| Citation: | Zhang FL, Su ZC, Li Z, Zhu Y, Gagrani N et al. High-speed multiwavelength InGaAs/InP quantum well nanowire array micro-LEDs for next generation optical communications. Opto-Electron Sci 2, 230003 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oes.2023.230003 |
High-speed multiwavelength InGaAs/InP quantum well nanowire array micro-LEDs for next generation optical communications
-
Abstract
Miniaturized light sources at telecommunication wavelengths are essential components for on-chip optical communication systems. Here, we report the growth and fabrication of highly uniform p-i-n core-shell InGaAs/InP single quantum well (QW) nanowire array light emitting diodes (LEDs) with multi-wavelength and high-speed operations. Two-dimensional cathodoluminescence mapping reveals that axial and radial QWs in the nanowire structure contribute to strong emission at the wavelength of ~1.35 and ~1.55 μm, respectively, ideal for low-loss optical communications. As a result of simultaneous contributions from both axial and radial QWs, broadband electroluminescence emission with a linewidth of 286 nm is achieved with a peak power of ~17 μW. A large spectral blueshift is observed with the increase of applied bias, which is ascribed to the band-filling effect based on device simulation, and enables voltage tunable multi-wavelength operation at the telecommunication wavelength range. Multi-wavelength operation is also achieved by fabricating nanowire array LEDs with different pitch sizes on the same substrate, leading to QW formation with different emission wavelengths. Furthermore, high-speed GHz-level modulation and small pixel size LED are demonstrated, showing the promise for ultrafast operation and ultracompact integration. The voltage and pitch size controlled multi-wavelength high-speed nanowire array LED presents a compact and efficient scheme for developing high-performance nanoscale light sources for future optical communication applications.-
Keywords:
- InGaAs/InP /
- quantum well /
- nanowires /
- LEDs
-

-
References
[1] Schubert EF. Light-Emitting Diodes 2nd ed (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006);http://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511790546. [2] Floyd R, Gaevski M, Hussain K, Mamun A, Chandrashekhar MVS et al. Enhanced light extraction efficiency of micropixel geometry AlGaN DUV light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express 14, 084002 (2021). doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ac0fb8 [3] Huang YG, Hsiang EL, Deng MY, Wu ST. Mini-LED, Micro-LED and OLED displays: present status and future perspectives. Light Sci Appl 9, 105 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-0341-9 [4] Ra YH, Rashid RT, Liu XH, Sadaf SM, Mashooq K et al. An electrically pumped surface-emitting semiconductor green laser. Sci Adv 6, eaav7523 (2020). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav7523 [5] Nami M, Rashidi A, Monavarian M, Mishkat-Ul-Masabih S, Rishinaramangalam AK et al. Electrically injected GHz-class GaN/InGaN core–shell nanowire-based μLEDs: carrier dynamics and nanoscale homogeneity. ACS Photonics 6, 1618–1625 (2019). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.9b00639 [6] Koester R, Sager D, Quitsch WA, Pfingsten O, Poloczek A et al. High-speed GaN/GaInN nanowire array light-emitting diode on silicon(111). Nano Lett 15, 2318–2323 (2015). doi: 10.1021/nl504447j [7] Rajbhandari S, McKendry JJD, Herrnsdorf J, Chun H, Faulkner G et al. A review of gallium nitride LEDs for multi-gigabit-per-second visible light data communications. Semicond Sci Technol 32, 023001 (2017). doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/32/2/023001 [8] Wen PY, Tiwari P, Mauthe S, Schmid H, Sousa M et al. Waveguide coupled III-V photodiodes monolithically integrated on Si. Nat Commun 13, 909 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28502-6 [9] Mauthe S, Baumgartner Y, Sousa M, Ding Q, Rossell MD et al. High-speed III-V nanowire photodetector monolithically integrated on Si. Nat Commun 11, 4565 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18374-z [10] Matsuda Y, Funato S, Funato M, Kawakami Y. Multiwavelength-emitting InGaN quantum wells on convex-lens-shaped GaN microstructures. Appl Phys Express 15, 105503 (2022). doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ac934e [11] Murillo-Borjas BL, Li X, Gu Q. High-speed nanoLEDs for chip-scale communication. Nano Commun Netw 30, 100376 (2021). doi: 10.1016/j.nancom.2021.100376 [12] Takiguchi M, Zhang GQ, Sasaki S, Nozaki K, Chen E et al. Direct modulation of a single InP/InAs nanowire light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett 112, 251106 (2018). doi: 10.1063/1.5037011 [13] Chen R, Ng KW, Ko WS, Parekh D, Lu FL et al. Nanophotonic integrated circuits from nanoresonators grown on silicon. Nat Commun 5, 4325 (2014). doi: 10.1038/ncomms5325 [14] Zhang GQ, Takiguchi M, Tateno K, Tawara T, Notomi M et al. Telecom-band lasing in single InP/InAs heterostructure nanowires at room temperature. Sci Adv 5, eaat8896 (2019). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aat8896 [15] Lauhon LJ, Gudiksen MS, Wang DL, Lieber CM. Epitaxial core–shell and core–multishell nanowire heterostructures. Nature 420, 57–61 (2002). doi: 10.1038/nature01141 [16] Herranz J, Corfdir P, Luna E, Jahn U, Lewis RB et al. Coaxial GaAs/(In, Ga)As dot-in-a-well nanowire heterostructures for electrically driven infrared light generation on si in the telecommunication O band. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3, 165–174 (2020). doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b01866 [17] Akamatsu T, Tomioka K, Motohisa J. Demonstration of InP/InAsP/InP axial heterostructure nanowire array vertical LEDs. Nanotechnology 31, 394003 (2020). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab9bd2 [18] Yang I, Zhang X, Zheng CL, Gao Q, Li ZY et al. Radial growth evolution of InGaAs/InP multi-quantum-well nanowires grown by selective-area metal organic vapor-phase epitaxy. ACS Nano 12, 10374–10382 (2018). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05771 [19] Zhang FL, Zhang XT, Li ZY, Yi RX, Li Z et al. A new strategy for selective area growth of highly uniform InGaAs/InP multiple quantum well nanowire arrays for optoelectronic device applications. Adv Funct Mater 32, 2103057 (2022). doi: 10.1002/adfm.202103057 [20] Yi RX, Zhang XT, Zhang FL, Gu LP, Zhang Q et al. Integrating a nanowire laser in an on-chip photonic waveguide. Nano Lett 22, 9920–9927 (2022). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c03364 [21] Yang I, Li ZY, Wong-Leung J, Zhu Y, Li Z et al. Multiwavelength single nanowire InGaAs/InP quantum well light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett 19, 3821–3829 (2019). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00959 [22] Fickenscher M, Shi T, Jackson HE, Smith LM, Yarrison-Rice JM et al. Optical, structural, and numerical investigations of GaAs/AlGaAs core–multishell nanowire quantum well tubes. Nano Lett 13, 1016–1022 (2013). doi: 10.1021/nl304182j [23] Sköld N, Wagner JB, Karlsson G, Hernán T, Seifert W et al. Phase segregation in AlInP shells on GaAs nanowires. Nano Lett 6, 2743–2747 (2006). doi: 10.1021/nl061692d [24] Tomioka K, Motohisa J, Hara S, Hiruma K, Fukui T. GaAs/AlGaAs core multishell nanowire-based light-emitting diodes on Si. Nano Lett 10, 1639–1644 (2010). doi: 10.1021/nl9041774 [25] Li N, Han K, Spratt W, Bedell S, Ott J et al. Ultra-low-power sub-photon-voltage high-efficiency light-emitting diodes. Nat Photonics 13, 588–592 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0463-x [26] Yang I, Kim S, Niihori M, Alabadla A, Li ZY et al. Highly uniform InGaAs/InP quantum well nanowire array-based light emitting diodes. Nano Energy 71, 104576 (2020). doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104576 [27] Khan MZM, Alhashim HH, Ng TK, Ooi BS. High-power and high-efficiency 1.3-μm superluminescent diode with flat-top and ultrawide emission bandwidth. IEEE Photonics J 7, 1600308 (2015). doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2015.2399442 [28] Rajendran V, Fang MH, Guzman GND, Lesniewski T, Mahlik S et al. Super broadband near-infrared phosphors with high radiant flux as future light sources for spectroscopy applications. ACS Energy Lett 3, 2679–2684 (2018). doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b01643 [29] Chang JR, Chang SP, Li YJ, Cheng YJ, Sou KP et al. Fabrication and luminescent properties of core-shell InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells on GaN nanopillars. Appl Phys Lett 100, 261103 (2012). doi: 10.1063/1.4731629 [30] Kusch G, Conroy M, Li HN, Edwards PR, Zhao C et al. Multi-wavelength emission from a single InGaN/GaN nanorod analyzed by cathodoluminescence hyperspectral imaging. Sci Rep 8, 1742 (2018). doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20142-5 [31] Tchernycheva M, Lavenus P, Zhang H, Babichev AV, Jacopin G et al. InGaN/GaN core–shell single nanowire light emitting diodes with graphene-based P-contact. Nano Lett 14, 2456–2465 (2014). doi: 10.1021/nl5001295 [32] Kitauchi Y, Kobayashi Y, Tomioka K, Hara S, Hiruma K et al. Structural transition in indium phosphide nanowires. Nano Lett 10, 1699–1703 (2010). doi: 10.1021/nl1000407 [33] Noborisaka J, Motohisa J, Fukui T. Catalyst-free growth of GaAs nanowires by selective-area metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett 86, 213102 (2005). doi: 10.1063/1.1935038 [34] Li ZY, Trendafilov S, Zhang FL, Allen MS, Allen JW et al. Broadband GaAsSb nanowire array photodetectors for filter-free multispectral imaging. Nano Lett 21, 7388–7395 (2021). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02777 [35] Deshpande S, Bhattacharya I, Malheiros-Silveira G, Ng KW, Schuster F et al. Ultracompact position-controlled inp nanopillar LEDs on silicon with bright electroluminescence at telecommunication wavelengths. ACS Photonics 4, 695–702 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00065 [36] Gao Q, Saxena D, Wang F, Fu L, Mokkapati S et al. Selective-area epitaxy of pure wurtzite InP nanowires: high quantum efficiency and room-temperature lasing. Nano Lett 14, 5206–5211 (2014). doi: 10.1021/nl5021409 [37] Zhu Y, Wang BW, Li ZY, Zhang J, Tang Y et al. A high-efficiency wavelength-tunable monolayer LED with hybrid continuous-pulsed injection. Adv Mater 33, 2101375 (2021). doi: 10.1002/adma.202101375 [38] Ikeda K, Horiuchi S, Tanaka T, Susaki W. Design parameters of frequency response of GaAs—(Ga, Al)As double heterostructure LED's for optical communications. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 24, 1001–1005 (1977). doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1977.18869 [39] Gagrani N, Vora K, Fu L, Jagadish C, Tan HH. Flexible InP–ZnO nanowire heterojunction light emitting diodes. Nanoscale Horiz 7, 446–454 (2022). doi: 10.1039/D1NH00535A -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for High-speed multiwavelength InGaAs/InP quantum well nanowire array micro-LEDs for next generation optical communications
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
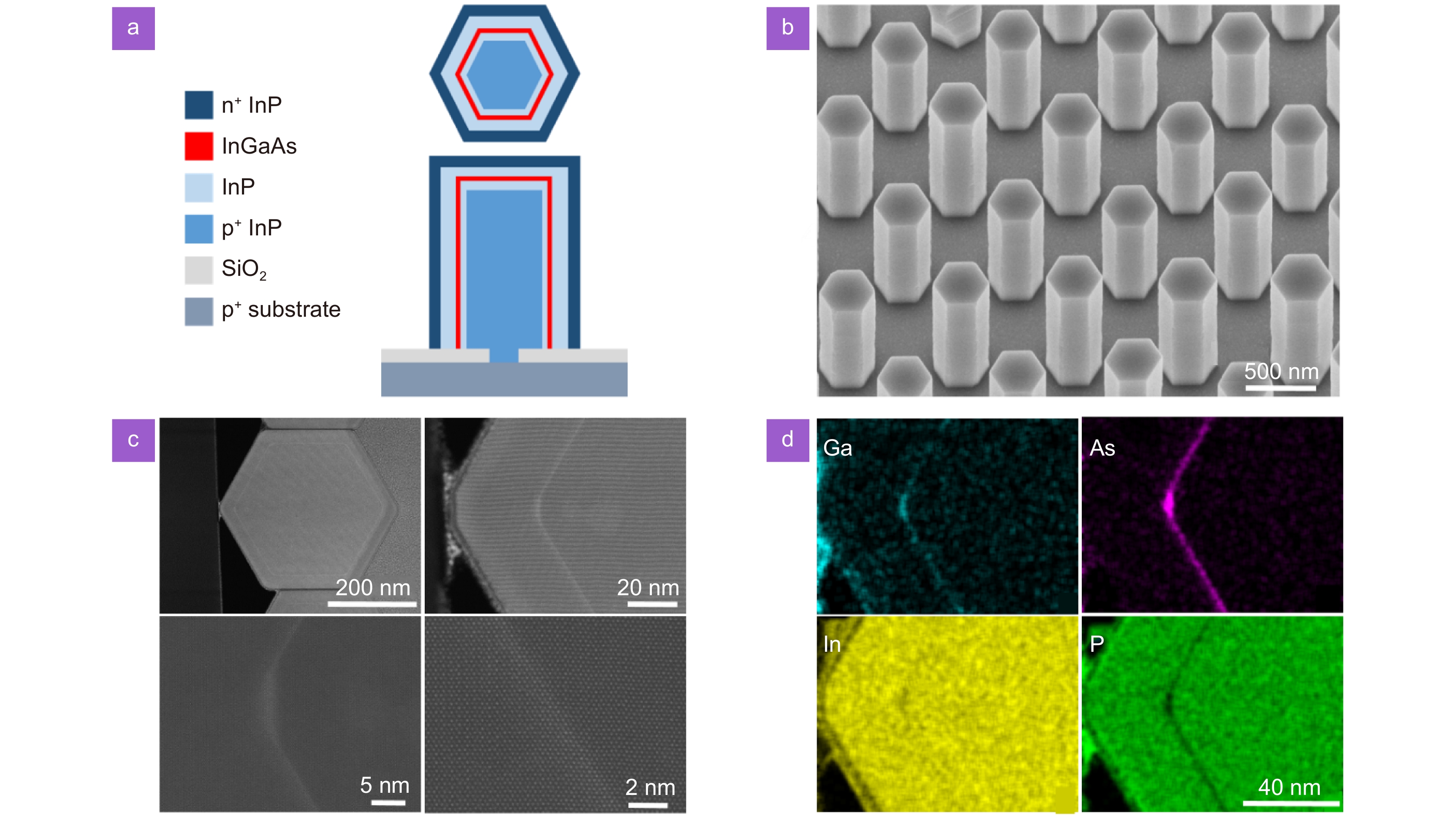
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of p-i-n InGaAs/InP single QW nanowire LED structure with lateral and vertical cross-sections. (b) 30° tilted view SEM image of the nanowire array with a pitch of 800 nm. (c) Cross-sectional STEM-HAADF image of a nanowire showing the hexagonal shape and radial QW under different magnifications. (d) EDX elemental maps of the cross-sectional region in (c).
-
Figure 2.
(a) SEM-CL spectral mapping of the InGaAs/InP single QW nanowire along the growth axis. The dashed rectangle indicates the relative position of the nanowire. (b) CL spectrum is acquired from the nanowire’s top, middle, and bottom region, respectively. (c) SEM image of the nanowire with the white arrow indicating nanowire growth direction. (d–e) Spectrally integrated intensity map at 1250–1350 nm and 1450–1550 nm. (f) Overlaid false-color CL image of (d–e), the pink and yellow region indicates the integrated CL intensity at 1250–1350 nm and 1450–1550 nm, corresponding to the emission from axial and radial QW, respectively.
-
Figure 3.
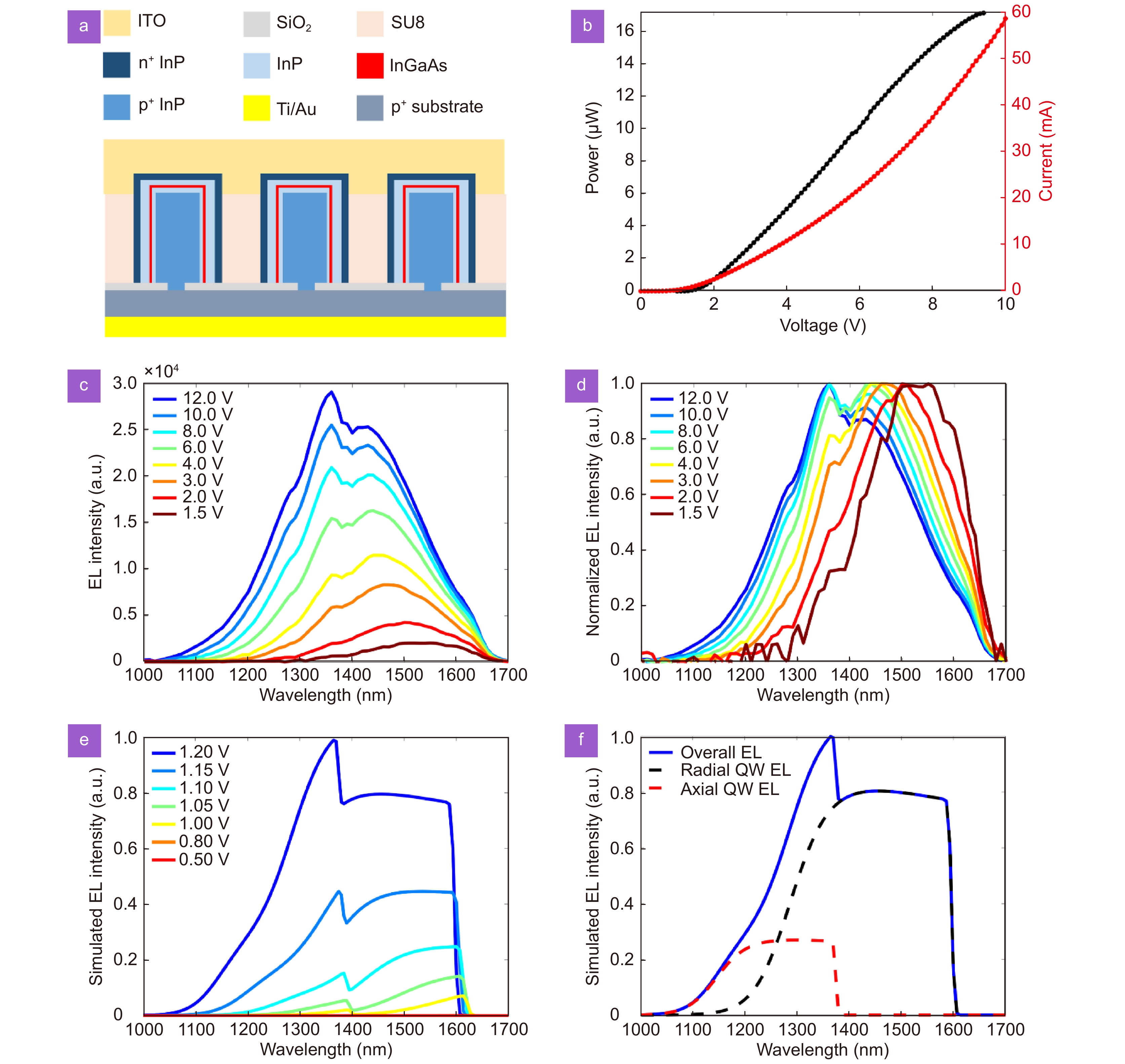
(a) Schematic of fabricated nanowire array LED. (b) L-I and I-V curves of a representative nanowire array LED. (c) Voltage-dependent EL spectra at room temperature. (d) Normalized voltage-dependent EL spectra from (c). (e) Simulated voltage-dependent spontaneous emission spectra. (f) Simulated emission spectrum at the bias of 1.2 V, with the decoupled contribution from axial and radial quantum wells.
-
Figure 4.
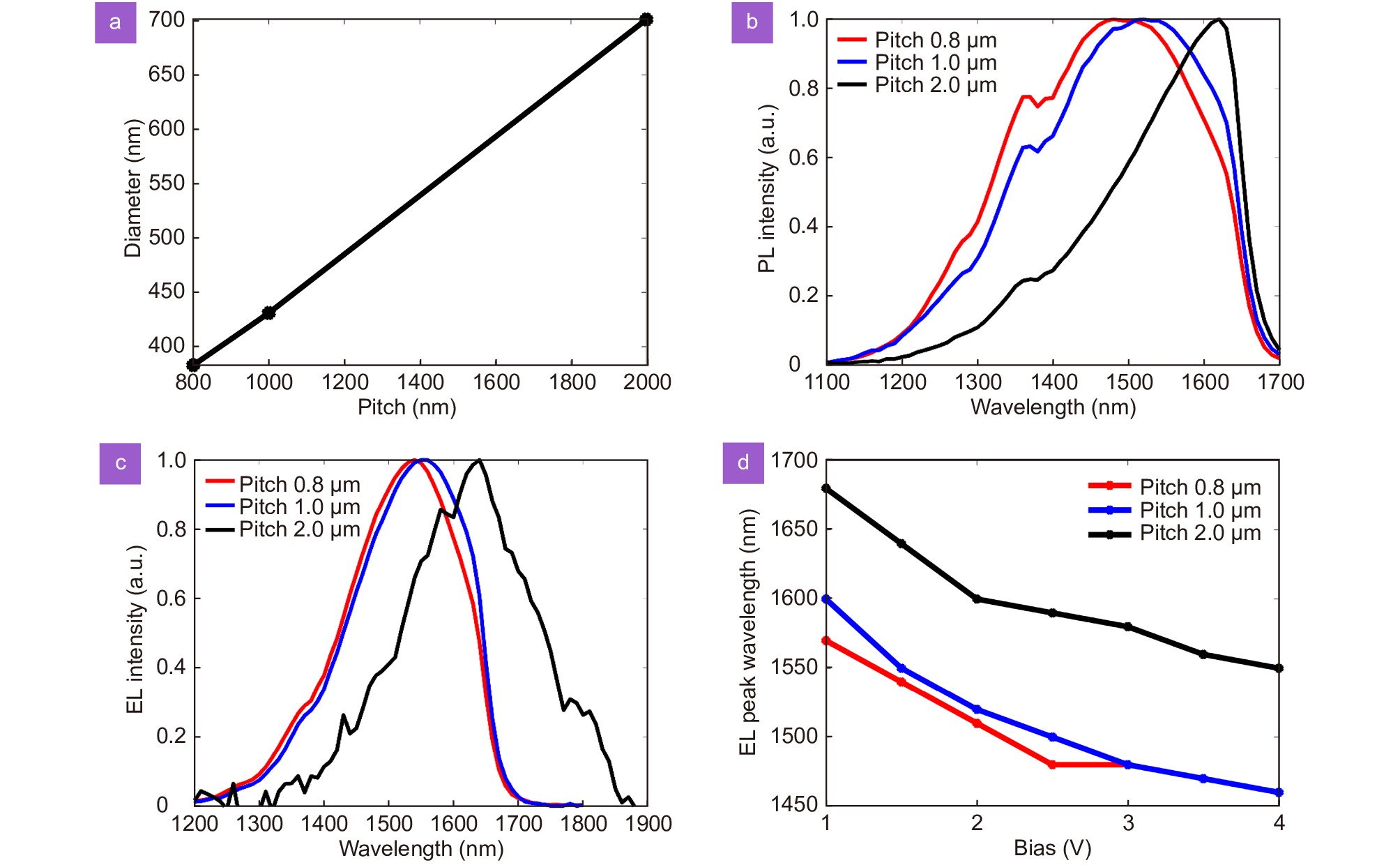
(a) Average diameter of InGaAs/InP single QW nanowire from arrays with a pitch size of 0.8, 1.0 and 2.0 μm. (b) Representative PL spectra measured from the top of the nanowire arrays with different pitch sizes. (c) EL spectra measured at a forward bias of 1.5 V from nanowire array LED with different pitch sizes. (d) Peak wavelength of the bias-dependent EL spectra from nanowire array LED with different pitch sizes.
-
Figure 5.
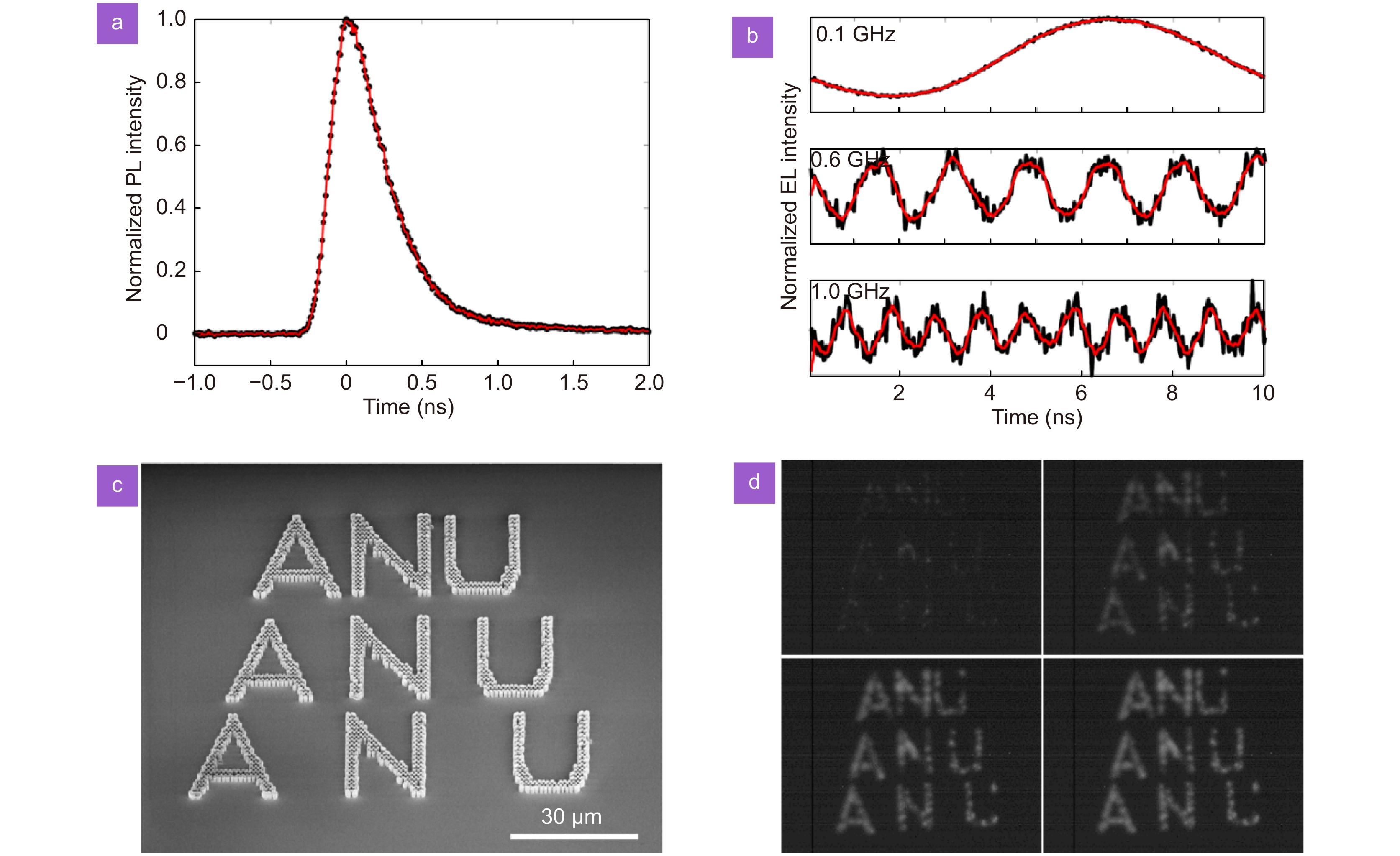
(a) TRPL decay curve measured from the top of the nanowire array. (b) TREL signal collected from pitch 0.8 µm nanowire array LED at modulation frequencies of 0.1, 0.6 and 1 GHz. (c) 30° tilted SEM image of the nanowire arrays arranged corresponding to the letters “ANU”. (d) Infrared camera image of the EL emission from nanowire array LEDs in (c) under various current injection levels.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: