using a subwavelength grating[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2005, 17(7): 1441–1443. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2005.848549
[6] Lerman G M, Levy U. Generation of a radially polarized light beam using space-variant subwavelength gratings at 1064 nm[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(23): 2782–2784. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.002782
[7] 周哲海. 轴对称偏振光束的生成、特性及应用[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010: 18–41.
Zhou Zhehai. Formation, properties and applications of axially symmetric polarized beams[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2010: 18–41.
[8] Ghadyani Z, Vartiainen I, Harder I, et al. Concentric ring metal grating for generating radially polarized light[J]. Applied Optics, 2011, 50(16): 2451–2457. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.002451
[9] Moharam M G, Grann E B, Pommet D A, et al. Formulation for stable and efficient implementation of the rigorous cou-pled-wave analysis of binary gratings[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1995, 12(5): 1068–1076. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.12.001068
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: